This step of mitosis is represented below.
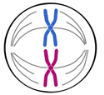
What is metaphase?
The process by which oxygen is transported to cells and carbon dioxide is transported from cells.
What is gas exchange?
Another name to describe a molecule that speeds up chemical reactions
What is catalyst? (will take enzyme)
The process that happens before translation can occur
What is transcription?
The four main biomolecules
What are Lipids, Proteins, Carbohydrates, and Nucleic Acids?
A cell of a living organism OTHER than the reproductive cells. This includes but is not limited to nerve cells, skin cells, heart cells, lung cells, etc.
What is somatic?
Transports water and dissolved minerals from the roots to the rest of the plant
What is the xylem?
The initial input of energy that is required to trigger a chemical reaction
What is activation energy?
Type of bond between the bases in DNA
What are hydrogen bonds?
Lipids can do this to damage blood vessels
What is have fat build up along blood vessels and cause blockages/blood clots?
A single set of chromosomes
What is haploid?
Carries sugars and other organic compounds produced during photosynthesis from the leaves (where they are made) to other parts of the plant, including roots and stems, through a process called translocation.
What is the phloem?
Denaturation results in disruption of the secondary, tertiary, or quaternary structure of the protein. Changes in what can result in denaturation. (name 2)
What is pH, temperature, and chemicals.
Process that happens after transcription and during translation
What is protein synthesis?
The name of the place on an enzyme where its molecule binds
What is the active site?
The exchange of genetic material in prophase 1 between homologous chromosomes is called this
What is crossing over?
The adaptations of plants to conserve water in dry environments (name at least 2)
What are thick leaves, deep roots, and reduced number of stomata?
Results in a compound with higher potential energy. Electrons are gained, oxygen is removed, hydrogen is gained.
What is reduction?
Has a sequence of three nucleotides that can base-pair with the mRNA codon
What is anti-codon?
The polarity of a water molecule, and its effect on other water molecules
What is Hydrogen atoms are slightly positive, and Oxygen atoms are slightly negative; this causes hydrogen bonding which makes water cohesive?
Unregulated cellular division can lead to this health diagnosis
What is cancer?
The relationship between humidity and rate of transpiration
What is high humidity slows down transpiration due to a smaller vapor pressure gradient, while low humidity speeds it up by creating a larger gradient for water to evaporate from the plant. (inverse relationship)
Rate of photosynthesis and absorbance of light by photosynthetic pigments is highest in this wavelength (color) of light
What is violet-blue?
Ribosome slides one codon towards the 3' end of the mRNA
What is translocation?
The three parts of a nucleotide (monomer of DNA/RNA)
What is Phosphate, Sugar, and Nitrogenous base?