Used for long term energy and controls water movement due to polarity
What is Lipids
Which chemical reaction based on the graph below is an enzyme present in? (A or B)
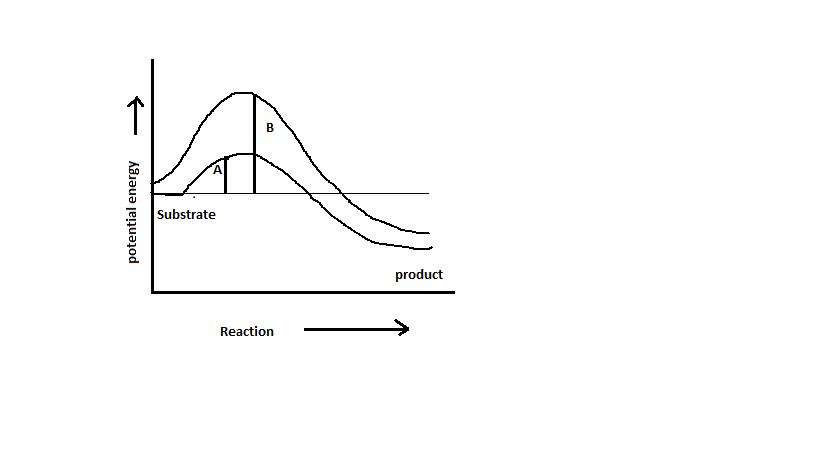
A
Creating chemical bonds stores or releases energy?
Stores.
What are the monomers of carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids
What is monosaccarides, amino acids, fatty acids, and nucleotides
Function of this macromolecule is enzymes used to speed up chemical reactions, muscle development, etc.
What are Proteins
What exactly do enzymes do?
Lower the amount of activation energy needed for a reaction to take place.
Based on the Law of Conservation of Matter, the mass of the products in a chemical reaction should be ______ to the mass of the reactants.
Equal
Describe the structure of the cell membrane
Phospholipids that contain 2 fatty acid tails which are hydrophobic and prevent water from freely passing through the membrane. Phospholipids sit tail to tail
Quick, short term energy - bonds are easily broken
What is carbohydrates
What is the function of Nucleic acids
Holds our genetic material / instructions for life
This fits into an enzyme to cause a chemical reaction to take place
What is substrate
Based on the diagram below, which has more energy products or reactants?

Reactants
Phospholipid is made up of?
What is Phosphate head that is polar or hydrophylic Fatty acid tails which are non-polar or hydrophobic
Rings of Carbon, Hydrogen, and Oxygen
What is a carbohydrate
When proteins or enzymes are exposed to high temperature or extreme chemicals these extreme situations permanently change the proteins function, it no longer works properly
What is denaturing?
Describe the energy diagram below in terms of energy being absorbed or released and endothermic or exothermic.
Released. Exothermic.
What is only true about about enzymes?
Not all catalysts can be used in biological systems because of the narrow limits of life.
Elements found in __________ are CHONP
Nucleic Acids
Lock and Key Model - Describe how this relates to enzymes and denaturing.
The enzyme is like the lock and has a certain shape. The substrate is like a key which also has a certain shape to fit perfectly into the lock. When the shapes are unaltered, the lock opens or chemical reaction takes place. If the shape changes (denaturing) the key no longer fits and the reaction cannot happen.
Is the chemical reaction below endothermic or exothermic? What happens to the bonds in this chemical reaction?
2H2O2 -> 2H2O + O2
Exothermic. Energy is released. The bonds are broken and eventually reformed.
