The heritable adaptation process that increases an organism's chances of survival
What is evolution?
A way of understanding by drawing structures with symbols instead of description
What is sketchnoting?
All forms of knowing and awareness, such as perceiving, conceiving, remembering, reasoning, judging, imagining, and problem solving. Along with affect and conation, it is one of the three traditionally identified components of the mind
What is cognition?
The philosophy of education pioneered by Jean Piaget
What is constructivism?
The Japanese concept that means "a reason for being"
What is Ikigai?
A concept used to modify behavioral decision-making; relies on our first impressions and plays on external or internal triggers that directly influence behavior
What is the nudge approach?
The neurotransmitter that plays a major role in motivation and addiction in the reward circuit of the brain
What is dopamine?
Interim memory process in between sensory memory and long-term memory
What is short-term (memory)?
This German psychologist developed the IQ test in 1912
Who is William Stern?
According to Piaget, these are the basic building blocks/units of knowledge
What are schemas?
The name for the mental exercise which consists of voluntarily focusing on the present moment without judgement
What is mindfulness?
A set of shared beliefs, values and techniques that form a consensus, turn an area of research into a discipline and provide a source of standardization of scientific practices
What is a paradigm?
The study of inherited genetic changes (active vs inactive genes) that don't involve changes to the DNA sequence, but do change the physical structure of the DNA and influence what phenotype is expressed
What is epigenetics?
Students with this attention problem would be helped by the following classroom setup:
Seating away from distractions, preferably front and center
Seating near a good role model
What is ADHD (Attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder)?
It's important to be aware of this type of "reasoning" because it could lead to invalid conclusions:
if A then B
not A
therefore...?
What is conditional reasoning?
Secure
Dismissive-avoidant
Anxious-ambivalent
Fearful-avaoidant (disorganized)
What are attachment styles?
The core topic of Ikigai workshops
What is purpose?
This experiment conducted by Bandura showed that children (ages 3-6) will change their behavior based on what they see others doing (they can learn social behavior through observational learning)
What is the Bobo doll experiment?
This phenomenon reduces synaptic connections in an infant brain to optimize neural circuits
What is neural pruning?
A condition in which one sensory pathway involuntarily evokes another sensory pathway in the brain (eg. associating/seeing specific colors with certain letters or words)
What is synesthesia?
The use of deliberate and controlled mental operations, often in a flexible manner, to solve novel problems that cannot be performed automatically; also referred as fluid intelligence (Gf)
What is fluid reasoning?
This unlabeled section represents what a learner can do with help from a more knowledgeable other
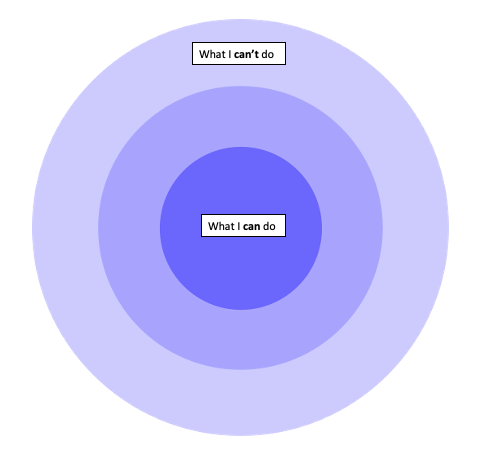
What is the Zone of Proximal Development?
A pathology that could be alleviated by a regular meditation exercise
What is stress?
According to Bandura, this term refers to “the belief in one’s capabilities to organize and execute the sources of action required to manage prospective situations”
What is self-efficacy?
Continuous stress accumulates this and can lead to atrophy of the brain and stress response system (HPA axis)
What is cortisol?
Broadbend’s theory depicting a trait of attention that selects information to be processed
What is the Bottleneck theory (or filter theory)?
Q: If a baseball bat and a ball cost 1,10£, and we know that the bat costs 1£ more than the ball, then how much does the ball cost?
A: 5 cents.
This is the name for the bias experienced by people who answer “10 cents”
What is attribute substitution (or substitution bias)?
Bruner’s theory which asserts that children depend on adult support when learning something new, but as they become more independent the support can be gradually reduced
What is scaffolding?
This American professor of medicine helped spread and promote the practice of meditation in Europe in the 1970s
Who is Jon Kabat-Zinn?
This theory explains the psychological phenomenon of why people tend to dislike losses more than they like (equivalent) gains; people are more willing to take risks to avoid losses compared to their willingness to take risks for gains
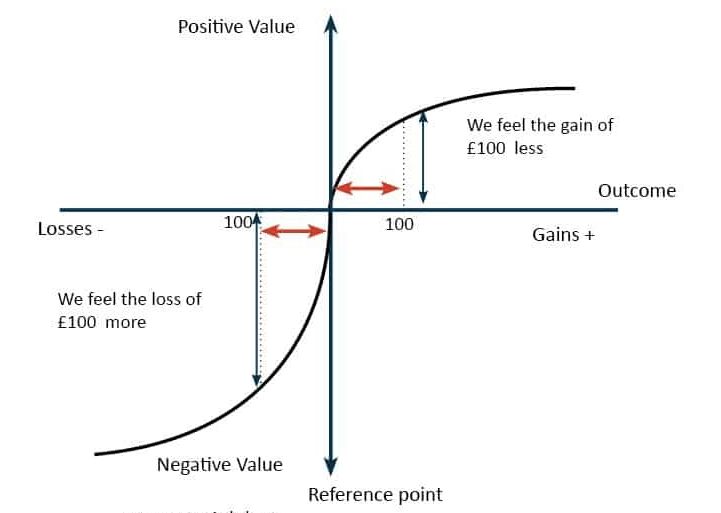
What is prospect theory?