What is the digestive system made of?
oral cavity, pharynx, larynx, esophagus, stomach, small and large intestines, cecum, & rectum ="GI Tract"/"Alimentary Canal". Other accessories are teeth, tongue, salivary glands, liver, gallbladder, pancreas
What prevents food from entering the trachea?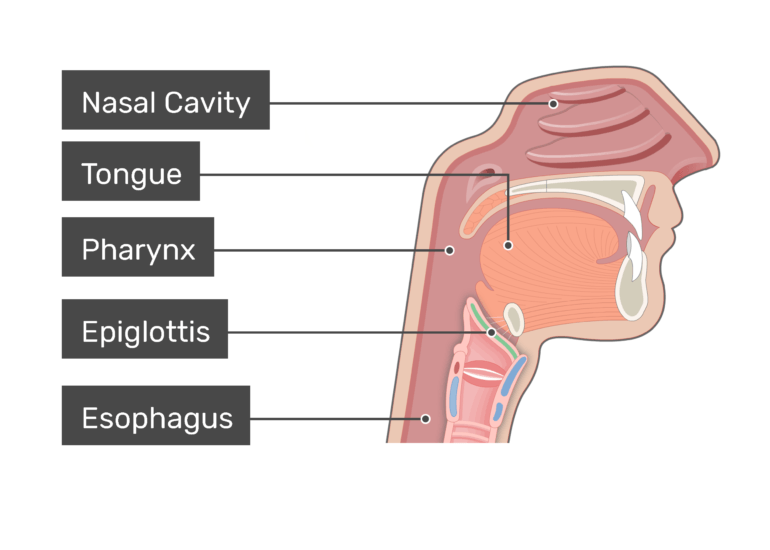
The Epiglottis.
What does HCL do in the stomach
HCl makes gastric juice very acidic. The acid denatures proteins to facilitate digestion. Acidity also converts pepsinogen into pepsin.
How does the Gallbladder play in this?
-acid chyme also mixes w/ bile; produced in liver, stored in gallbladder, released through common bile duct.
contains bile salts/bile acids: amphipathic, emulsifies lipids, alkaline, also helps neutralize acid chyme, pH of liquified food at duodenum: 7-8
What are the functions of the large intestine?
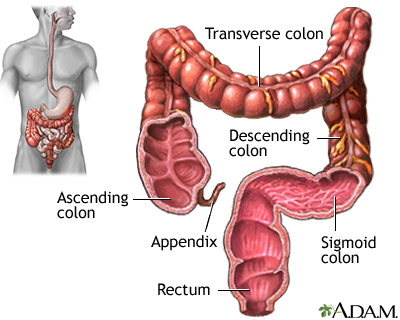
main function: recover water from undigested food
removal of water from undigested food produces feces; some electrolytes and Vitamins B, and K absorbed
What is the function of the digestive system?
metabolize/digest biomolecules in food into smaller, absorbable substances.

Peristalsis of esophagus pushes food into stomach.*muscle makes wave-like contractions. gastroesophageal sphincter: constricts, prevents acid reflux
HCL in Stomach P.2
every 20s, stomach contracts (auto) and mixes food w/ gastric juice. acid chyme is produced (fluid partially digested food). lining of mucous prevents ulcers. also mucous in constantly reformed
How do bile Salts work?
separates individual lipid molecules and breaks up fat globules, thus emulsifying lipids and increasing solubility – this increases access for lipases to break down lipids
What does the colon gut flora hold and produces
houses over 700 spp of bacteria, along w/ some archaea, protozoa, and fungi. Over 100 trillion microbes, almost 0.5 lb. Metabolizes undigested polysacchs.(ex. cellulose) into fatty acids
also produces Vit. K and biotin (a Vit. B)
produces flatus as byproduct; mainly CO2, N2, O2, etc ;-hydrogen sulfide, etc produces odor
What are the step of precessing the food we eat?
Ingestion: internalization of food. Digestion: mechanical and chemical breakdown of biomolecules. Absorption: uptake of breakdown products into blood. Elimination: removal of undigested material. Burping / Farting: self entertainment, male bonding
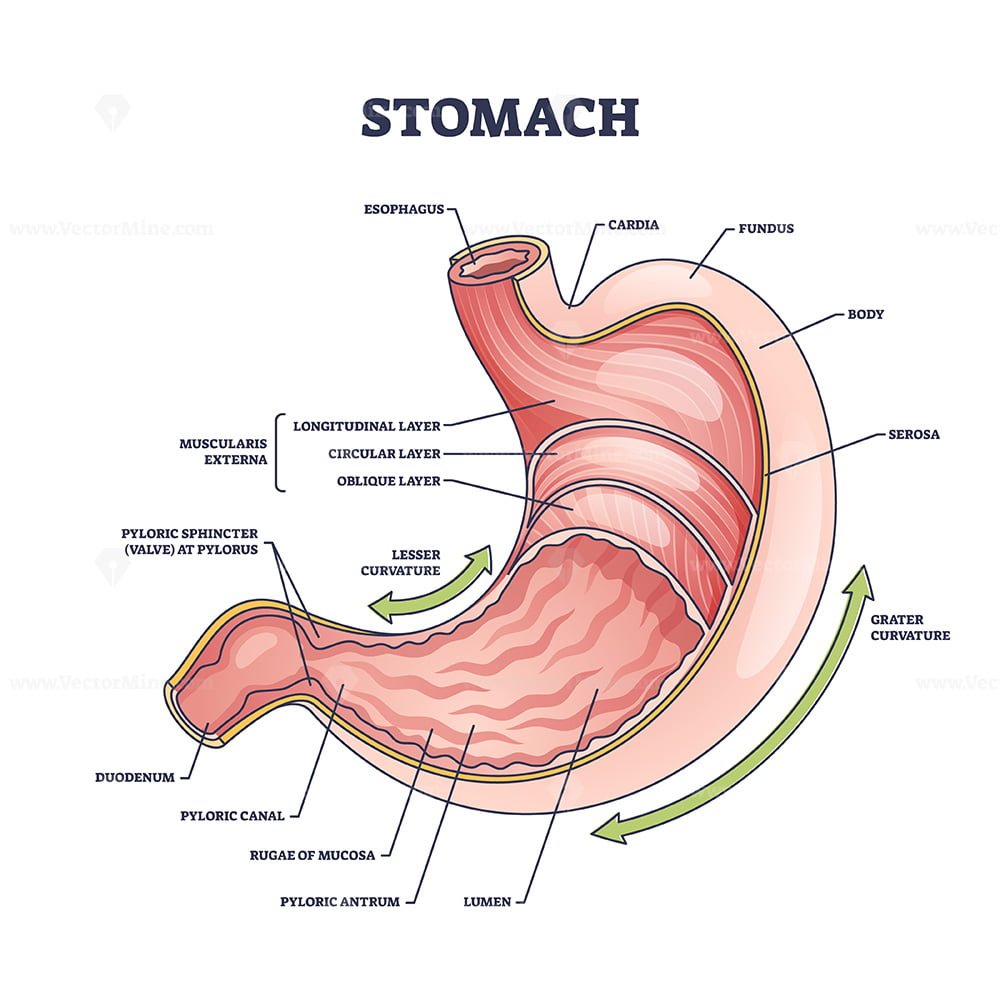
DIAGRAM OF THE STOMACH!!!!
Stomach/Peptic Ulcer: how to treat/handle it
inhibit HCl production(ex. Prilosec, Nexium); reduce HCl production (ex. Zantac, Pepcid); neutralize HCl (ex. antacids); provide extra protective layer (ex. Pepto-Bismol). *avoid small substances like caffeine, alcohol and NSAIDs
LOOK AT BIOMOLECULE BREAKDOWN REVIEW IN YOUR PRINTED NOTES
More About the Oral Cavity
food mixes w/ saliva. saliva contains mucin, antibiotics, amylase and is produced at 1L/day. mastication (chewing): for mechanical digestion, mixes food w/ saliva, and increases surface area of food
what does the stomach do, how much does it hold, and what it produces?
performs chemical digestion (mainly proteins) but very little absorption
elastic: holds ~2L of food/liquid
produces gastric juice: acidic: pH 1-3, contains pepsin (a protease = enzymes that break down proteins)
Acid chyme is slowly released where

acid chyme is slowly released into the duodenum: controlled by the pyloric sphincter
Absorption at Villi (jejunum, ileum)
what are the large folds and finger-like projections
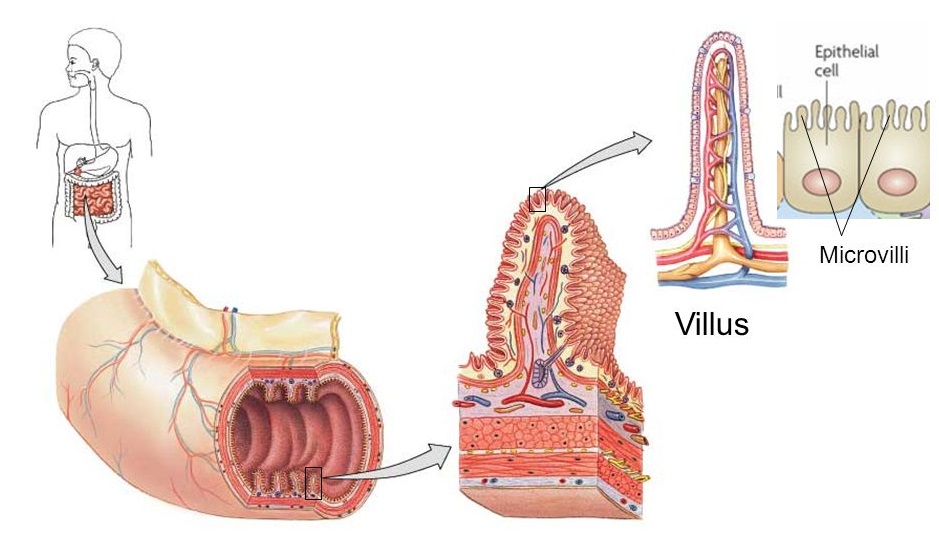
inner surface area increased by foldings and projections
large folds are plicae circulares; microscopic finger-like projections are villi
More About oral Cavity P.2
-tongue manipulates food into bolus (small, swallowable portion
–allows food to be swallowed w/out damaging trachea)
GASTRIC PITS AND GASTRIC GLAND DIAGRAM!!!!! *I THINK THIS IS THE TUMMY

How does the pancreas play in this

-acid chyme mixes w/ pancreatic juice, produced by pancreas, and released through the pancreatic duct
contains: bicarb (acts as a buffer), amylase, lipases, nucleases, proteases; trypsin (example protease): made as trypsinogen (zymogen), converted to active form by enteropeptidase in duodenum
What does the Villus do?
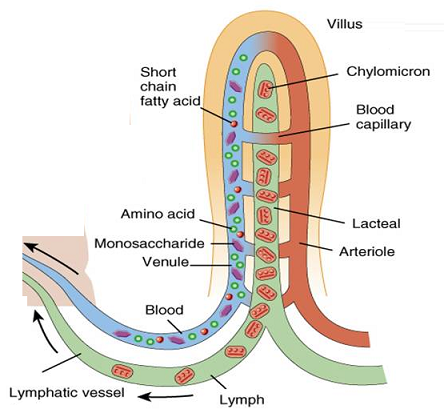
breakdown products of biomolecule digestion (ex. amino acids, fatty acids, monosaccharides, etc) are absorbed through the villi and into associated blood capillaries