For how long do you have to wait until you can consider ICD placement in HFrEF?
What are 3 months?
This type of intervention is recommended for patients with hemodynamically unstable AF.
What is cardioversion?
This heart sound, often heard in mitral stenosis, occurs shortly after the second heart sound and is caused by the abrupt halting of the stiff mitral valve during diastole.
What is an opening snap?
When transferring a STEMI patient from a non-PCI hospital, PCI should be performed within this maximum number of minutes from the first medical contact.
What is 120 minutes?
What congenital heart abnormality is a fixed splitting of S2 associated with?
What is ASD?
Name one etiology that can cause low pro-BNP levels?
What is obesity?
In the CHADS-VASc score, this many points are assigned for a history of stroke, TIA, or thromboembolic disease.
What is 2 points?
What is the anticoagulant of choice for patient with mitral stenosis and atrial fibrillation?
What is warfarin?
For a diagnosis of STEMI, men must have ST elevation of at least this many millimeters in leads V2 and V3.
What is 2 mm?
A chest x-ray shows inferior rib notching. What congenital heart disease is this finding associated with?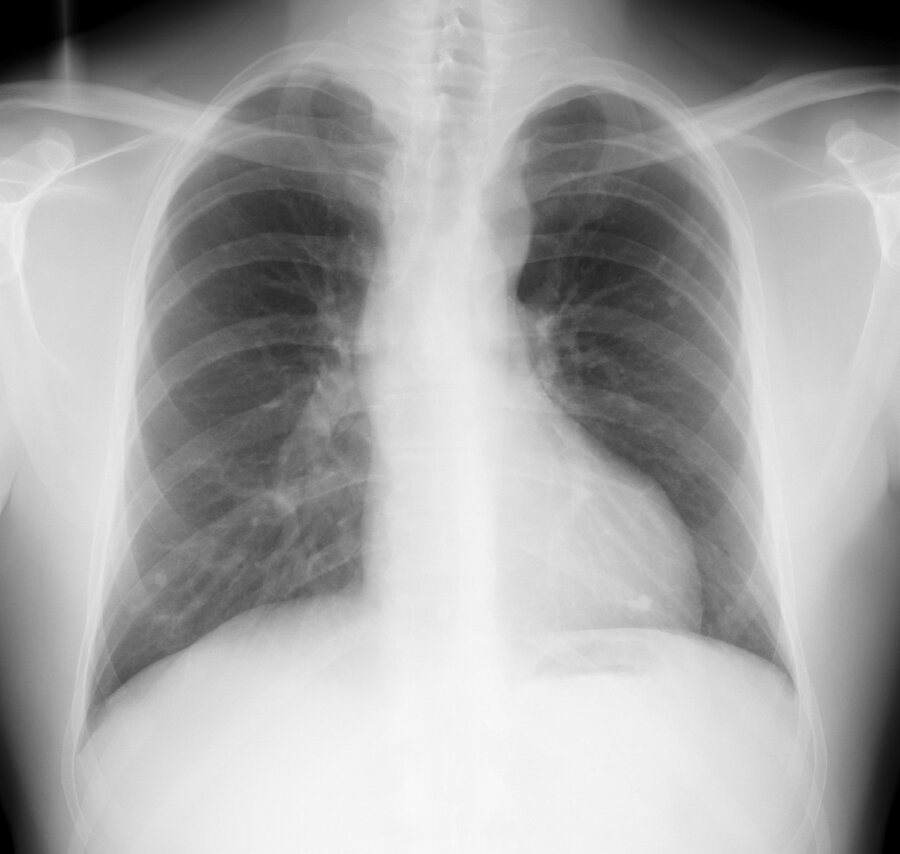
What is aortic coarctation?
This drug combination is recommended as an alternative when ACE inhibitors or ARBs cannot be tolerated in HFrEF.
What is hydralazine plus nitrates?
These three types of medications should not be started in patients with AF and WPW syndrome due to the risk of worsening the arrhythmia.
Name 1 and get the points.
What are calcium channel blockers, β-blockers, and digoxin?
What is the preferred intervention for an 81-year-old man with dyspnea and severe aortic stenosis?
What is TAVI?
A blood pressure greater than this threshold is a contraindication for thrombolytic therapy in ACS patients.
What is 180/110 mm Hg?
This syndrome, characterized by pulmonary hypertension and right-to-left shunt reversal, is a late complication of a large unrepaired VSD.
What is Eisenmenger syndrome?
This class of medications should not be prescribed to patients with decompensated heart failure due to their potential to worsen symptoms.
What are β-blockers?
This treatment is the first-line intervention for a stable patient with Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome who presents with atrial fibrillation and a wide-complex tachycardia.
What is IV procainamide?
What is the target therapeutic INR in a patient with a mechanical mitral valve?
What is 2.5-3.5?
Based on the EKG, what is likely occluded artery?
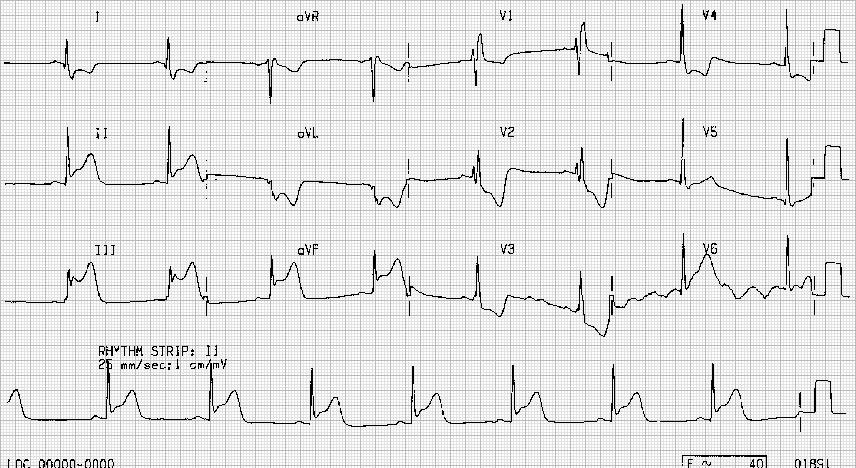
What is RCA?
A 35-year-old woman reports cold feet and leg cramping when walking long distances. BP is 160/90 mm Hg. Cardiac examination shows a sustained apical impulse, an early systolic ejection sound, and an early systolic murmur at the upper right sternal border. What is the potential congenital heart disease?
What is aortic coarctation?
In patients with LVEF ≤35% and NYHA class II-IV, this device improves LVEF and reduces symptoms and mortality when LBBB is present with a QRS duration >150 ms.
What is cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT)?
What does this EKG show?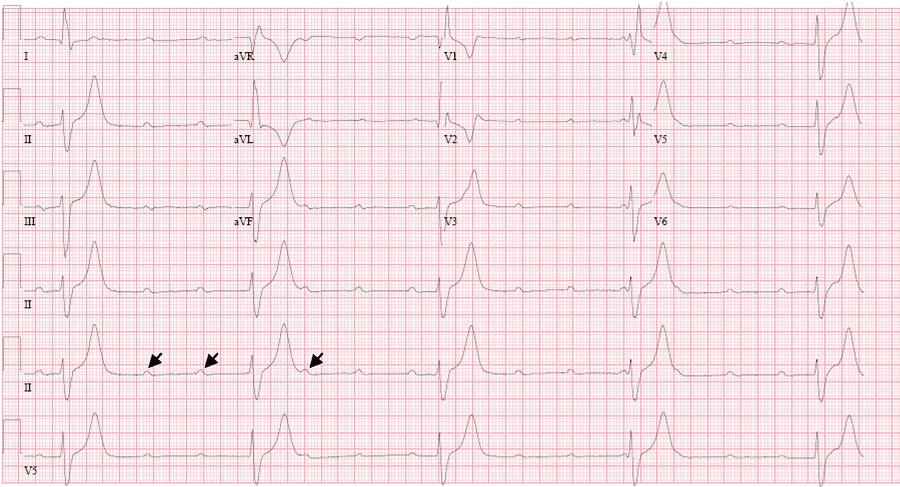
What is third degree heart block?
This ejection fraction threshold in asymptomatic patients is an indication for aortic valve replacement in severe aortic stenosis.
What is less than 50%?
57-year-old male develops chest pain 3 days s/p stent placement in LAD. EKG shown below. What is the diagnosis?
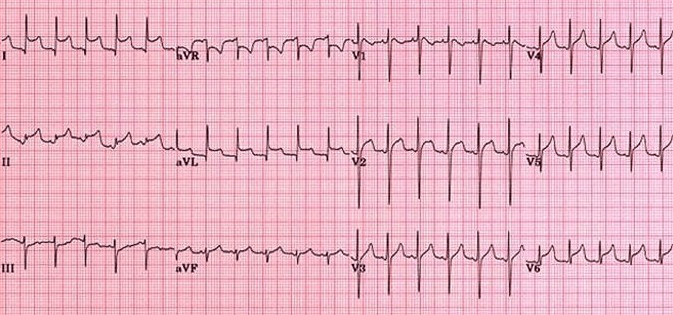
What is pericarditis?
When this vessel remains open after birth, it creates a pathway between the aorta and the pulmonary artery, affecting circulation.
What is PDA?
This drug is used to treat HFrEF patients with EF ≤35% in sinus rhythm with a heart rate ≥70/min despite maximal β-blocker therapy.
What is ivabradine?
What does this EKG show?
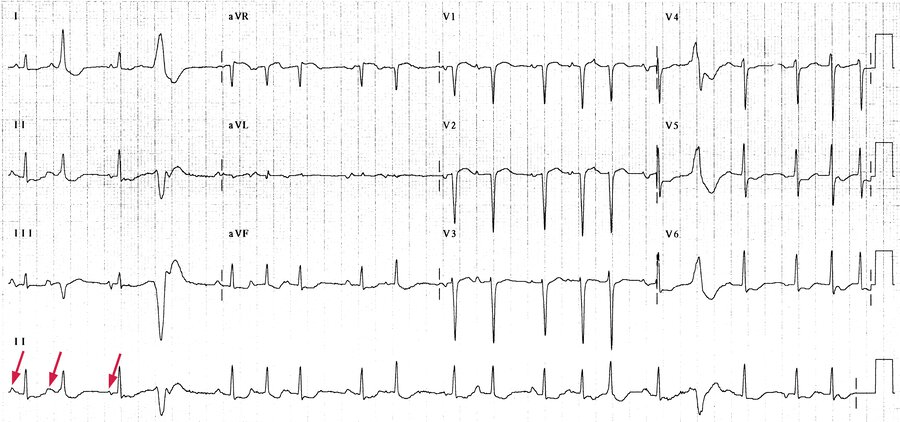
What is multifocal atrial tachycardia?
These medications are used as a bridge to surgery in patients with acute severe aortic regurgitation.
What are sodium nitroprusside and IV diuretics?
In unstable angina/NSTEMI, a TIMI score above this threshold suggests the need for early revascularization rather than predischarge stress testing.
What is 2 (i.e., intermediate to high risk scores of 3-7)?
Surgical closure of an ASD is contraindicated in patients with this shunt direction due to pulmonary hypertension.
What is right-to-left shunt reversal?