In Griffith's experiment in 1928, he discovered a molecule (DNA) that was capable of "transforming" what into what?
What is a harmless bacterium into a virulent (pathogenic) bacterium?
In the Hershey & Chase experiment in 1952, they used this type of microbe--which was smart, because it contains only the molecules DNA and protein:
What is a virus (phage)?
The structure of DNA is described as a "____ _____":
What is a double helix
If a particular DNA molecule has 20% T bases, it will have this % of C bases:
What is 30%?
DNA replication occurs during the __ phase of interphase.
What is the S phase?
In Griffith's experiment, the genetic difference between the harmless bacteria and the pathogenic strain was the gene for this:
What is a capsule?
In the Hershey & Chase experiment, 32P -- a radioactive form of phosphorus-- was used to radioactively label this molecule:
What is DNA?
DNA is a long chain (polymer) made up of individual monomers called this:
What is a nucleotide?
Based on the comparison is base composition, the DNA molecule with the higher Tm (melting temperature) would be this one:
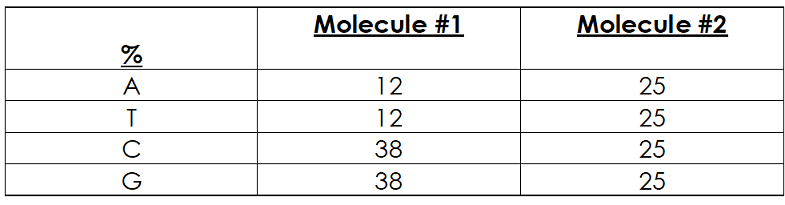
What is molecule #1?
This is the primary enzyme needed to create new strands of DNA during DNA replication:
What is DNA Polymerase?
In Griffith's experiment, when he injected a mouse with heat killed bacteria or with live harmless bacteria, this is what happened to the mouse:
What is it lived?
In the Hershey & Chase experiment, 35S -- a radioactive form of sulfur-- was used to radioactively label this molecule:
What is protein?
Every DNA nucleotide consists of a base, a phosphate group & a sugar called this:
What is deoxyribose?
This part of the DNA nucleotides forms the "backbone" of the molecule:
What are the sugar and phosphate groups
During DNA replication, this many strand(s) in the DNA molecule are used as a template strand:
What is 2?
In Griffith's experiment, when he mixed heat killed virulent bacteria with live harmless bacteria, this molecule was picked up by the harmless bacteria and it changed (transformed) them into virulent bacteria:
What is DNA (the capsule gene)?
In the experiment using 35S, when the bacterial cells were centrifuged (pelleted), the following result revealed that the radioactive protein (shown in red) was here:

What is outside of the bacterial cells?
These are the 4 possible bases in a DNA nucleotide:
What are A (adenine), C (cytosine), T (thymine) and G (guanine)
This part of the DNA nucleotide is the "informational" part of the nucleotide:
What is the base?
DNA replication is semi-conservative. Therefore, after 1 round of DNA replication, all of the new DNA molecules will contain this % of newly synthesized DNA:
What is 50%?
In Avery's experiment, this enzyme was able to degrade (destroy) the "transformation principle" and blocked the changing of the harmless bacteria into lethal bacteria:
What is DNase?
In the experiment using 32P, when the bacterial cells were centrifuged (pelleted), the following result revealed that the radioactive DNA (shown in red) was here:
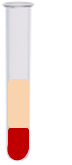
What is inside the cells?
In complementary base pairing in DNA, this base pairs with C (cytosine):
What is G (guanine)?
The two strands of nucleotides in a DNA molecule are said to be _____, which means they run in opposite directions:
What is anti-parallel?
A DNA template strand reads:
C A G G T C A A
Therefore, this will be the sequence of the new strand of DNA:
What is G T C C A G T T