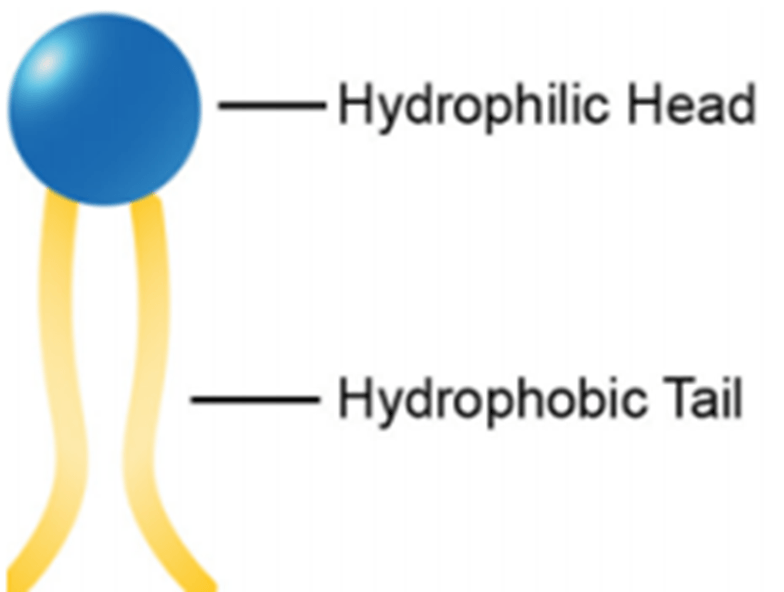
What is a phospholipid?
This biomolecule is used for long term energy storage.
What is a lipid?
CHON
What is a protein
The monomer of a carbohydrate.
What is Monosaccharide?
Examples of this biomolecule are oils, fats and waxes.
What is a lipid?
The optimal pH of an acidophile.
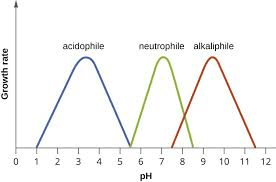
What is 3?
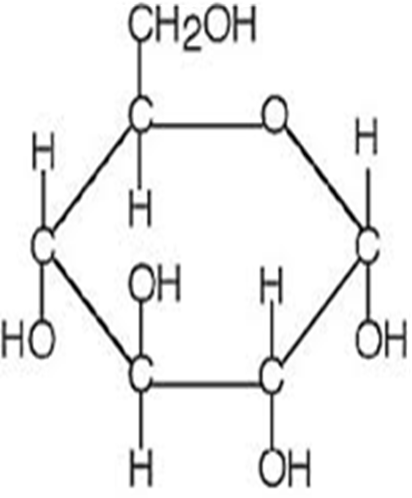
What is a Carbohydrate? A monosacchaide.
This biomolecule is used for structure, support and transportation.
What is a protein?
CHO in the ratio of 1:2:1
What is a carbohydrate?
The monomer of a protein.
What is an amino acid?
Examples of this biomolecule are sucrose, fructose, lactose and maltose.
What is a carbohydrate?
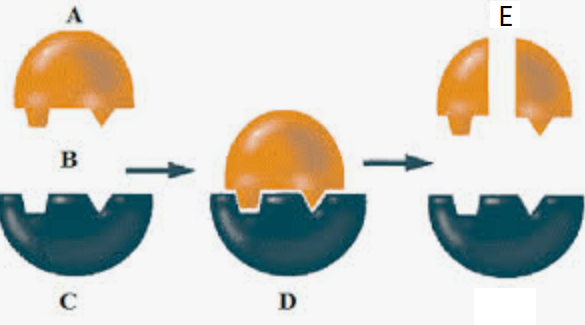
A. Substrate
B. Active Site
C. Enzyme
D. Enzyme-Substrate Complex
E. Products
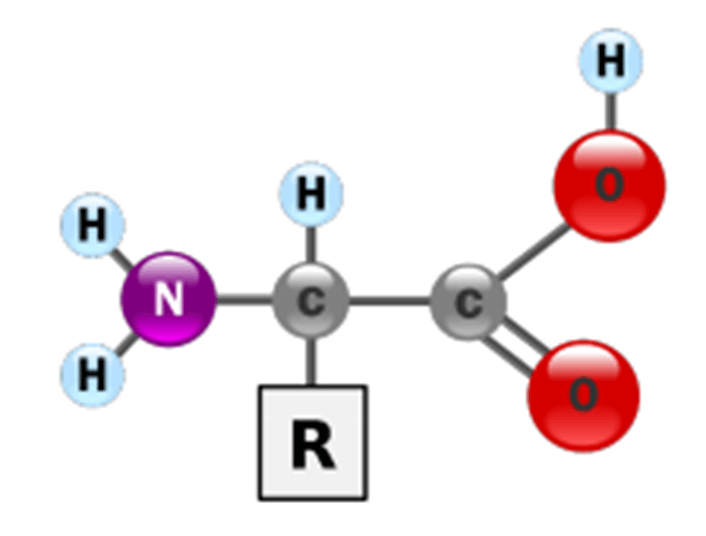
What is a Protein? An amino acid.
This biomolecule provides short term energy.
What is a carbohydrate?
CHO with most C's and H's in the "tail" region.
What is a lipid?
The monomer of a Nucleic Acid.
What is a nucleotide?
The biomolecule group these 2 molecules belong to.
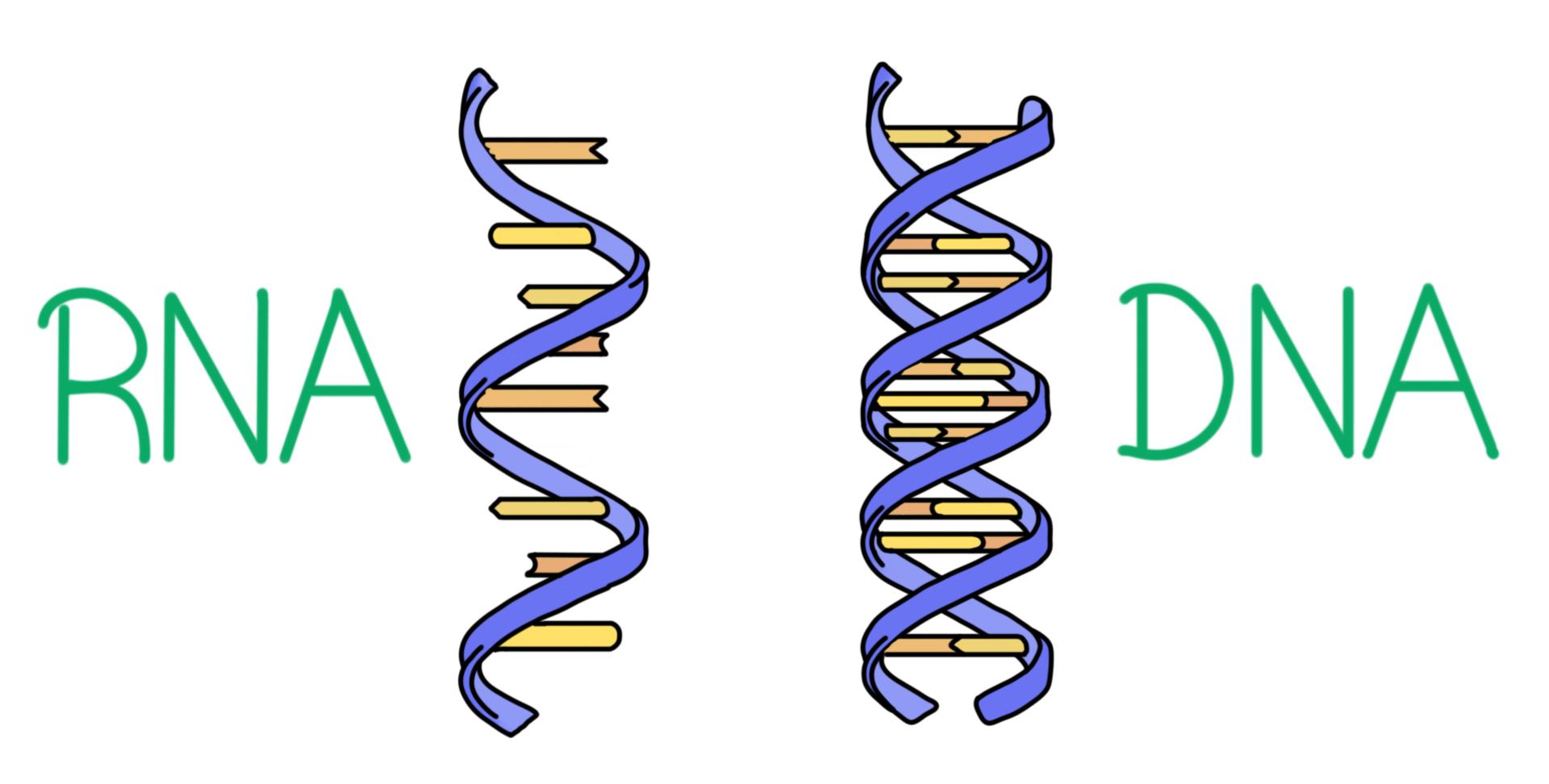
Nucleic Acids
When temperature or pH cause an enzyme to change shape.
What is denature or denaturation?
Type of Molecule? Saturated or unsaturated?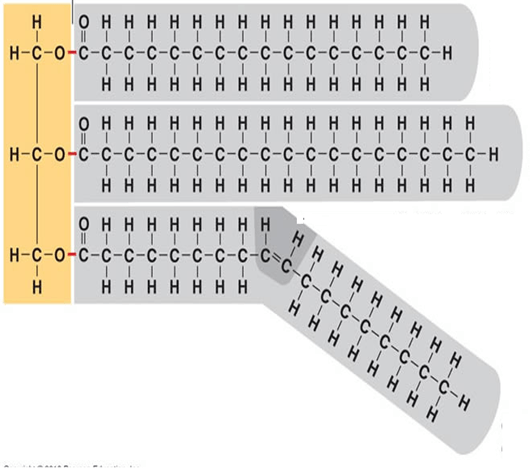
What is a Lipid, triglyceride, unsaturated?
This biomolecule is stored by plants in the form of cellulose or starch.
What is a carbohydrate?
CHONP
What is a nucleic acid?
Name the two parts of a lipid such as a triglyceride.
What are Glycerol and Fatty Acids.
Organic or Inorganic?
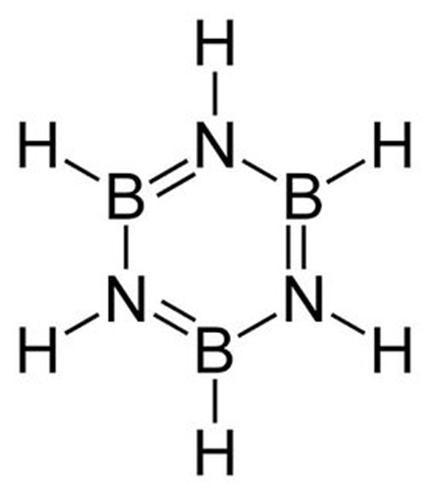
Inorganic
These molecules catalyze reactions by lowering the activation energy of the reaction.
What are enzymes?
Which biomolecule is this?
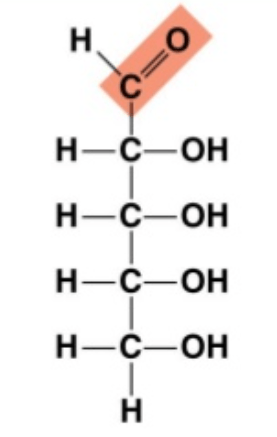
What is a carbohydrate?
Certain types of this molecule make up the cell membrane.
What is a lipid?
How do you tell the difference between Carbs (CHO) and Lipids (CHO)?
Carbohydrate monomers are in the ratio of 1:2:1 or CH20.
These molecules go through multiple folding and bonding processes to form each level of structure.
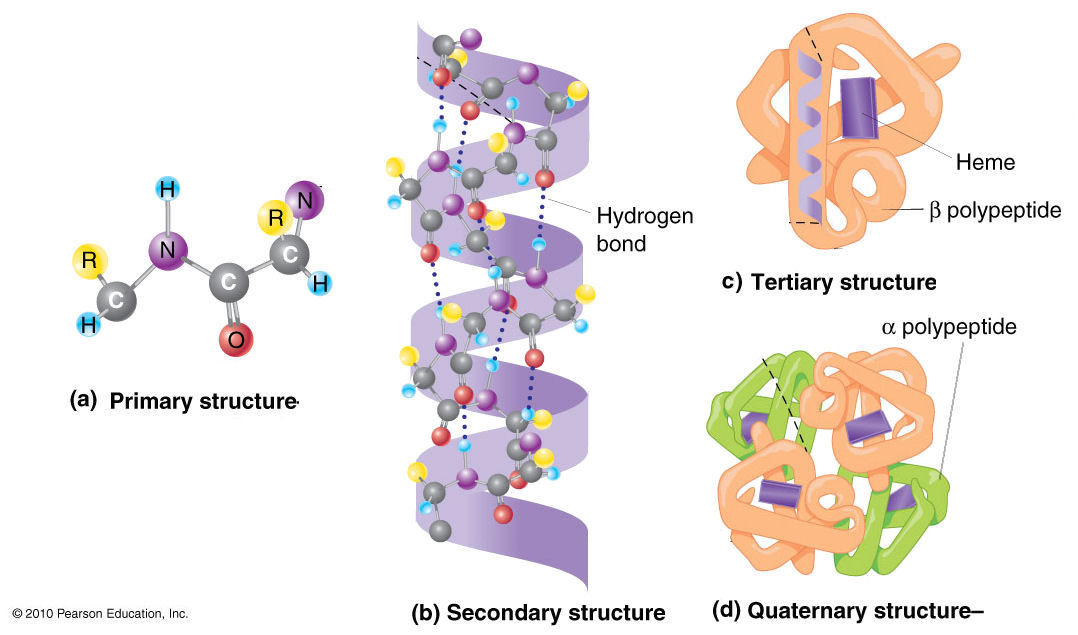
What are proteins?
Nucleic Acids
Factors that affect the rate or ability of enzymes.
What are?
Concentration
pH
Temperature
Inhibitors