and
Photosynthesis
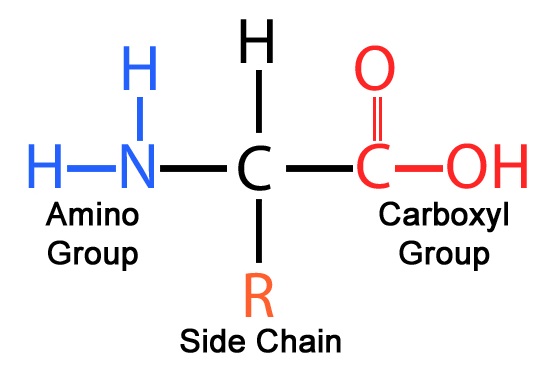
Draw an amino acid.
List the two transport tissues in plants
Xylem and Phloem
Differentiate between cohesion and adhesion in a plant
Cohesion- H bonds between water bonds in one long chain
Adhesion - H bonds between the water molecule and the structural tissue of the plant (xylem)
Name a difference in structure between amylose and amylopectin.
-amylose is unbranched, while amylopectin is branched.
-amylose consists of linear chains of glucose molecules linked by α-1,4 glycosidic bonds. Amylopectin, also uses α-1,4 glycosidic bonds for the main chain, but also includes α-1,6 glycosidic bonds at branch points, which are responsible for the branching structure
Outline the reaons why earth has was on it to retain liquid water (HL) to support life on earth
Earth is large enough for gravity to be strong ; warm enough for ice to melt (Goldilocks zone- distance from the sun is perfect for the right temp for water to exist)
Describe the processes for water to leave a plant
Cohesion - the ability of water molecules to "stick" together. This is seen in trees to bring water up from the roots into the tree.
Transpiration pull- loss of water vapour from the leaves through the stomata creates tension to pull the cohesive column of water up the plant
Differentiate between the four levels of protein structure (HL)
primary structure is defined as the amino acid sequence of its polypeptide chain;
secondary structure is the local spatial arrangement of a polypeptide's backbone in an alpha helix or beta pleated sheet;
tertiary structure refers to the three-dimensional structure of an entire polypeptide chain (forms due to H bonds, ionic bonds, disulphide bonds and hydrophobic interactions);
quaternary structure is the three-dimensional arrangement of the subunits in a multisubunit protein
List a difference between DNA polymerase III and DNA polymerase I. (HL)
DNA polymerase III - synthesizes new strand by adding nucleotides onto the template strand DNA polymerase I - removes the primer and replaces it with DNA
Explain how phloem is adapted for translocation
thin, non lignified cell wall; one sieve tube with space (and no organelles) for sap to flow; a sieve plate has pores for the sap to move in either direction, companion cells border the phloem cell with nucleus, mitochondria to prove energy to move the sap from source to sink.