Rosetta stone was discovered by soldiers of this army.
The French army
Mesopotamian hero Gilgamesh was a king of this city.
Uruk
The old name of the ISAC was...
Oriental Institute
The typical form of a Mesopotamian temple is known as...
Ziggurat

This ancient city is expected to become the site of the final battle between good and evil.
Megiddo. 
This famous palette represents the pharaoh named...
Narmer (or Menes)
Tablets containing correspondence between Egyptian pharaohs and rulers of Near Eastern kingdoms is known as...
Amarna Letters
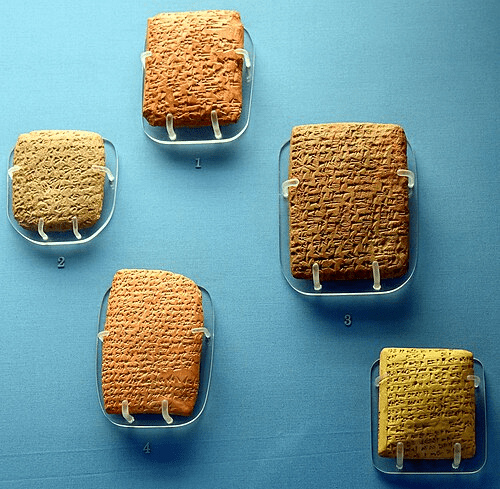

The second part of the Rosetta stone is written in this language.

Demotic 
Kush was one of the historical names for
Nubia
In antiquity he Nile Valley was called Kemet. It translates as...
Black Land
This plant provided Ancient Egyptians with the essential textile fibers for weaving and making clothing.
Flax

Behistun Inscription was important in decipherment of this script.
Cuneiform. 
A slab of stone, decorated or undecorated, often used in the ancient world as a grave marker but also for dedication, commemoration, and demarcation.
Stela 
The king represented on this stone ruled in this ancient city.
Babylon
This beautiful monument is named after a goddess.
Ishtar Gate
This Egyptian god typically wears a crown that looks like a bowling pin.

Osiris
This king from the Northern Mesopotamian kingdom had a huge library. He also sacked the Egyptian city of Thebes in the 7th century BCE

Ashurbanipal
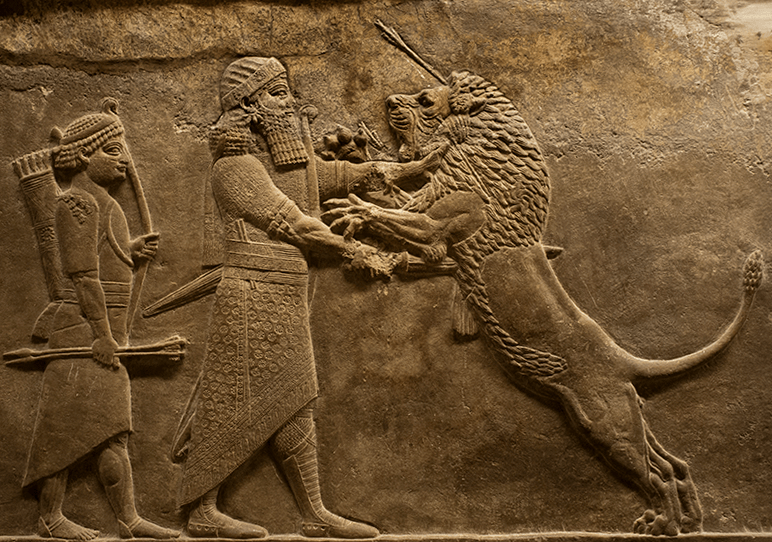

Ostracon is typically ...
a chip of pottery or limestone

Ancient Levant was also known as...
Canaan
Nineveh was one of the major cities of this empire.
Assyria
This city was the first capital of unified Egypt.
Memphis
Edgar J. Banks has created a foundation of this collection of the Oriental Institute.
Mesopotamian collection.
An Egyptian priest Manetho is famous for writing this.
The first comprehensive history of Egypt
The embodiment of truth, justice, and balance in Egyptian mythology.
Maat. 
Derived from Greek for "flesh-eating," this type of coffin was often used in Egyptian and Greco-Roman cultures.
Sarcophagus
Egyptian boats with unfurled sail go in this direction.
South
Clay figurines from Jarmo, Iraq date back to this period.
Neolithic period. 9000-7000 BC
He invented the method of sequence dating.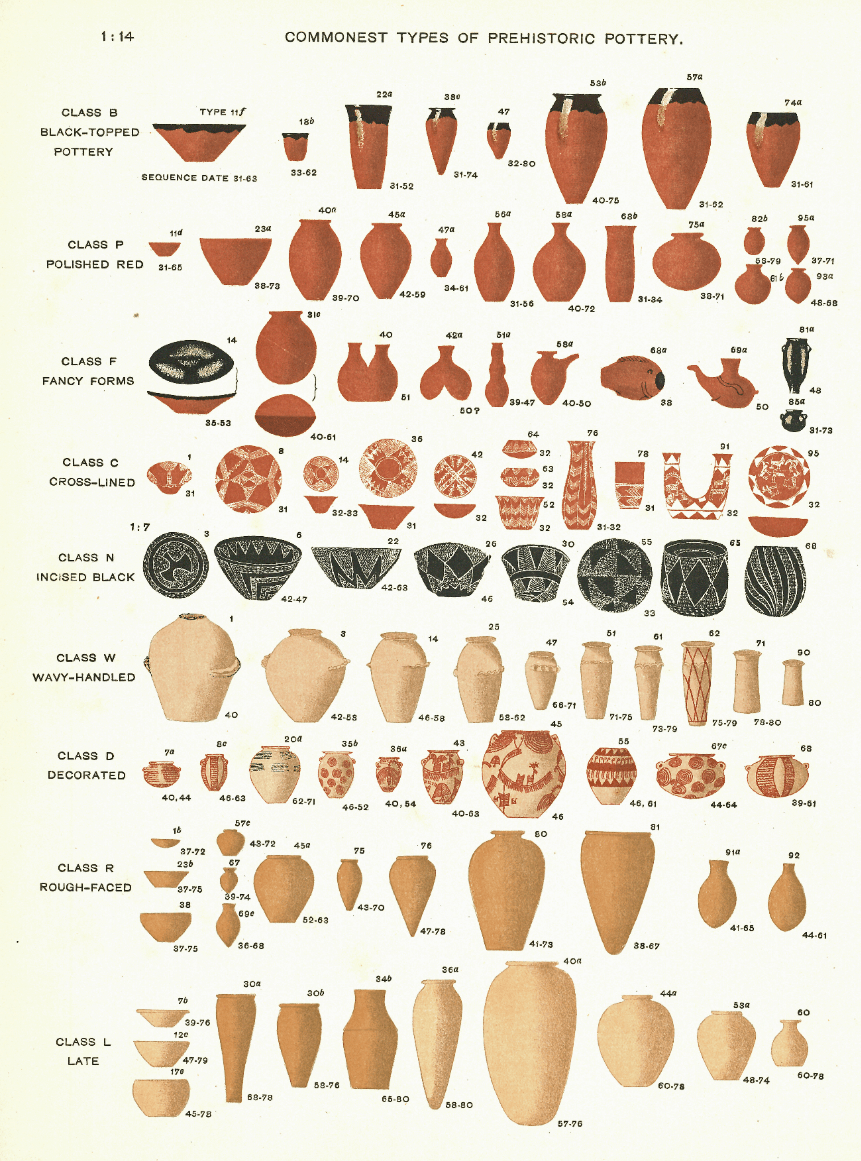
Sir Flinders Petrie

A treasure hunter Giuseppe Ferlini is responsible for destruction of a large number of these monuments
Nubian pyramids

People who lived in the village of Deir el-Medina were famous for creating these monuments.
Tombs in the Valley of the Kings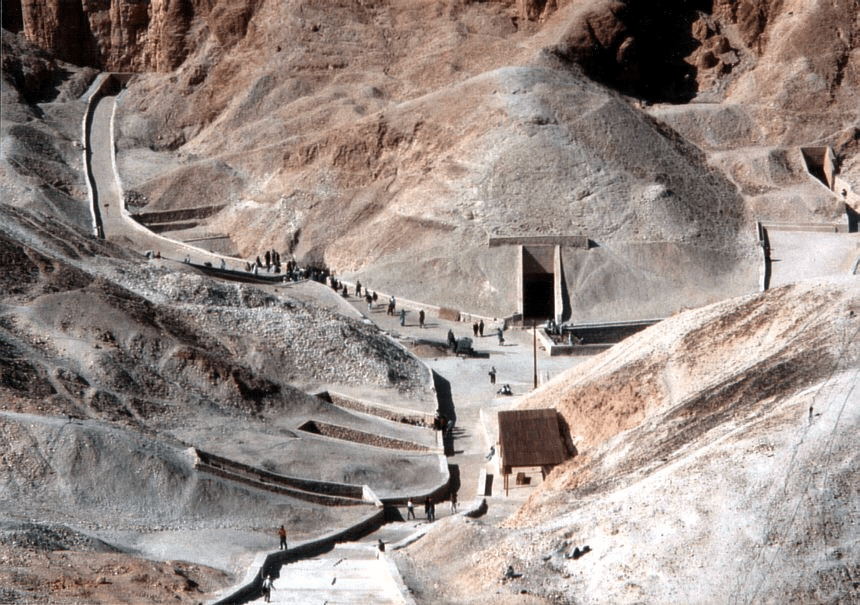 
The Hyksos invasion of Egypt falls on this historical period.
The Second Intermediate Period (c. 1782 - c.1570 BCE)
The Museum of Egyptian Antiquities (the Egyptian Museum) was founded by this person
Auguste Mariette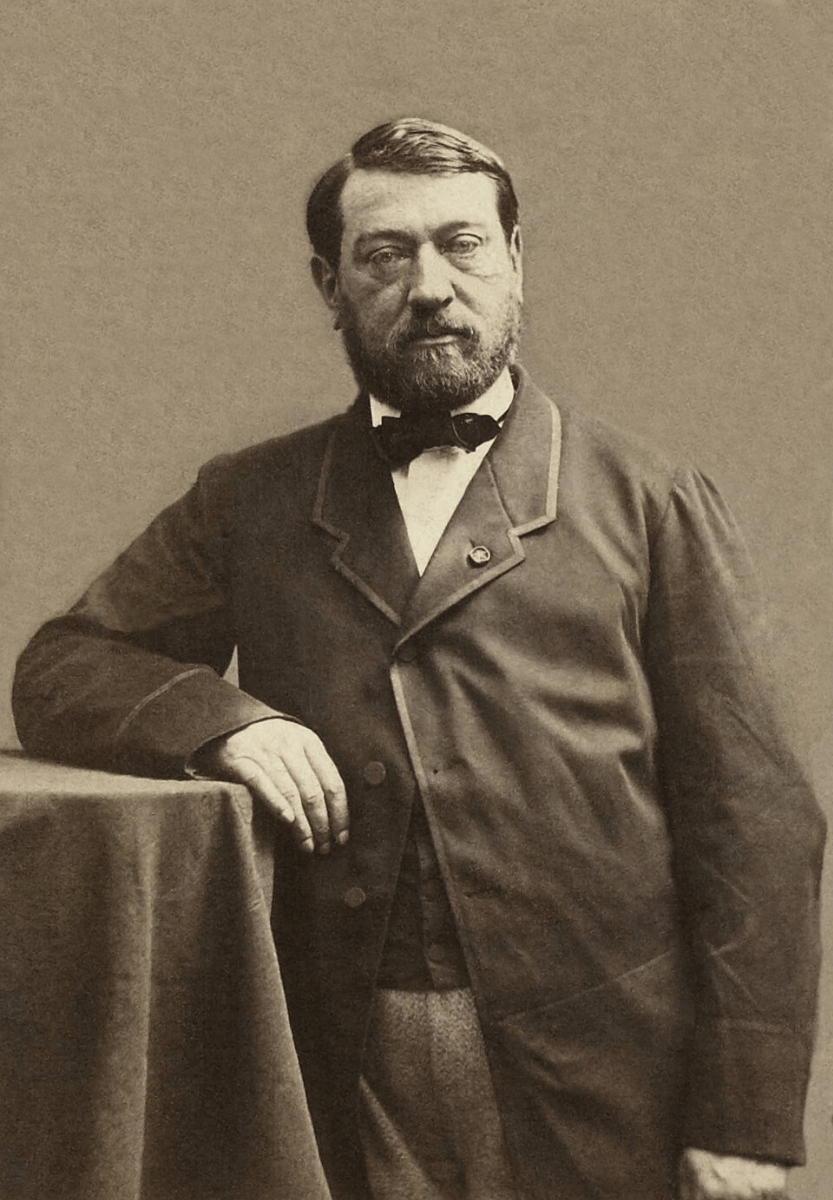
Palermo stone contains royal annals for this period of Egyptian history
Old kingdom. First five dynasties. 
The names of these two ancient lands (East of Mediterranean sea) refer to the idea of "the lands of the rising sun."
Anatolia and Levant
Pharaohs renewed their divine powers and proved their physical ability to rule the country at this major festival.
Sed festival.
