Xerosis
What is dryness of skin and/or mucosal membrane?
Name what is being assessed.

What is skin turgor?
This skin coloration is caused by increased bilirubin in the blood.
What is jaundice?
A client goes to the clinic complaining of low energy and poor concentration. Upon assessment you see the following picture. How would you document this?
What is pallor?

What is ecchymoses?
Pruritus
What is itchy and dry skin?
Name an example of hypopigmentation patch.
What is vitiligo?
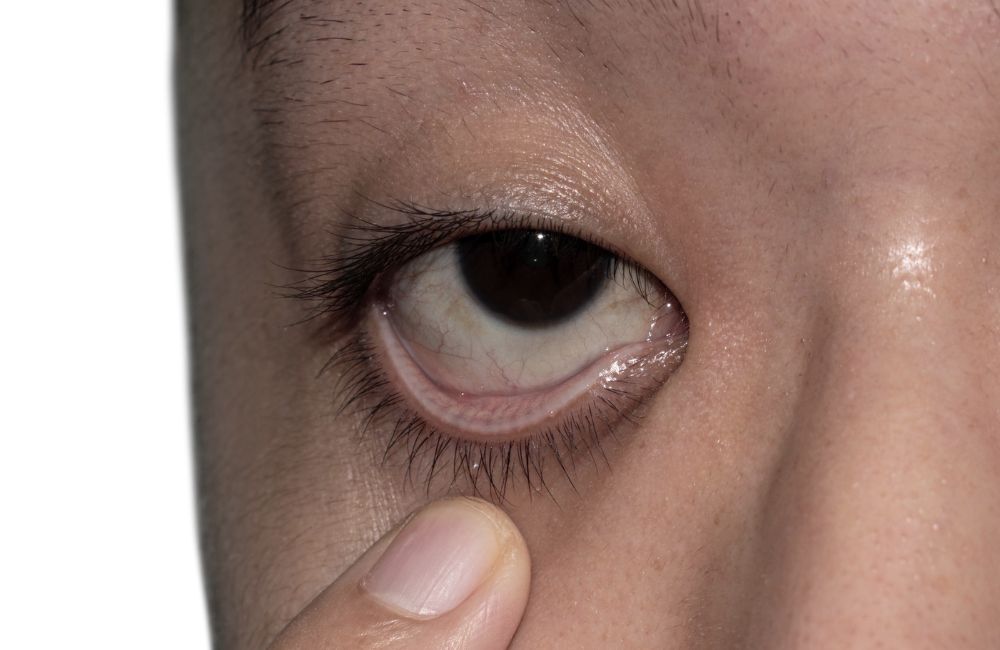
This coloration is caused by anemia, shock, or fear.
What is pallor?
Client is complaining of RUQ pain. You assess the client and notice their skin color is abnormal. How would you assess this?
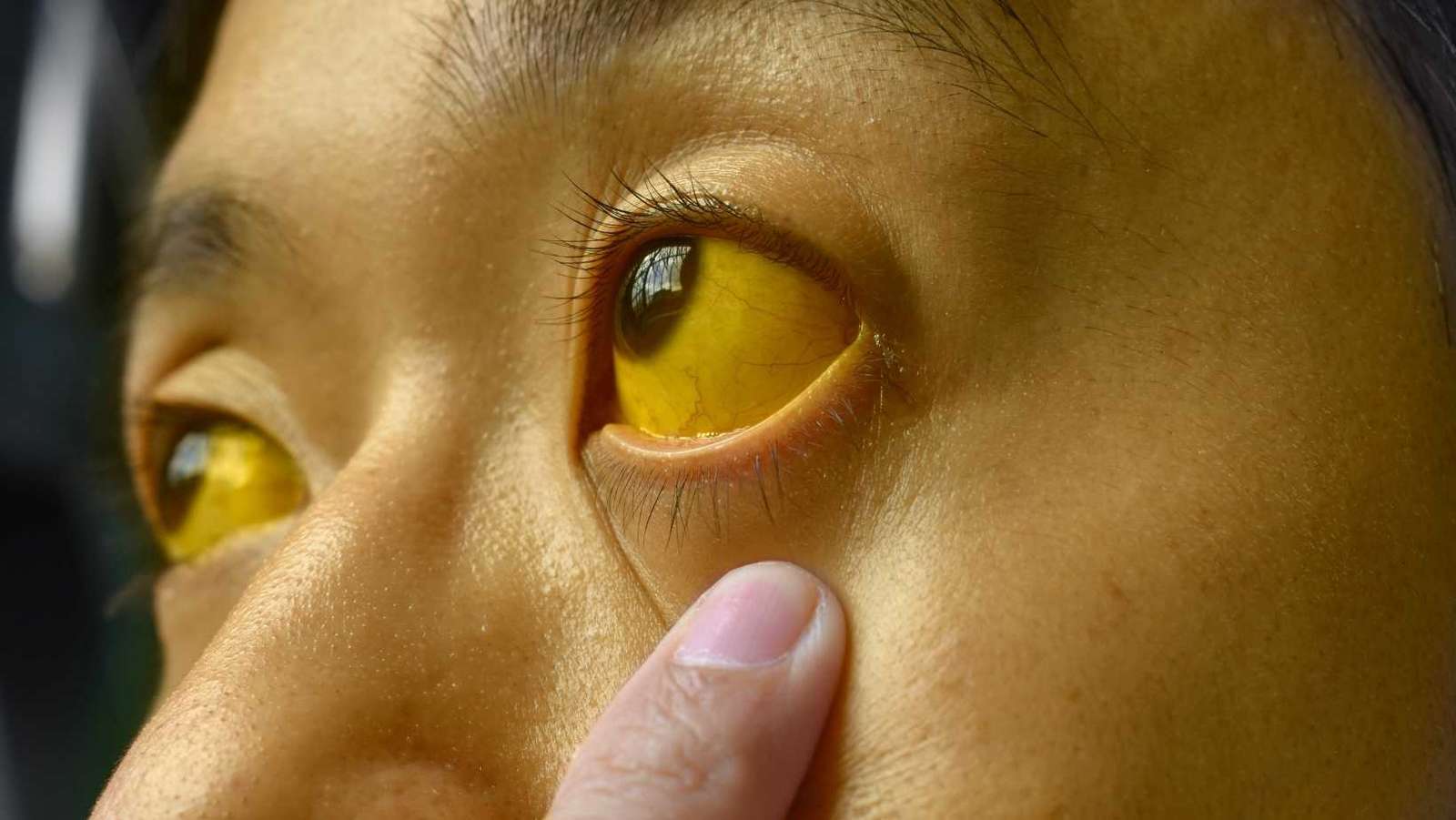
What is jaundice?

What is a stage 3 pressure injury?
Seborrhea
What is oily skin or hair?
State what this means: ABCDE and what we are assessing for.
What is assessing for skin cancer: asymmetry, boarder, color, diameter, and evolution?
This coloration is caused by sunburns, burns, anger, or rosacea.
What is erythema?
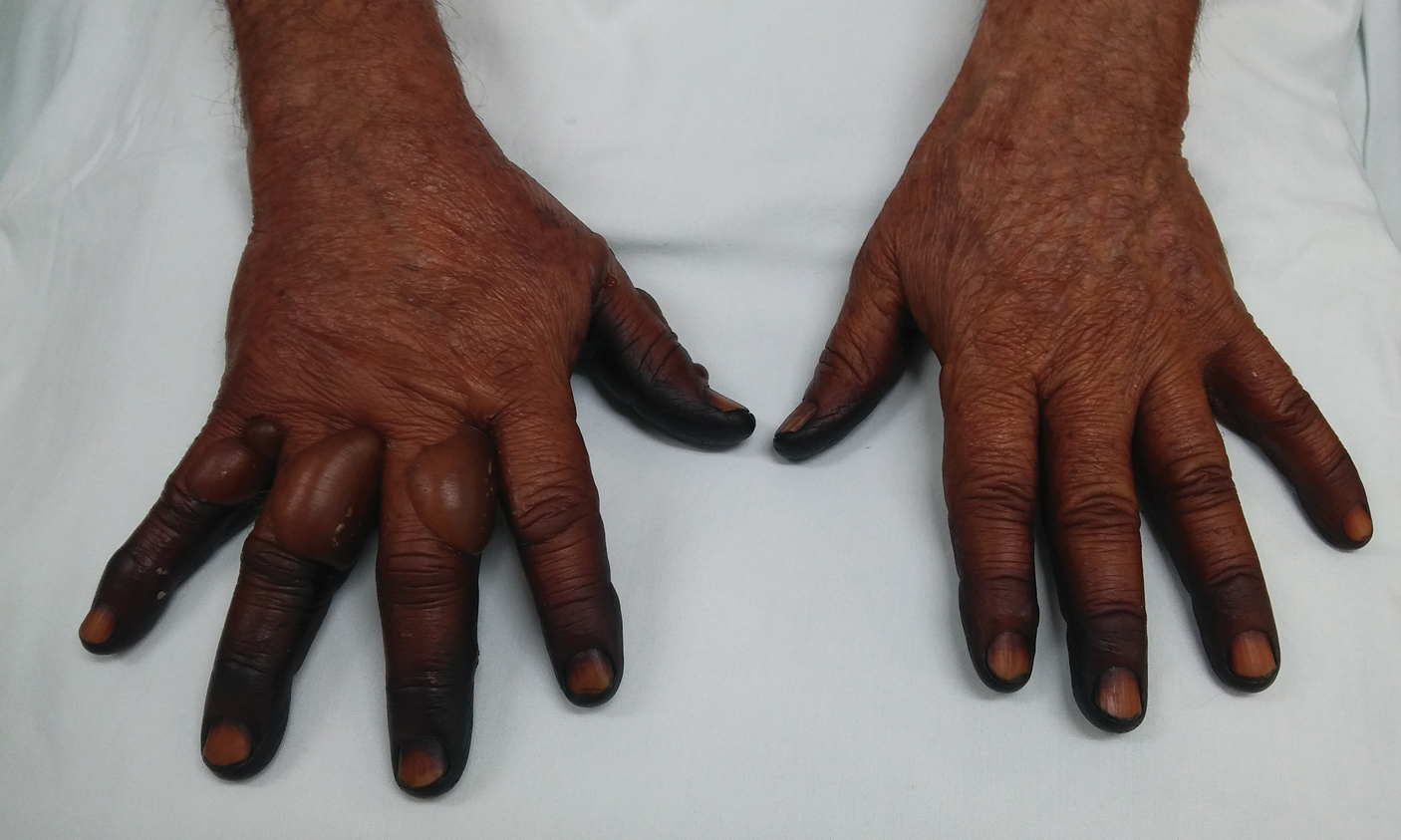
A client is seen in the clinic, and upon assessment, you notice their hands appear just as seen in the following picture. How would you document the color?
What is cyanosis?
Coolness in only one foot or leg, pallor, elevational pallor, and dependent rubor; diminished pulses; systolic bruits; signs of malnutrition (thin, shiny skin; thick-ridged nails; atrophy of muscles); distal gangrene. Ulcers occur at toes, metatarsal heads, heels, and lateral ankle and are characterized by pale ischemic base, poor granulation, well-defined edges, and no bleeding; they look dry and punched out; may have eschar, indicating necrosis. Arterial ulcers are more common in those with smoking, diabetes, hyperlipidemia, and hypertension
What is an arterial ulcer?
senile purpura
What is vascularity of the skin diminishes while the vascular fragility increases; a minor trauma may produce dark red discolored areas?
State expected findings in the aging adults.
What is loss of melanocytes causing white or grey hair, loss of subcutaneous fat, loss of collagen and elasticity?
This coloration is caused by hypoxia.
What is cyanosis?
A client with low platelets is being admitted to your unit. Upon a head-to-toe skin assessment, you notice this on their back and chest. How would you document this?
What is purpura?
VTE:
S:Sudden onset of intense, sharp, deep muscle pain.
O:Increased warmth; swelling (to compare swelling, observe usual shoe size as in above photo); redness; dependent cyanosis is mild or may be absent; tender to palpation
CVI:
S:Aching, heaviness in calf, easy fatigability, restless legs, burning, throbbing, cramping. Localized itching, tingling, burning, or pain in these veins.21
O:Dilated, tortuous veins. New varicosities sit on surface of muscle or bone; older ones are deep and feel spongy. May see generalized leg swelling.
Vitiligo
What is the complete absence of melanin pigment in patchy areas of white or light skin on the face, neck, hands, feet, and body folds and around orifices?
What is hirsutism is male-pattered baldness or facial hair growth (shaggy or excessive hair), and alopecia is the loss of hair?
This coloration is caused by a loss of pigmentation.
What is hypopigmentation?
A client with heart failure is being seen for a follow-up visit. You assess their extremities and note edema in bilateral lower extremities. How would you document their edema?

What is a +2?
Your uncle hears you are in nursing school and decides to ask you health questions. He pulls up his pant leg and say, "Would you mind taking a look at this?" He says he has aching pain in calf that is worse at end of day. The pain gets worse with prolonged standing or sitting but lessens with leg elevation. He also notes there is itching. State what you believe your uncle is experiencing.
What is a chronic venous insufficiency?