The general term for the smallest unit of a macromolecule. (building block of carb, lipid, or protein)
What is a monomer?
An organic compound made up of sugar molecules
What is a carbohydrate?
A defining property of Lipids is that they are (interaction with water:)
What is hydrophobic?
The name for a chain of amino acids (amino acid polymer).
What is a polypeptide?
In a folded protein, how are the hydrophobic/hydrophilic amino acids arranged?
what are hydrophobic amino acids on the inside, hydrophilic amino acids on the outside?
What type of macromolecule are enzymes (carbohydrate, protein, lipid)
What is a protein?
A carbohydrate monomer
What is a monosaccharide?
Two-sugar unit
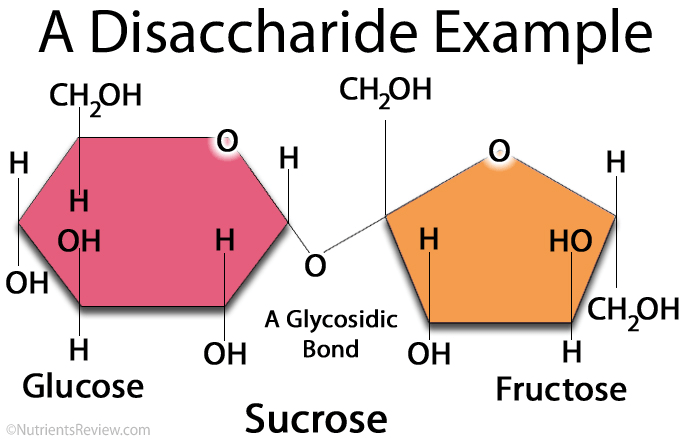 What is a disaccharide?
What is a disaccharide?
A fat with the maximum number of hydrogen atoms bonded to the carbon backbone
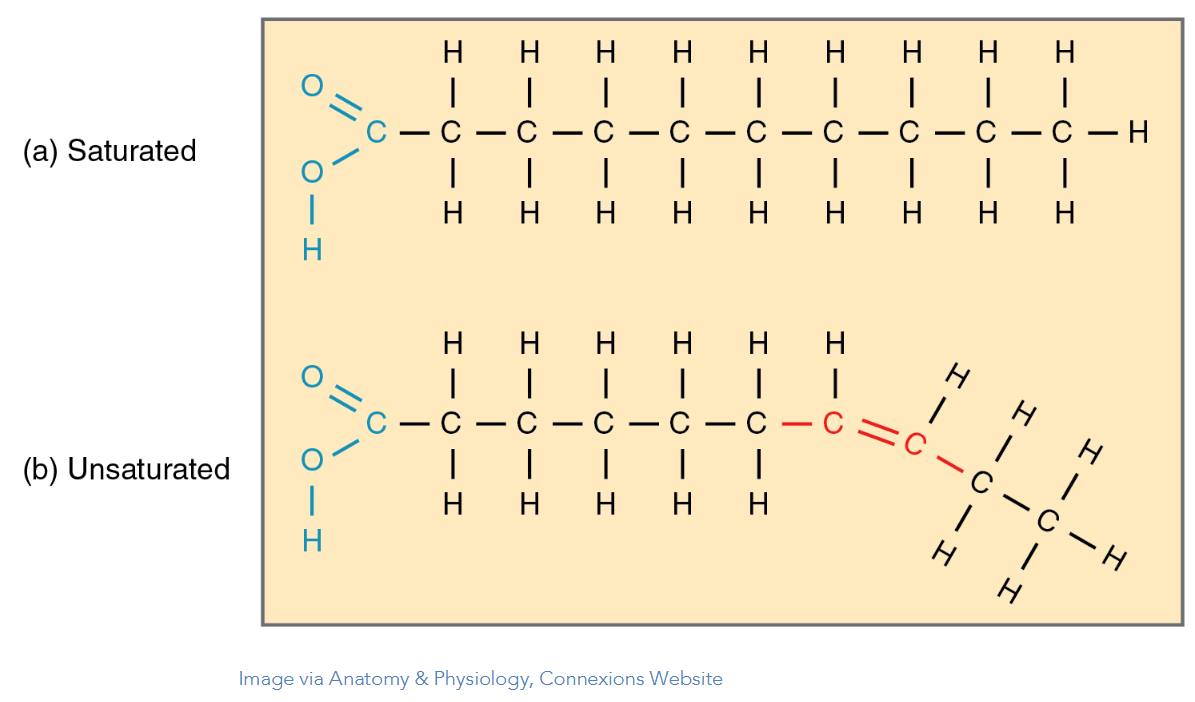 What is saturated?
What is saturated?
Amino Acids are connected via a ________________ reaction
what is a dehydration reaction?
What are the two most common protein folding patterns in secondary structure.
1) Alpha helix
2) Beta sheet
The amount of energy needed to break enough bonds to start a reaction
What is Activation Energy?
A protein monomer
What is an Amino Acid?
Long chain of sugar molecules (Sugar polymer)
What is a polysaccharide?
What state are unsaturated fats in at room temperature? (solid, liquid, gas)
What is liquid at room temperature?
The bond between two amino acids is called.
What is a peptide bond?
What type of interactions are primarily responsible for holding secondary protein structures in place?
what are hydrogen bonds?
This catalyst speeds up reactions by lowering the amount of energy needed to break a bond.
What is an enzyme?
Several monomers together is a...
What is a Polymer?
Give one example of a carbohydrate monosaccharide, OR one example of a carbohydrate disaccharide.
Carbohydrate monomers: glucose, fructose, galactose
Carbohydrate disaccharide: Maltose (glucose + glucose) Sucrose (glucose + fructose)
The structural difference that distinguishes an unsaturated fat from a saturated fat.
What is a double carbon bond?
Amino acids are similar in structure with the exception of
what are side (or R) groups?
Two or more tertiary protein structures aggregated together
what is quaternary structure?
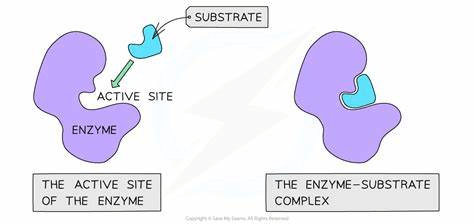
The area on the enzyme where the substrate binds
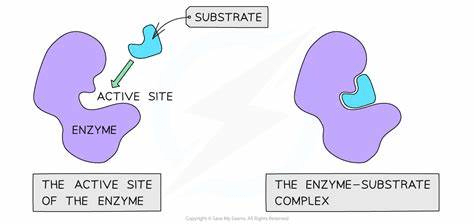 What is the active site?
What is the active site?
for ALL of the macromolecules discussed this chapter, which type of reactions make and what type of reactions break the bonds in between monomers?
What are hydration/dehydration reactions?
The three elements that comprise carbohydrates
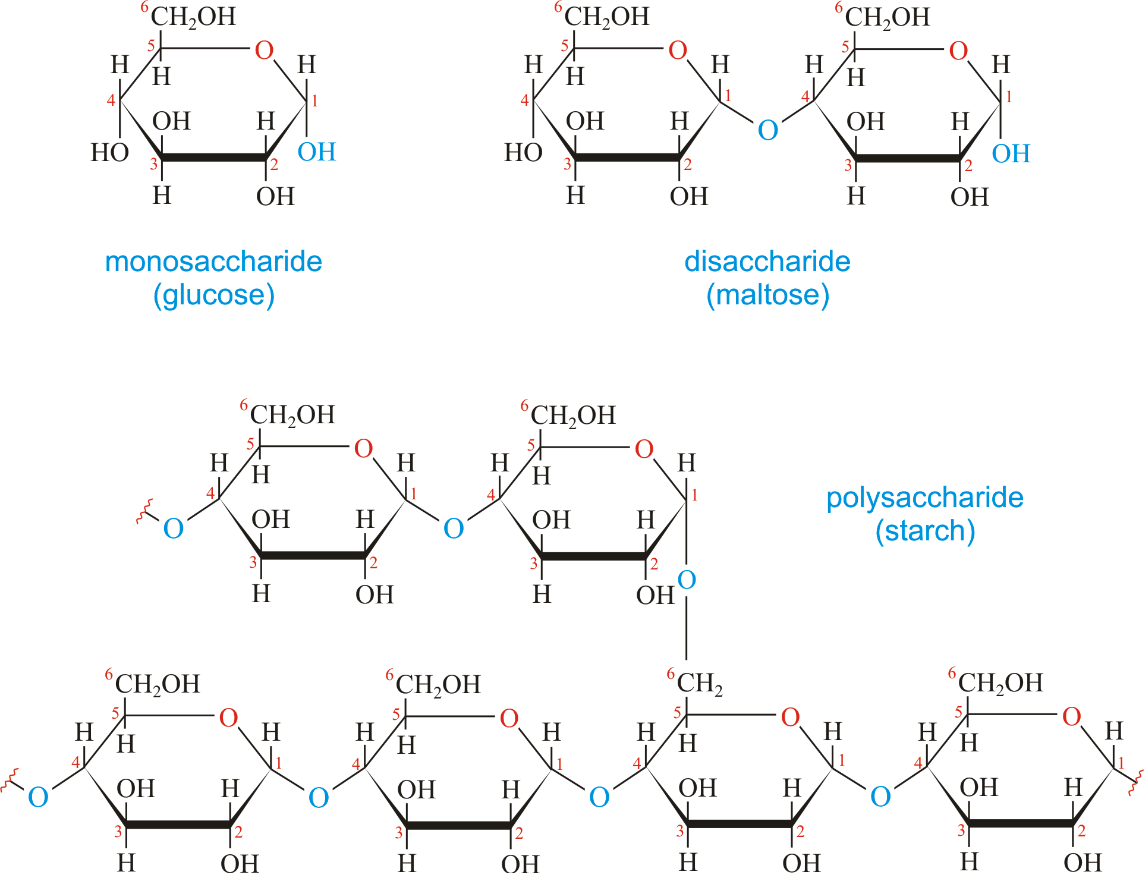 What is Carbon Hydrogen, Oxygen.
What is Carbon Hydrogen, Oxygen.
DRAW the general structure of a lipid (glycerol backbone and fatty acids)
Sort the following from most easily useable energy source to more difficult (Protein, Carbohydrates, Lipids)
Carbs, Lipids, Protein
What is protein denaturation, what causes it, and how does it affect the function of the protein?
- unraveling of a protein
- caused by changes of pH, increase in temperature
- protein becomes non-functional
Draw an enzyme, labeling the 1) enzyme 2) substrate 3) active site