What are the otolith organs and what type of head motion is detected by them?
The otolith organs (utricle + saccule) detect linear acceleration and gravity.
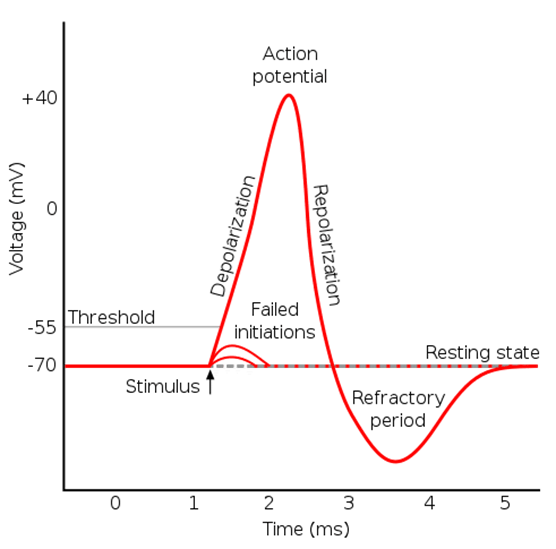
A brief electrical event typically generated in the axon that signals the neuron as 'active’. Includes a rapid POSITIVE change in voltage across a cell membrane.
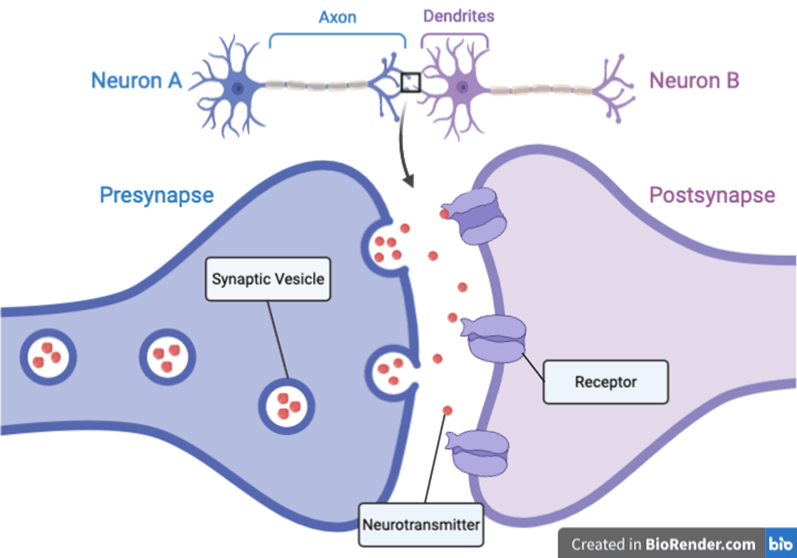
An ACTION POTENTIAL travels the length of the axon and causes release of neurotransmitter into the synapse.
What part of the brainstem is the Cochlear Nucleus in?
Medulla
The SOC is involved in sound localization by comparing timing and intensity differences of sounds received from each ear. Describe Interaural Time Differences (ITDs).
ITDs refer to the difference in the time it takes for a sound to reach each ear. When a sound source is closer to one ear, it arrives at that ear slightly earlier than it does at the other ear.
The Lateral Lemniscus + Inferior Colliculus generate one wave together on the ABR. What wave is that?
Wave V (I will ask you about all the waves on your exam!)
The Auditory Cortex is the last structure on the ASCENDING or DESCENDING auditory pathway?
ASCENDING (Outer Ear -- > Cortex)
Why do otolith organs (but not semicircular canals) detect gravity?
Because the otolithic membrane contains otoconia, making it heavier than endolymph—this allows it to shift under gravity.
The cupula has no otoconia and has the same density as endolymph, making it gravity-neutral.
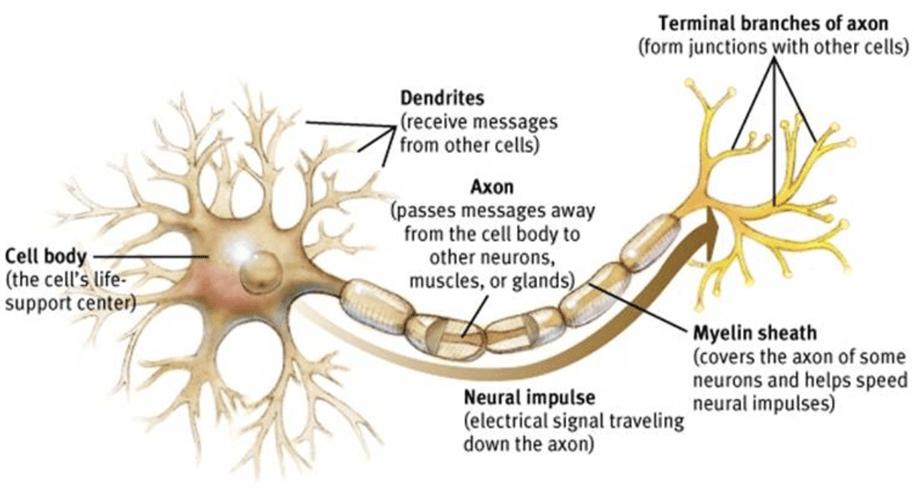
A(n) __________ is a receiving part of the neuron.
A(n) ________ transmitting part of the neuron.
DENDRITES and AXONS
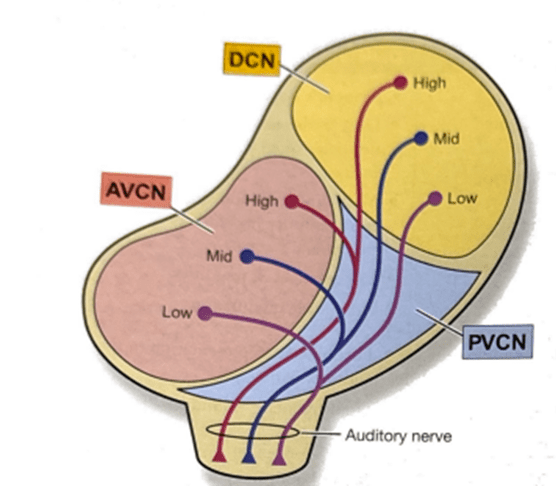
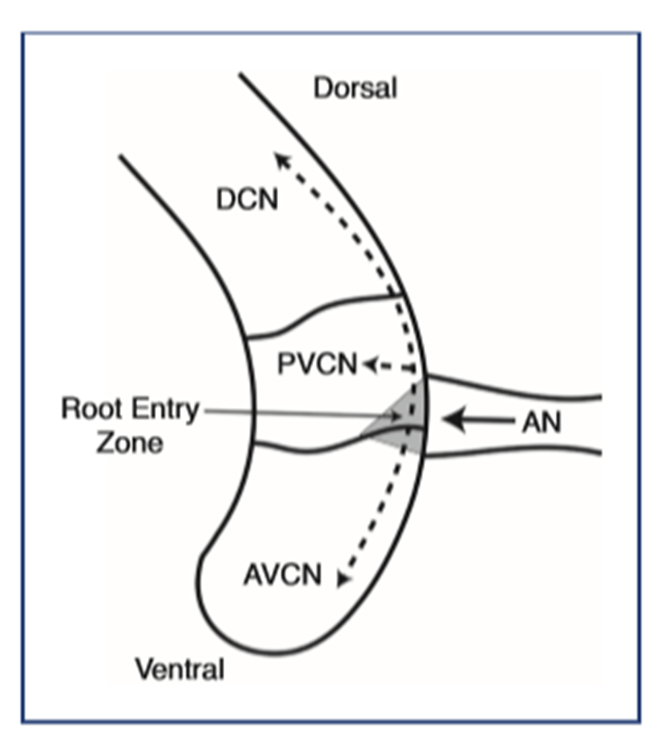
What are the two main divisions of the cochlear nucleus?
Which is both bigger and has two sub-divisions within it?
- Ventral cochlear nucleus (VCN) (Further divided into the AVCN and PVCN)
- Dorsal cochlear nucleus (DCN)
What part of the brainstem is the Superior Olive in?
Pons
The Inferior Colliculus is the “main point of convergence” in the brainstem. What does this mean?
The central nucleus of the IC receives input from the LL, but also the rest of the lower central auditory system (including the CN, SOC and LL). Everything meets here before heading to the MGB.
___________ _______________ are pathways that connect the auditory cortex back to the MGB in the thalamus and vice vesa.
Corticothalamic Projections
What is the functional difference between Type I and Type II vestibular hair cells?
Type I = phasic, fast, transient responders detecting quick dynamic changes (onset of motion).
Type II = tonic, sustained responders detecting static tilt or slow continuous motion.
Chemical messengers that carry signals between nerve cells - from the presynapse to the postsynapse
Neurotransmitters
The precise area where auditory nerve fibers (coming from the cochlea) enter the cochlear nucleus in the brainstem.
ROOT ENTRY ZONE
What are the three nuclei of the superior olive?
-Lateral Superior Olive (LSO)
-Medial Superior Olive (MSO)
- Medial Nucleus of the Trapezoid Body (MNTB)
What part of the brainstem is the Inferior Colliculus in?
Midbrain
Most of the auditory system, starting at the basilar membrane, is tonotopically organized. What part of the auditory cortex does NOT have ROBUST tonotopicity?
The Secondary Auditory Cortex (A2) and Auditory Association Areas
What is BPPV and what structure becomes misplaced to cause it?
Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo occurs when otoconia detach from the macula and fall into a semicircular canal—most often the posterior canal.
True or False: Neurons only receive information from 1 other neuron.
False. Neurons typically receive input from many other neurons (often hundreds or even thousands) through their dendrites.
This convergence of information allows the nervous system to integrate and process complex signals.
The three main fiber pathways through which auditory information travels through most of the brainstem.
- Dorsal Acoustic Stria
- Intermediate Acoustic Stria
- Ventral Acoustic Stria
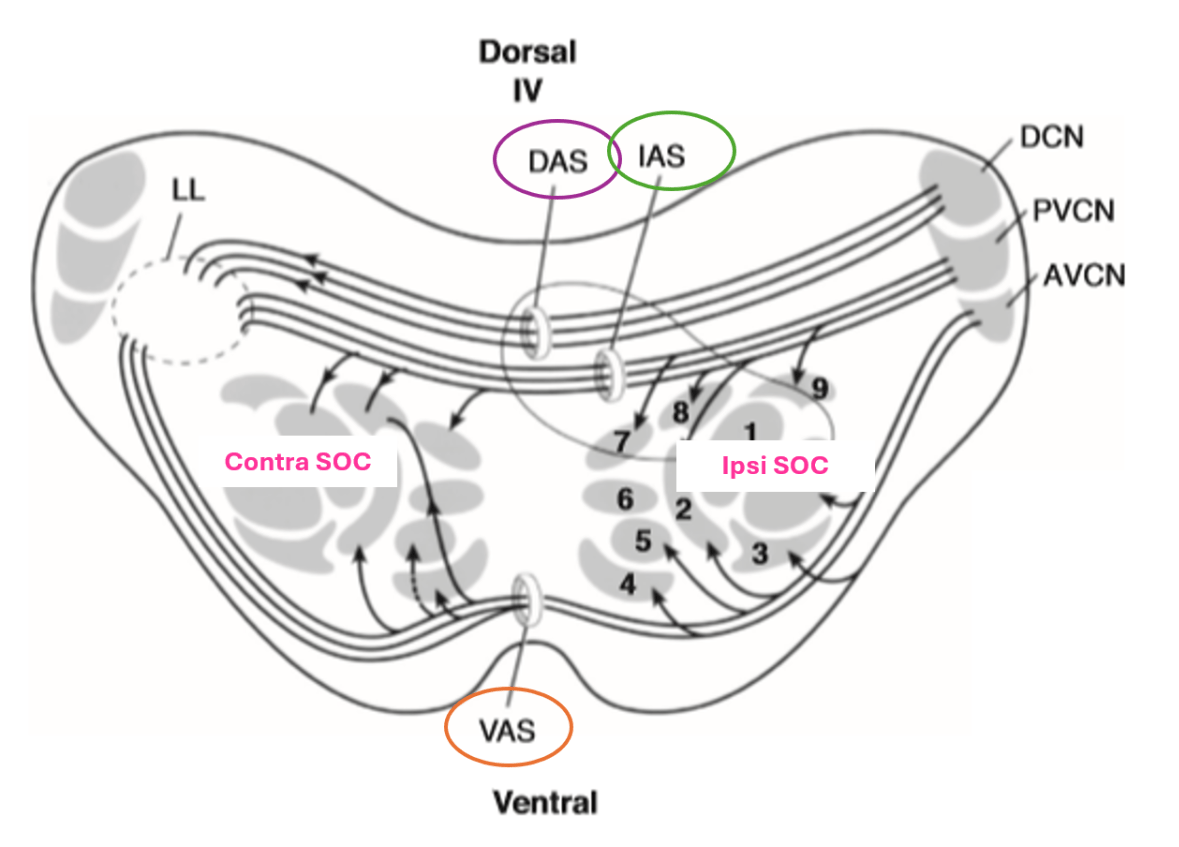
Fibers from the Cochlear Nucleus travel to the Superior Olivary Complex next on the ascending pathway. What is unique about the paths they take that hasn't happened in the auditory system until now?
Fibers from the Cochlear Nucleus are going to travel to both the IPSILETERAL and CONTRALATERAL Superior Olive.
True or False: the startle reflex is a conscious process
FALSE.
The startle reflex is an automatic, rapid response to sudden, loud, or unexpected sounds. It involves a series of neural and motor pathways that allow the body to react quickly to potential threats, bypassing conscious processing for a faster response.
We learned about 5 different Auditory Association Areas. Name some.
- Insular Cortex
- Broca’s Area
- Wernicke’s Area
- Planum Temporale
- Angular Gyrus