WILD CARD: Experimental Design
You are testing the effect of water on plant growth. You give each plant a different amount of water, and measure the height of the plant after 8 weeks. What is the independent variable in your experiment?
Amount of water added (this is what YOU changed between the plants).
What atoms are both cards and lipids made of?
Carbon, hydrogen, oxygen
What type of macromolecule are enzymes?
Proteins
Monomers of nucleic acids are called...
Nucleotides
Lactase is a _______ (protein/carbohydrate/lipid/nucleic acid), which lactose is a _______ (protein/carbohydrate/lipid/nucleic acid)
Protein, carbohydrate
In organic chemistry, What name do we give small molecules that join together to make larger molecules?
Monomers
Monosaccharides
WILD CARD: EXPERIMENTAL DESIGN
You are interested in how a certain medication affects blood pressure. You give 20 mice the medicine and monitor their blood pressure before and after getting the medication. What is the dependent variable in this experiment?
Blood pressure of mice.
Mutations refer to changes in which important molecule? Name the molecule.
DNA
Lactose breaks down into two monomers, called.....
Glucose and galactose
What process is shown here?
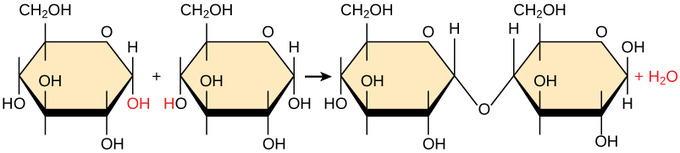
Dehydration Synthesis
Are phospholipidps carbs or lipids? Monomers or polymers?
Lipids, polymers
What is a likely temperature for the hot springs referenced in this image?
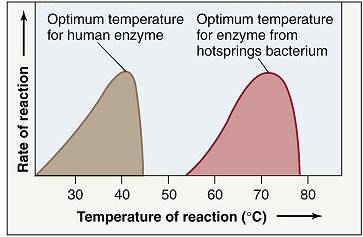
70 Degrees Celsius
1. It assume the mice can change their characteristics, but they can't (I can't choose to be taller, faster, etc).
2. The mutations that make natural selection happen are RANDOM, not by choice.
Lactase speeds up the breakdown of the polymer lactose into two monomers. The chemical name we give this breakdown process is ________.
Hydrolysis.
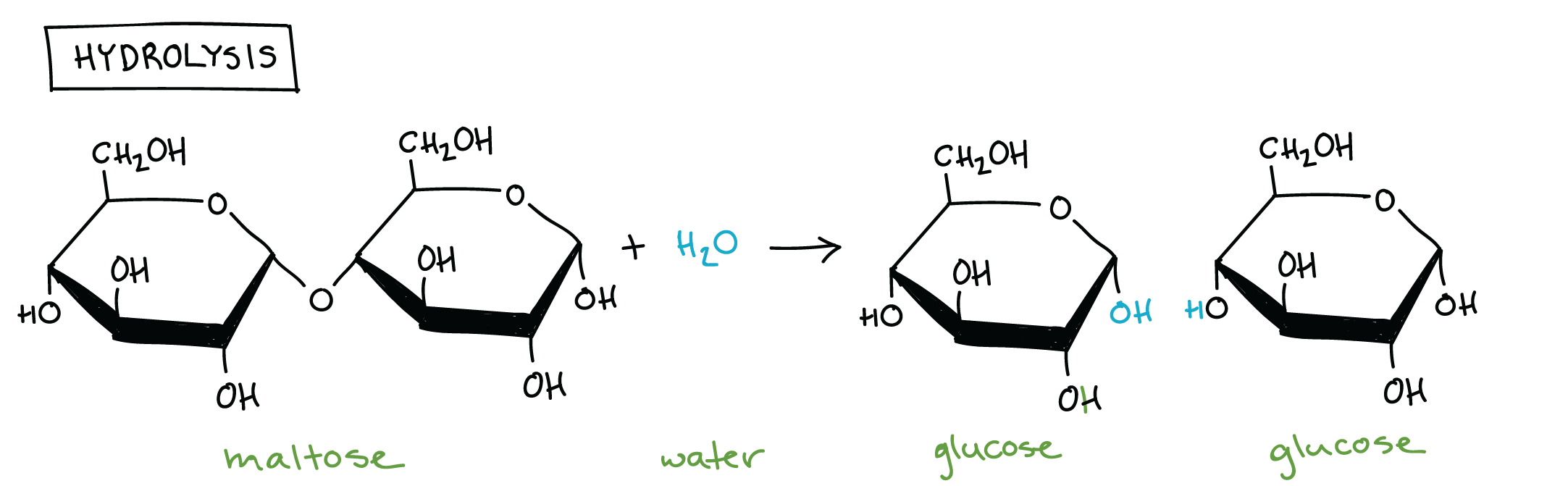
Pictured is the molecule maltose.
If you were to add a single water molecule (H2O) to this molecule, draw what you think the product (outcome) of that reaction would look like below, and name the reaction.

Starch is an example of a ______saccharide, which is a type of ________.
Poly, carbohydrate
In the Chew On This simulation we saw briefly in class, the enzyme amylase was breaking down down starch. What process does the amylase help make happen more quickly, in this case?
Who are the "mutants" - people that produce lactase as adults, or people that cannot produce lactase as adults?
People who can produce lactase as adults (who have lactose persistence) are the mutants. They have a mutation in their DNA that allows lactase to keep being made all through their lives.
Pictured below are lactose and a very similar polymer called sucrose. Can lactase break down sucrose, yes or no?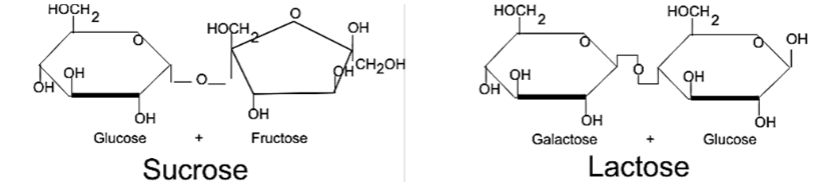
No - enzymes are specific to substrates. They only work with one substrate, so lactase only works with lactose.
WILD CARD: Experimental Design
You are interested in how salinity affects how many eggs mummichogs produce. You have 10 tanks, each with 20 mummichogs in them. You set each tank to a slightly different salinity and measure the amount of eggs produced in each tank.
1. Name at least two constants in this experiment.
2. Name a control trial that is needed for this experiment.
1. Anything that stays the same between tanks - so temperature, size of tanks, food fed to the mummichogs, type of habitat in the tanks, etc.
2. A tank with a salinity of 0ppt so you can test the the results with "no" independent variable - so no salinity added.
Fill in the blanks.
Molecules that are _______ love water and dissolve easily in it, like __________, which have special parts called _______ (-OH).
Molecules that are _______ avoid water and don’t dissolve, like fats and oils, which are types of _______.
Molecules called _______ have both hydrophilic and hydrophobic regions, making them _______.
Hydrophilic, carbohydrates, hydroxyl groups
Hydrophobic, lipids
Phospholipids, Amphipathic
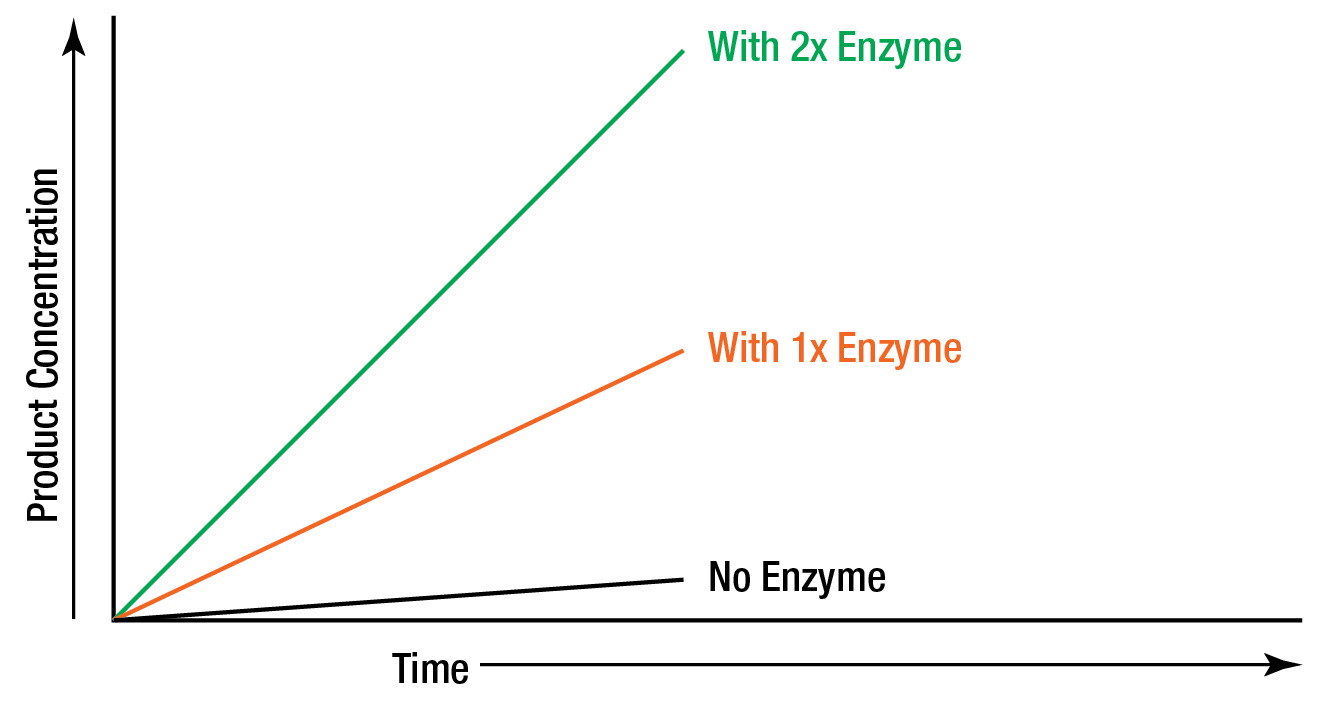
This graph shows the amount of product produced in a chemical reaction over time WITH an enzyme present. Redraw this graph, then draw another line representing a likely product amount over time WITHOUT an enzyme for the same chemical reaction. (So you should draw a graph with two lines total).

Second line should be lower for than the first, BUT NOT ZERO. Remember, enzymes speed up reactions, but they don't make them happen - some product will still be made! This graph is an example showing that:
What is the relationship between natural selection, mutation, proteins, and nucleic acids? Explain.
Natural selection requires variability to occur, which means that a trait varies in a population. This occurs when individuals are born with random variations (changes) in their DNA, just be chance. An example is hair color in humans - there are lots of variations in hair color! Any difference in a DNA sequence is called a mutation (and they aren't all bad!).
Since DNA contains the instructions for making proteins, differences in DNA (mutations) can lead to different proteins being made in the body, and different proteins can lead to different traits. For instance, some of the DNA in the rock pocket mice led to proteins that made dark fur, and some had DNA that coded for proteins with light fur.
Since DNA is genetic material, these mutations are heritable and passed from parents to offspring. Therefore, natural selection can occur if one mutation is an advantage over another in the environment where the organism lives.
Draw a model comparing the large and small intestines of someone who has lactase persistance vs someone who is lactose intolerant.
Must look like this:
Must include lactose, lactase, glucose, galactose, bacteria, and at least one symptom. In the person with lactase persistance, hydrolysis of lactose occurs quickly and glucose and galactose are moved from the small intestine to the blood to provide energy. With lactose intolerant individuals, it doesn't happen quickly enough. Lactose is too big to pass through the cell membrane of the small intestine cells, so it keeps going. Bacteria in the large intestine then break it down, but produce a bunch of bad symptoms as a result!