Supraventricular tachycardia/arrhythmia
- why? narrow QRS with rapid ventricular excitation
Name a cardiac condition that is an indication for dental procedure prophylaxis.
Ans: prosthetic valve, cardiac transplant patient with a cardiac valvulopathy, congenital heart disease, previous EC
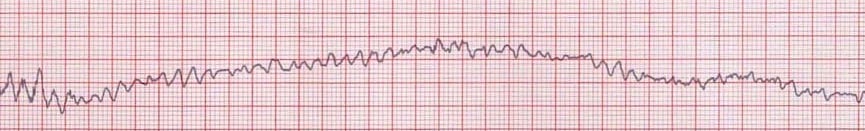
Ventricular fibrillation
Why: Chaotic irregular deflections without identifiable P-QRS-T waves
What is the preferred treatment for torsade’s de pointes?
IV magnesium sulfate
Beck's Triad signs and symptoms
HYPOtension, JVD, Muffled Heart Sounds
How does ventricular rhythm differ from supraventricular rhythm?
There is a WIDE QRS with slower depolarization.
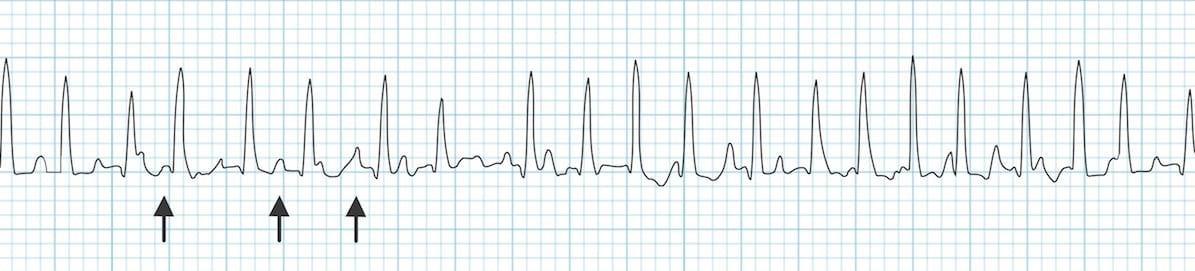
Multifocal Atrial Tachycardia (MAT)
Electrocardiographic Features
- Heart rate > 100 bpm (usually 100-150 bpm; may be as high as 250 bpm).
- Irregularly irregular rhythm with varying PP, PR and RR intervals.
- At least 3 distinct P-wave morphologies in the same lead.
- Isoelectric baseline between P-waves (i.e. no flutter waves).
- Absence of a single dominant atrial pacemaker (i.e. not just sinus rhythm with frequent PACs).
- Some P waves may be nonconducted; others may be aberrantly conducted to the ventricles.
What is the preferred treatment for sustained ventricular fibrillation?
CPR and defibrillation
Definitive Treatment for Pericarditis
Pericardiectomy
What do monomorphic and polymorphic ventricular arrrythmias have in common?
Elevated rate and wide QRS
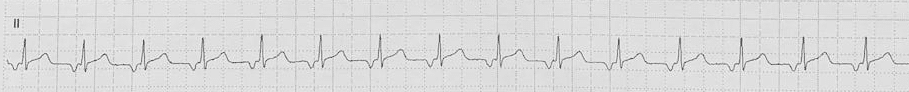
Focal atrial tachycardia (FAT): Consistent, abnormal P wave morphology indicating an ectopic focus
What is the most common cause of sudden cardiac death?
Torsades De Pointes
Emergency pericardiocentesis is performed with a needle inserted into what intercostal space?
5th intercostal
Autosomal dominant condition that affects cardiac sodium channels and puts individuals at risk for polymorphic dysrhythmia?
Brugada Syndrome
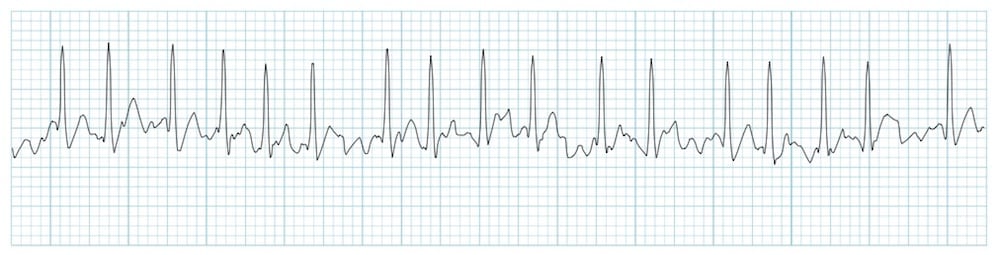
Atrial fibrillation: Irregularly irregular ventricular rate without visible P waves
Which is a presenting symptoms for atrial fibrillation?
- Shortness of breath
- Heart palpitations
- Confusion
- chest pain
What is the primary difference between MI and Acute Pericarditis?
Diffuse ST elevations
Monomorphic V fib
Why? Because QRS complexes are pretty much the same.
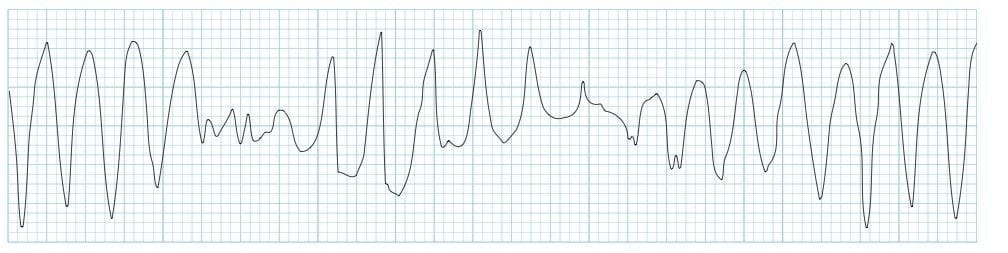
Torsades de pointes
Torsades de pointes (TdP) is a specific form of Polymorphic ventricular tachycardia (PVT) occurring in the context of QT prolongation — it has a characteristic morphology in which the QRS complexes “twist” around the isoelectric line.
What population is at risk for Brugada syndrome?
Asian Males
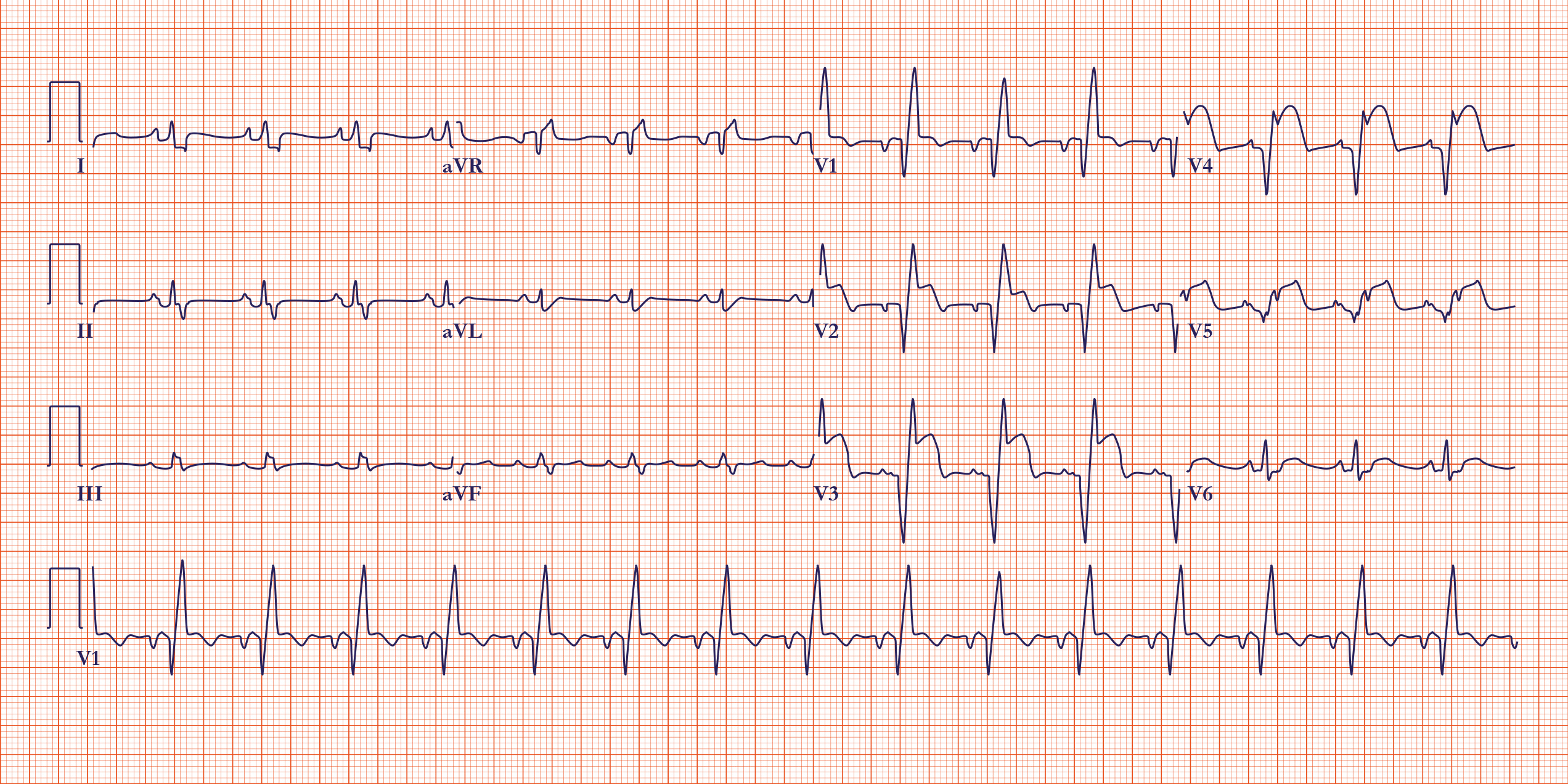
ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction