The shape of DNA
Double Helix
What RNA is copied from
DNA
Where it takes place
nucleus
where it takes place
ribosome
What a mutation is
Three parts of a DNA nucleotide
Where it is made
nucleus
How much of a chromosome is transcribed at one time
One gene
What is a codon?
A unit of three nitrogenous bases in mRNA read by the ribosome
What kind of mutation?
AGA ->ATA
Point/substitution
Complete the complementary DNA strand:
ATG CAT GGC
TAC GTA CCG
What type of RNA is this?
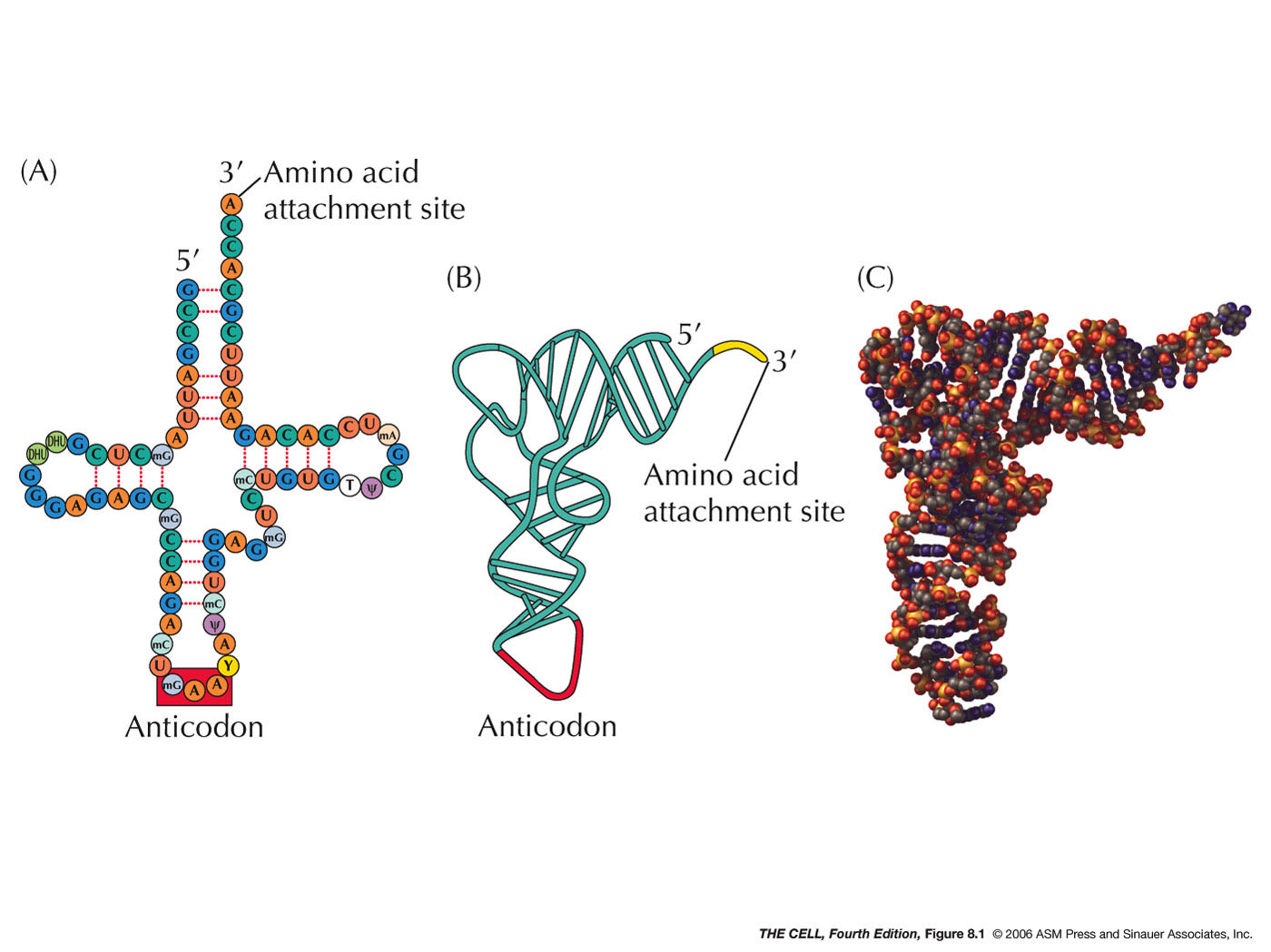
tRNA
Which letter is transcription?
Which letters are involved with translation?
DEFG
What kind of mutation?
Original: TACGGCTAGTCGA
Mutant: TACGCTAGTCGA
Deletion/Frameshift
The enzyme that builds new strands of DNA
DNA polymerase
3 types of RNA
mRNA, tRNA, rRNA
Why transcription must take place in the nucleus
DNA is too large to leave the nucleus
Translate the following RNA sequence
AUG
Met/Methionine
What effect this mutation will have:
Original: TAC GCT ATC
Mutant: TAC GCG ATC
None: silent mutation
The type of bonds that connect nitrogenous bases
Hydrogen bonds
3 structural differences between DNA and RNA
DNA: Thymine, 2 strands, deoxyribose
RNA: Uracil, 1 strand, ribose
Transcribe the DNA below:
TAC TGG CGA ACT
AUG ACC GCU UGA
What protein will result from this DNA sequence:
GGC ATG TAG
Proline Tyrosine Isoleucine
Introduce one substitution to create a nonsense mutation:
TTT ACG GCA
ACG -> ACT