This is the opening of the skull that allows the passage of the spinal cord as well as nerves and blood vessels.
What is the foramen magnum?
This is the maneuver to open an airway in a suspected spinal injury.
What is the jaw thrust?
What is a traumatic brain injury (TBI)?
This is the number of cranial nerves there are in a human body.
What are 12?
Will only accept 13 if they can explain cranial nerve 0/ terminal nerve.
This is the common test that most medics use to screen for concussions or TBI.
What is the Military Acute Concussion Evaluation (MACE)?
These are the most posterior bones that sit on the same horizontal plane as the eyes.
What are the occipital bones?
This is the minimum oxygen saturation to maintain for a suspected TBI.
What is 90%?
Will also accept >90%
This is the common term for periorbital ecchymosis, often indicating a basilar skull fracture.
What are raccoon eyes?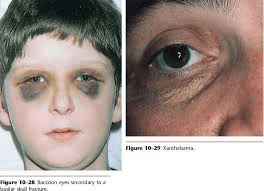
This cranial nerve you can test using the Snellen Chart.
What is the optic nerve (II)?
The MACE screens for concussions and brain injuries over 4 sections. Concussion screening, neurological exam, symptom screening, and this.
What is Cognitive Exam?
This lobe of the brain controls important cognitive skills including emotional expression, language, problem solving, and judgement.
What is the frontal lobe?
If the patient is showing signs of increased intracranial pressure, this is the rate of breaths per minute you should deliver.
What is 20 breaths per minute?
Red flags for suspected TBI include seizures, repeated vomiting, inability to recognize people, and unequal pupils. These signs will lead you to take this action.
What is refer to Medical Officer (MO) and/or transport.
Injury to this cranial nerve is most often seen as swaying while walking, or tinnitus.
What is the vestibulocochlear nerve (VIII)?
In the new MACE2, there is an added section to test vestibular/ocular-motor screening (VOMS). In this section you are to test 2 variations of saccades, these are those variations.
What are horizontal and vertical?
This is the innermost delicate layer of the meninges.
What is the pia mater?
This type of wound to the head is the only time a pressure dressing is indicated.
What is a complex scalp wound?
These postures, which receive a 3 and 2 on the Glascow Coma Scale respectively, are signs of a severe brain injury.
What is decorticate and decerebrate?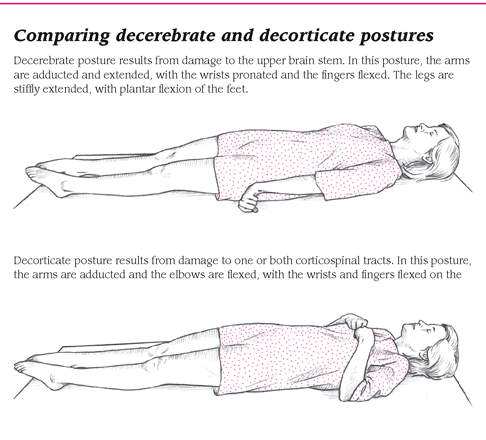
This cranial nerve may be injured if the patient was hit over their frontal bone. They may be thankful they can't smell after this!
What is the olfactory nerve (I)?
The MACE lists of numbers and words are to test this cognitive function.
What is recall?
This controls vital body functions such as cardio-respiratory function.
What is the brainstem?
These type of respirations are indicative of increasing intracranial pressure.
What are Cheyne-Stokes?
Anything above this size difference in pupils is considered abnormal.
What is 1.0 mm?
This cranial nerve innervates all intrinsic and extrinsic muscles of the tongue.
What is the hypoglossal nerve (XII)?
This reflex is the only superficial reflex that is commonly tested in unconscious patients. It stimulates the sole of the foot, and extension of the big toe (Babinksi's sign) is considered abnormal unless your patient is under 2 years.
What is plantar reflex?