What organelle does cellular respiration take place in?
Mitochondria
What are the 2 stages of photosynthesis in order?
1. Light Dependent Reactions
2. Calvin Cycle (Light Independent Reactions)
What is NOT available in Anaerobic respiration?
(It is available in Aerobic Respiration)
Oxygen (O2)
Carbohydrates have what 3 elements in them?
Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen (CHO)
When cells are able to skip the cell cycle checkpoints, this is called_________
Cancer
Where does ATP break to release energy?
(D) Between the 2nd and 3rd phosphate
What are the 2 energy carriers (Batteries) that are made in stage 1 in order to power stage 2?
ATP and NADPH
How much ATP is made in Aerobic respiration?
36 ATP
1. Enzymes (can/can't) be reused.
2. Enzymes work on (one/more than one) substrate.
1. CAN be reused
2. ONE substrate
Interphase is made of 3 smaller parts; list them in order.
G1, S, G2
How are the cellular respiration equation and photosynthesis equation similar?
The products of one are the reactants of another
(They are flipped around)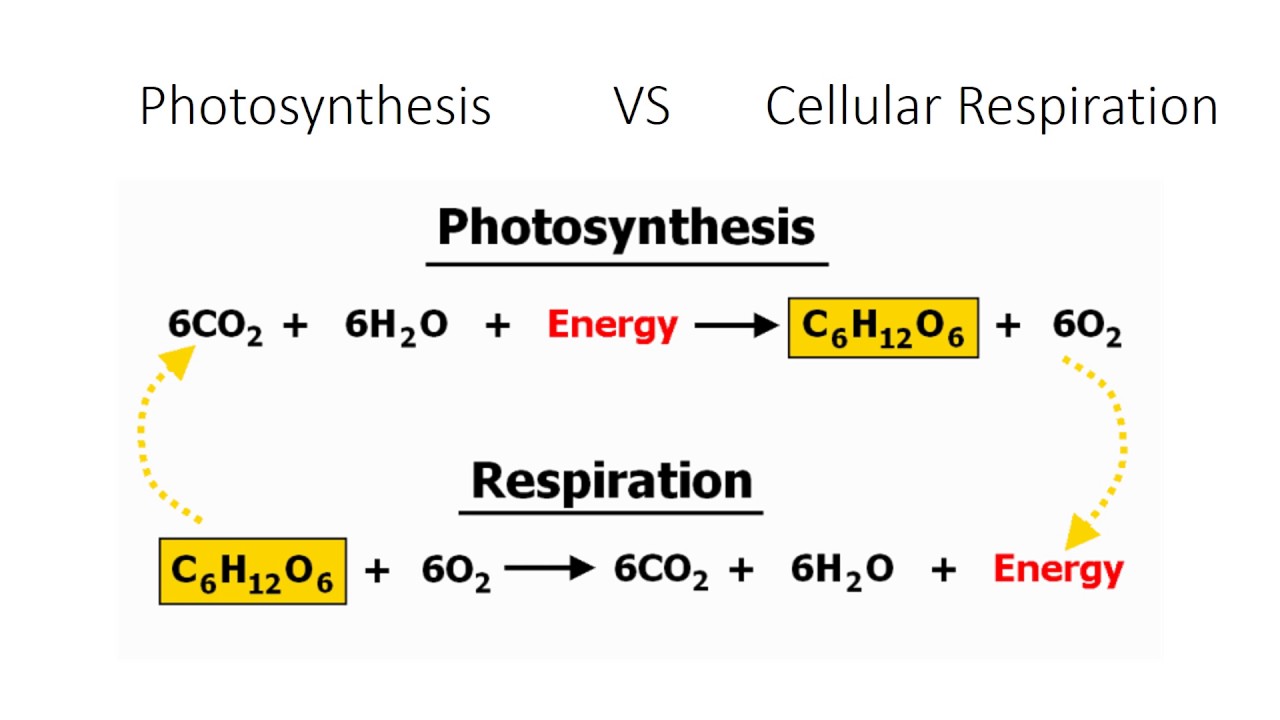
What is split by light energy to make oxygen?
Water (H2O)
What are the 2 types of Anaerobic respiration (fermentation)?
Lactic Acid Fermentation
Alcoholic Fermentation
List the other 2 things that ALL cells have:
1. Cell membrane
2. DNA
3.________
4._______
3. Cytoplasm
4. Ribosomes
If a cell with 10% salt solution is placed in a solution with 2% salt solution, which way will the water move?
Into the cell
Label A, B, C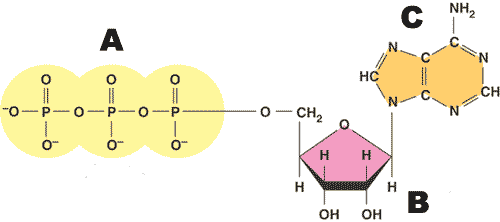
A--Phosphates
B--Ribose
C--Adenine
Photosynthesis takes energy from ______ and turns it into chemical energy in glucose
Light/the sun
What are the 3 parts of Aerobic Cellular Respiration in order?
1. Glycolysis
2. Krebs Cycle
3. Electron Transport Chain (ETC)
1. This organelle provides genetic instructions (DNA)
2. This organelle makes proteins
1. Nucleus
2. Ribosome
This type of transport moves molecules from LOW to HIGH concentration ("up the hill")
Active Transport (Protein Pump)
What does ATP stand for?
Adenosine Tri Phosphate
Glucose is made by photosynthesis, but if a more complex carbohydrate was needed--- what should the plant do with the glucose molecules?
Chain them up
During alcoholic fermentation yeast will make 2 ATP, some alcohol and ______
Hint: it's a gas
Carbon dioxide CO2
Which macromolecule is being described:
enzyme, catalyst, structural function
Protein
Why does every cell in your body have the exact same DNA, yet there are so many different types of cells?
Different genes are activated in different cells