What are the three main parts of the cell theory?
1. All living things are made of cells
2. Cells are the basic unit of structure and function
3. All cells come from preexisting cells.
What is the correct order of biological organization from smallest to largest?
Cell → Tissue → Organ → Organ system → Organism
Which macromolecule is the body's main source of quick energy?
Carbohydrates
What is the location on an enzyme where a substrate binds called?
Active site
Which organelle stores DNA and controls the cell?
What is one major difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
Eukaryotes have a nucleus; prokaryotes do not.
Which scientist first observed cork and named the tiny boxes "cells"?
Robert Hooke
Red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets together are an example of which level?
Tissue (blood tissue)
Which macromolecule is made of amino acids?
Proteins
Why does increasing temperature from 25°C to 37°C speed up an enzyme reaction?
It moves closer to the enzyme's optimal temperature.
Which organelle makes ATP energy?
Mitochondria
Which type of cell has membrane-bound organelles?
Eukaryotic cells
Which scientist concluded that all plants are made of cells?
Matthias Schleiden
A group of tissues work together to pump blood. Which organ is this?
Heart
Which macromolecule stores genetic information?
Nucleic acids (DNA and RNA)
What happens to enzymes at extremely high temperatures?
They denature and lose shape.
A protein is made by ribosomes and sent through the ER. Which organelle packages it?
Golgi apparatus
Give an example of a prokaryotic cell.
Which scientist concluded that all animals are made of cells?
Theodor Schwann
Which organ system moves blood, gases, and nutrients through the body?
Circulatory system
A molecule made mostly of carbon and hydrogen used for long-term energy storage is which macromolecule?
Lipid
A stomach enzyme works best at pH 2. What happens at pH 7?
Activity decreases because the pH is not optimal.
Which organelle breaks down waste and old cell parts?
Lysosomes
Name a structure found in plant cells but not animal cells.
Cell wall (also chloroplasts, large central vacuole)
Which scientist stated that all cells come from preexisting cells?
Rudolf Virchow
What does this model show about multicellular organisms?
Cells form tissues, tissues make organs, and organs work in systems.
What is one structural difference between DNA and RNA?
DNA is double-stranded; RNA is single-stranded.
What does the peak represent?
The optimal temperature
Which two organelles work together to make and transport proteins?
Ribosomes and ER
Which cell type has a cell wall made of chitin?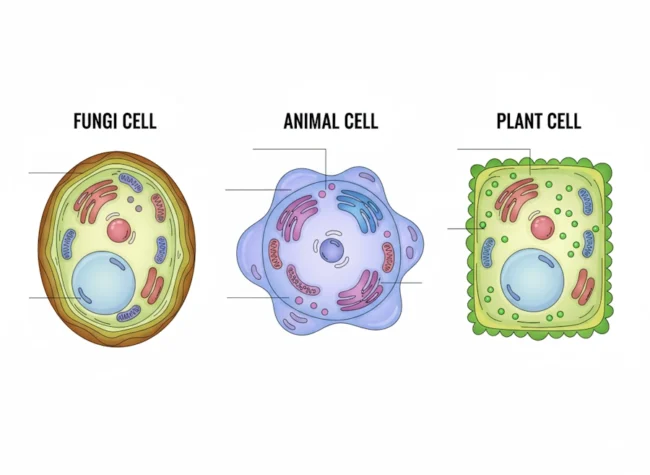
Fungal cell
A student watches skin heal as new cells replace old cells. Which cell theory part does this support?
All cells come from preexisting cells.
Skeletal muscle is made of long cells that contract to move the body. Which two levels does this describe?
Cells and tissue
Which one contains a phosphate group?
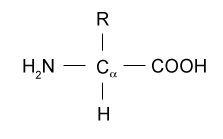
Nucleotide (nucleic acid)
What happens when substrate concentration increases but enzyme concentration stays the same?
Reaction rate increases, then levels off when enzymes are saturated.
What is the main function of chloroplasts?
Capture sunlight to make glucose
What is one thing all eukaryotic cells (plant, animal, fungal) have in common?
They all have a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles.
Seeing that both plant and animal cells have similar structures supports which idea?:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/animal_cell_vs_plant_cell-58b45d8f5f9b5860460ceb88.jpg)
Cells are the basic unit of structure and function.
Why can organs perform more complex functions than tissues?
They contain multiple tissue types working together.
Why do proteins have more functions than carbohydrates?
They are made of 20 amino acids that fold into many shapes.
What variable must stay constant when testing how pH affects enzymes?
Temperature
What does the cytoskeleton do?
Provides structure and movement inside the cell
Why do prokaryotic cells reproduce faster than eukaryotic cells?
They have simpler structures and fewer things to make.
Which two scientists together proved that all living organisms are made of cells?
Schleiden and Schwann
Match these: Digestive system and Nervous system.
Digestive breaks down food; Nervous sends signals
Which macromolecule builds enzymes, antibodies, and muscle tissue?
Proteins
Enzyme activity is highest at pH 6, lower at pH 4, and very low at pH 10. What conclusion can be made?
The enzyme works best near pH 6
How do chloroplasts and mitochondria work together?
Chloroplasts make glucose; mitochondria convert it to ATP
Which structure in plant cells stores water and helps maintain shape?
Large central vacuole