Name 3 causes of constrictive pericarditis
What is viral, idiopathic, TB, malignancy, AI, IgG4 RD, post-cardiac surgery, post-radiation, uremic, trauma, drug-induced, asbestosis, sarcoidosis
Adult with purpura, arthralgia, abdominal pain, and hematuria. Diagnosis?
IgA nephropathy

ID lesion
Pityriasis rosea
Multiple erythematous, scaly papules and plaques on the trunk in a "Christmas tree" distribution
What are the different kinds of shock? Give at least one example of each.
●Hypovolemic (hemorrhagic/nonhemorrhagic),
●Distributive (septic, neurogenic, anaphylactic, drug induced, endocrine),
●Cardiogenic (cardiomyopathy, arrhythmogenic, mechanical),
●Obstructive (PE, PTX, tamponade, constrictive pericarditis, restrictive cardiomyopathy),
●Mixed
A 40-year-old with CML on imatinib develops new splenomegaly, basophilia, and anemia. Bone marrow shows increased blasts. What has occurred?
Blast crisis transformation of CML
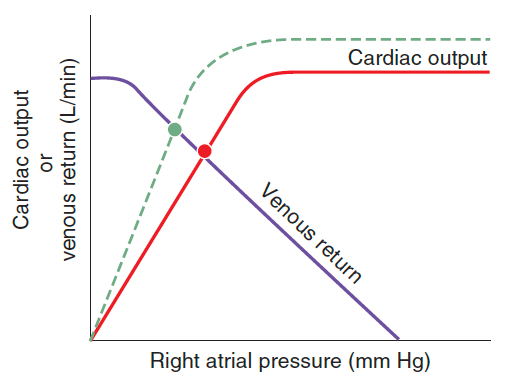
The dashed line illustrates the effect of what? Give a specific example of this.
Increased contractility/inotropy; accept any inotropic condition (catecholamines, dobutamine, milrinone, digoxin, exercise)
Mechanism of rhabdomyolysis induced AKI. Name at least 1.
Volume depletion resulting in renal ischemia, tubular obstruction due to heme pigment casts, and tubular injury from free chelatable iron all contribute to the development of renal dysfunction
Name atleast 1 pathology associated with this finding
RAPD; MS
What is the pathophysiologic reason to not aim for 100% SpO2 in COPD patients?
Takes away physiologic vasoconstriction>increases blood flow to areas of poor ventilation>worsen V/Q mismatch and increase dead space
Which transfusion reaction presents with fever, chills, and dyspnea within 6 hours, CXR showing bilateral infiltrates, and no evidence of circulatory overload?
TRALI
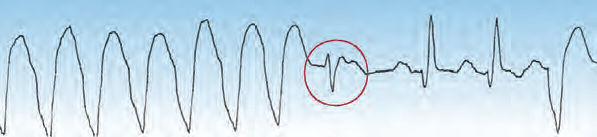
What is the beat circled in red?
An example of a fusion beat (circled in red), which is a hybrid QRS complex produced by the collision of a ventricular ectopic impulse and a supraventricular (e.g., sinus node) impulse. The presence of fusion beats is evidence of ventricular ectopic activity.
What are the mechanisms of nephropathy caused by multiple myeloma, name atleast 2
1. Intratubular cast formation: Light chains precipitate in the tubules as a result of binding with uromodulin (formerly called Tamm-Horsfall mucoprotein, or THMP)
2. Direct tubular toxicity: intracellular light chain accumulation, ROS, proinflammatory cytokines > lysosomal and overall cell dysfunction
3. Deposition of light and heavy chains: amyloidosis
A previously healthy 48-year-old woman presented to the dermatology clinic with a 1-day history of a rash on her right ear that was preceded by 2 days of ear pain and an inability to move the right side of her face
ID Disease State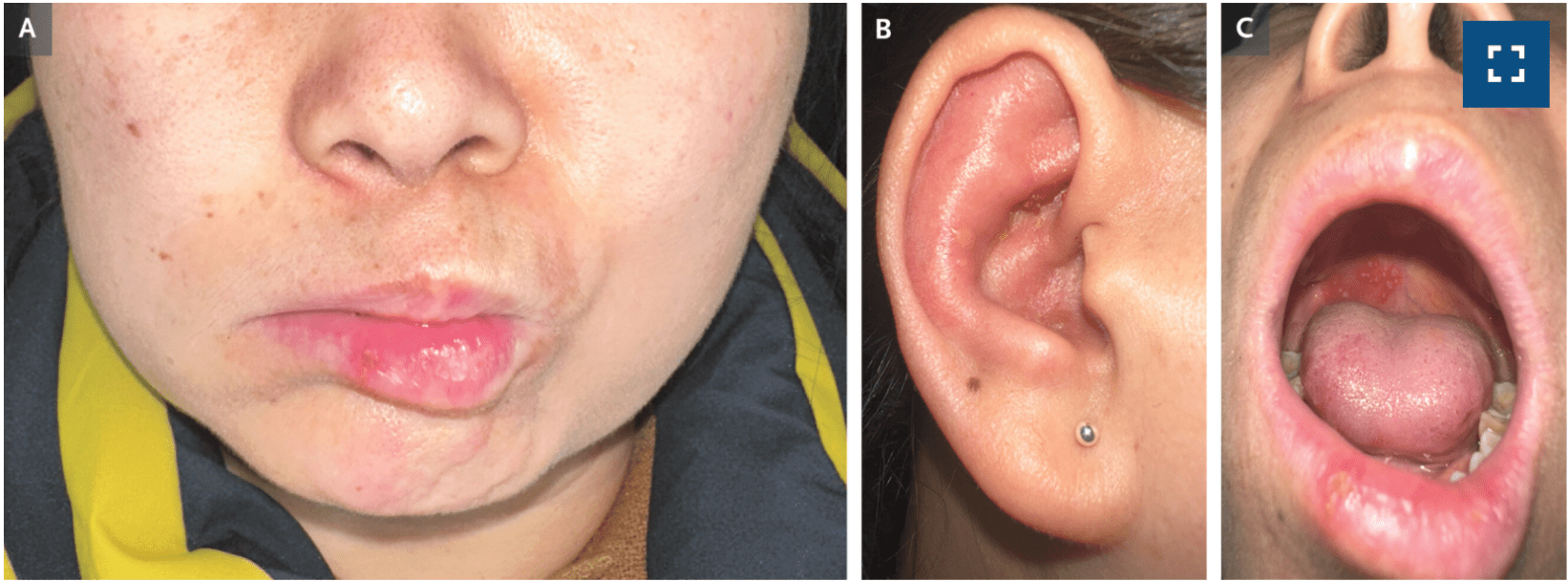
Physical examination shows facial-nerve palsy on the right side (Panel A) and erythema with a few vesicles and some crusting on the pinna of the right ear (Panel B). An oral examination revealed vesicles on the right side of the hard palate, patchy erythema of the anterior tongue, and an ulceration on the right lower lip (Panel C). Consistent with a diagnosis of Ramsay Hunt syndrome
Patient on VC-AC: TV 6 mL/kg, RR 16, FiO₂ 0.5, PEEP 8. ABG: pH 7.29, PaCO₂ 60. Best first vent change?
Increase respiratory rate (increases minute ventilation) before TV
A 47-year-old man presented to the hospital with a 2-day history of weakness and fever. His blood pressure was 64/47 mm Hg, heart rate 110 beats per minute, and temperature 39.0°C. On physical examination, the patient had swelling and redness of the left thigh, which aroused concern about the presence of an abscess. Laboratory studies showed pancytopenia.
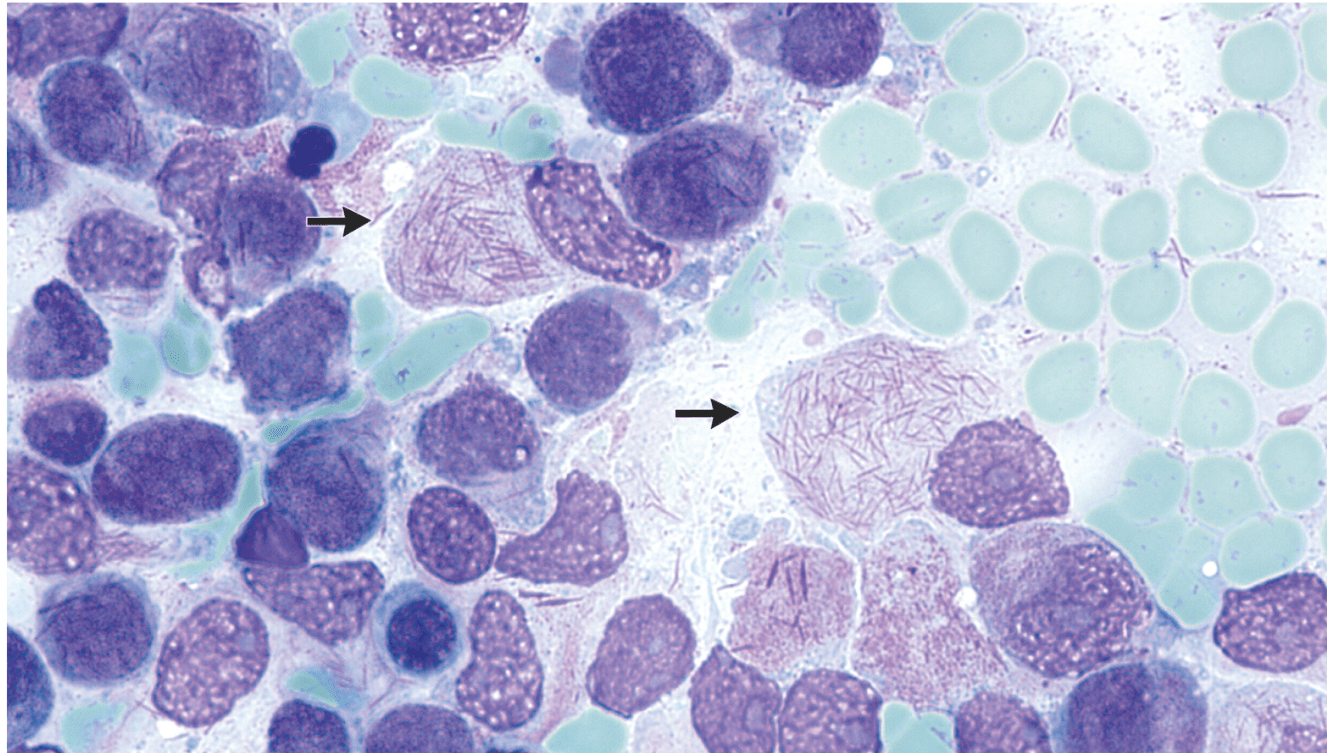
ID likely disease state and what the arrow is pointing to
APML
Promyelocytic blast cells with intracellular Auer rods — needle-shaped cytoplasmic structures specific for myeloid neoplasms — were seen on a peripheral-blood smear.
2 parts:
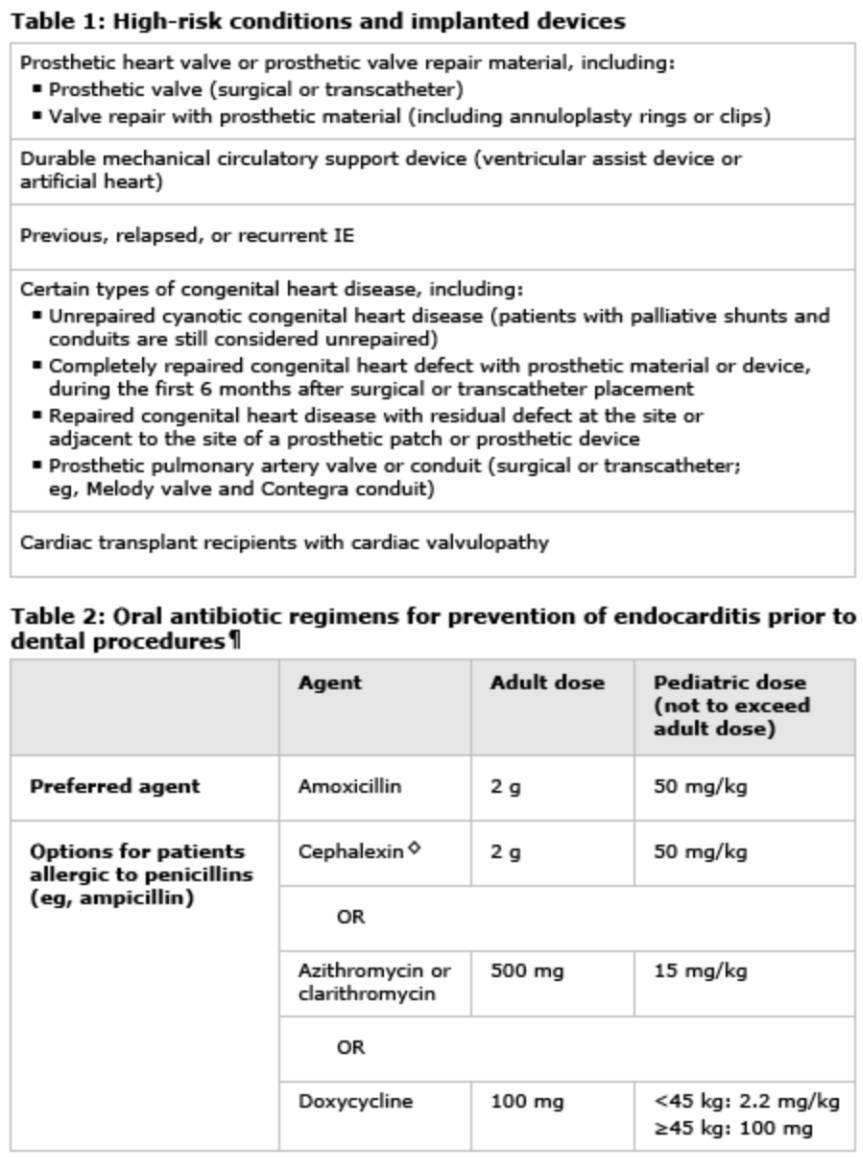
1) What are ALL the indications for endocarditis antibiotic prophylaxis in a patient undergoing dental procedures
2) What do you give if the patient is allergic to penicillin?
Rapidly progressive GN with hemoptysis shows linear IgG along GBM. What is the pathology and best initial disease-modifying therapy combo?
Goodpasture; High-dose IV glucocorticoids + cyclophosphamide and urgent plasmapheresis.
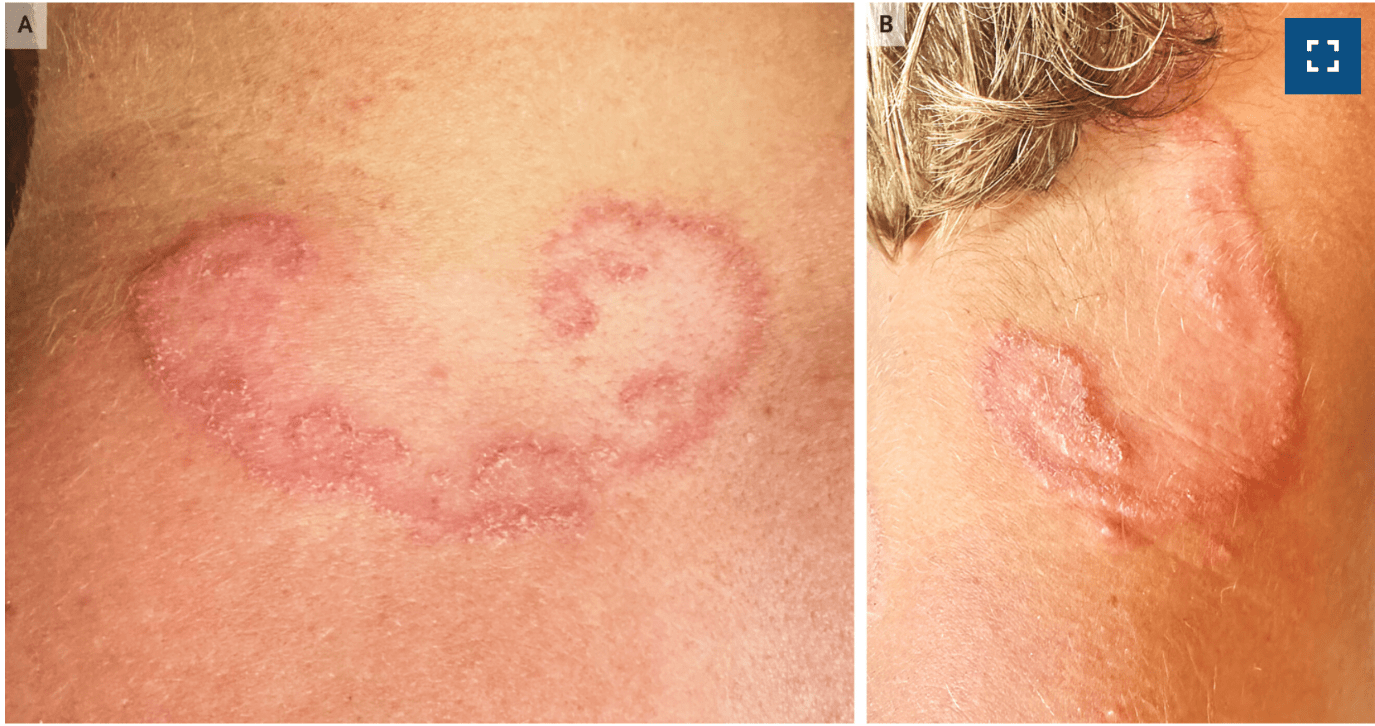
ID lesion
Cutaneous Larva Migrans
1. What is ARDS and its diagnostic criteria?
2. What vent settings guidelines should you use?
- Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) is acute, diffuse lung inflammation characterized by poor oxygenation and reduced compliance.
A diagnosis of ARDS requires 4 criteria to be met:
Acute onset: Symptoms must appear within one week after some insult.
Bilateral opacities on imaging: typically chest radiography or CT - must show bilateral opacities. POCUS can also be used.
Edema origin is not primarily cardiac: Edema must not be fully explained by cardiac failure or fluid overload. Cardiac causes can be present, but must be judged to not be a
Hypoxemia is present - usually defined by the P/F ratio. The P/F ratio or PaO2/FiO2 ratio is also how we grade the severity of ARDS in the US, though in resource limited settings SpO2/FiO2 can be used.
Vent: ARDSnet protocol: lung protective ventilation (high peep low TV to minimize VILI)
A 70-year-old woman with newly diagnosed, rapidly progressive breast cancer develops confusion and palpitations. On presentation to ED, she develops multiple bouts of wide complex tachycardia. What should you be worried about and how should you treat?
Spontaneous TLS. Treat with: aggressive hydration, electrolyte correction and supportive care, rasburicase, renal replacement if needed
What are the two major physiologic mechanisms through which a balloon pump works and what are absolute contraindications for its use (name 3)?
1.Inflation during diastole > increase peak diastolic pressure > increases MAP and thus systemic blood flow. Inc DBP increases coronary blood flow
2.Deflation at the onset of ventricular systole > suction effect > reduces afterload
3.CI: Severe AI, dissection, severe PAD, recent aortic surgery
A 30-year-old woman with SLE develops nephrotic-range proteinuria. Biopsy shows wire-loop lesions and subendothelial deposits. Which class of lupus nephritis is this, and what is the mainstay of treatment?
Class IV lupus nephritis; high-dose corticosteroids + mycophenolate mofetil (sub: cyclophos) as dual therapy or triple therapy with addition of CNI/belimumab
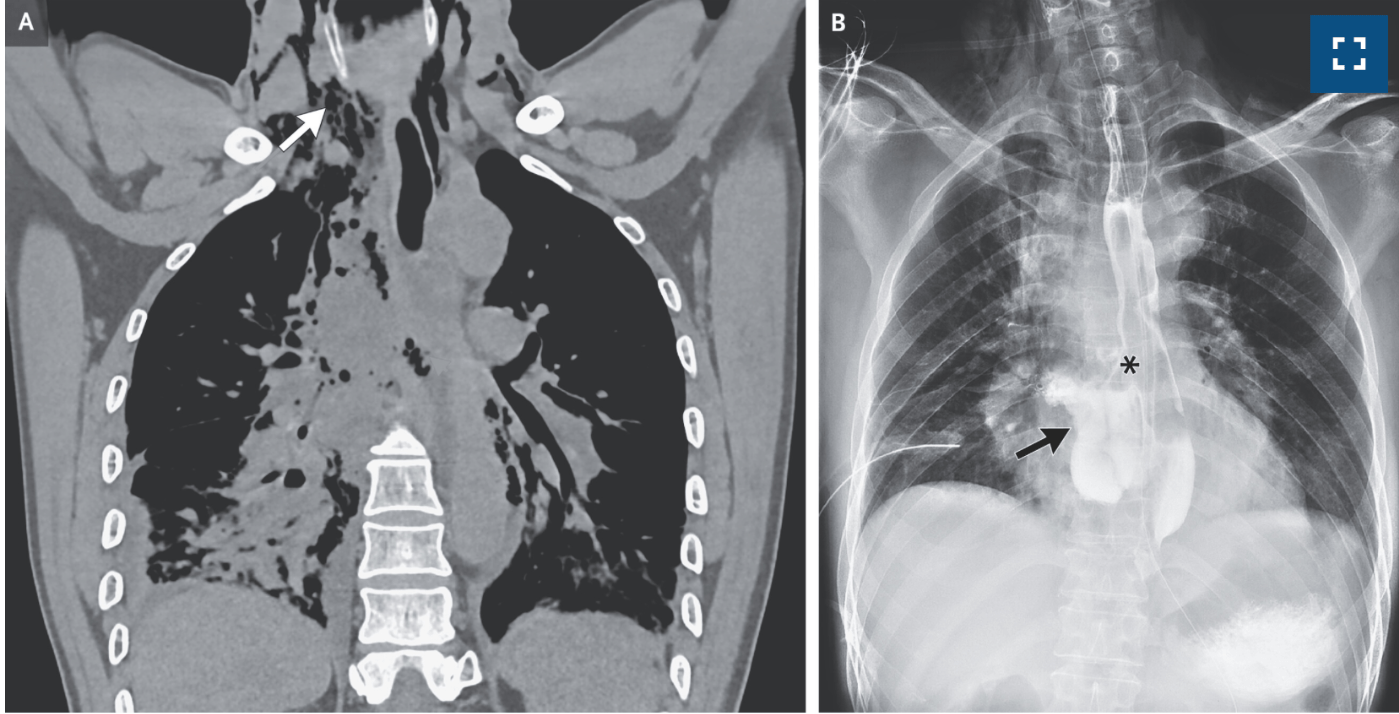
What is the pathology?
Boerhaave Syndrome

Computed tomography of the chest revealed air in the mediastinum extending up to the neck (Panel A, arrow), a perforation of the esophagus, a pleural effusion on the right side, and atelectasis in the right lung.
An esophagram that was obtained with the use of water-soluble contrast material confirmed a large laceration of the esophagus (Panel B, asterisk) with extravasation of the contrast material into the mediastinum (Panel B, arrow).
Name the classes of pulmonary hypertension and give an example of each.
Group 1: PAH (idiopathic, heritable, assoc with rheumatologic disease, drugs, schisto)
Group 2: PH associated with left heart disease
Group 3: PH associated with lung diseases and/or hypoxia
Group 4: PH associated with pulmonary artery obstructions
Group 5: PH with unclear and/or multifactorial mechanisms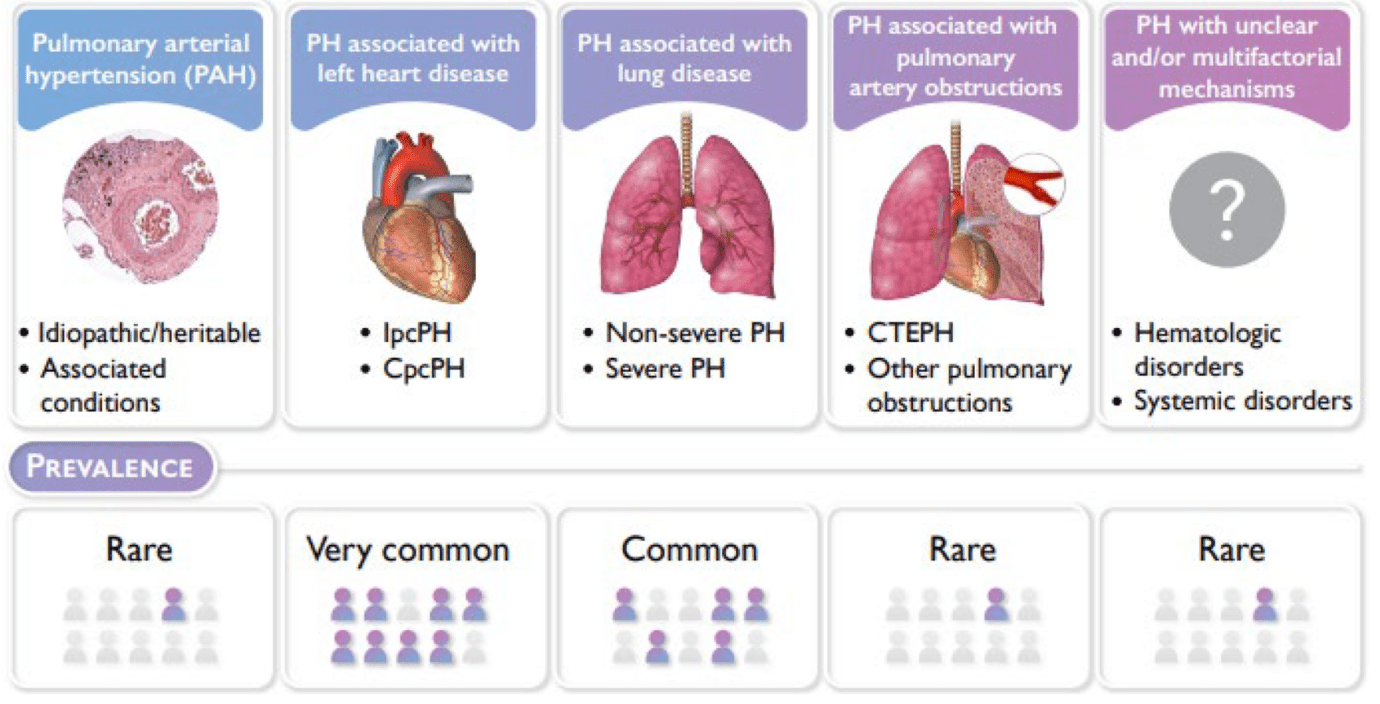
A 35-year-old woman presents with confusion. Labs show Hgb 7.8, platelets 18K, creatinine 1.4.
1) What pathology do you suspect?
2) What diagnostic score will you use to assess this patient?
3) How will you treat?
1) TTP
2) PLASMIC score
3) Plasmapheresis, steroids, rituxan, caplacizumab. Don't give platelets unless bleed