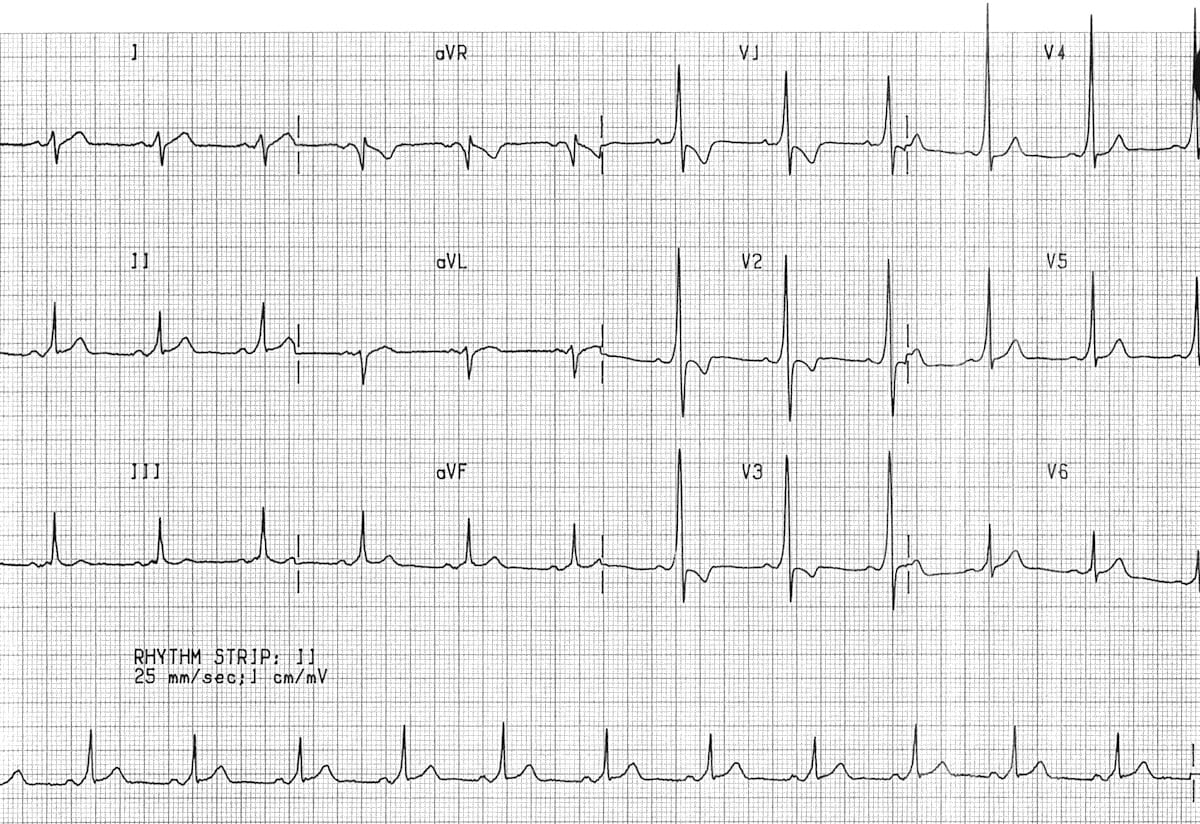
Sinus rhythm ~75bpm with Wolff Parkinson White morphology
Describe the electrical conduction pathway of the heart.
Beginning at the sinoatrial node (SA node), conducting through the atria to the atrioventricular node (AV node) through the bundle of His, down the left and right bundle branches and to the purkinjie fibres.

Ventricular standstill
What are the rate parameters for sinus bradycardia, sinus rhythm and sinus tachycardia?
Bradycardia <60bpm
NSR 60-100bpm
Sinus tachycardia >100bpm

Extensive Anterior STEMI
"Tombstone" morphology STE throughout precordial leads and high lateral leads.

Sinus rhythm with CHB and ventricular escape rhythm at 40bpm.
Describe 2nd Degree AV block.
Hint: There is 2
Wenckebach/Mobitz I: progressive lengthening of the PR interval until a non-conducted p-wave occurs.
Mobitz II: intermittent non-conducted P waves WITHOUT progressive prolongation of the PR interval
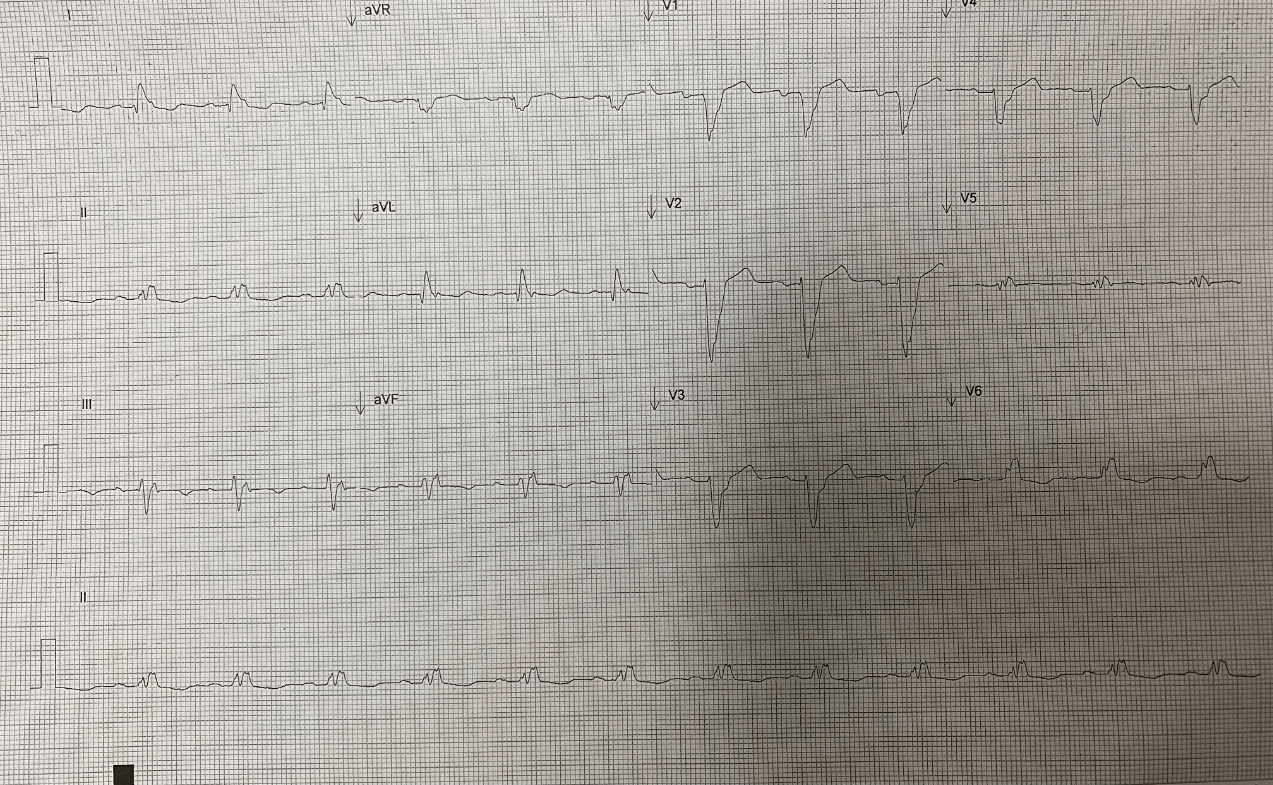
Sinus rhythm 75bpm with LBBB
Describe the mechanism of the R on T phenomenon

STE in inferior leads, reciprocal changes anterior leads
Inferior infarct
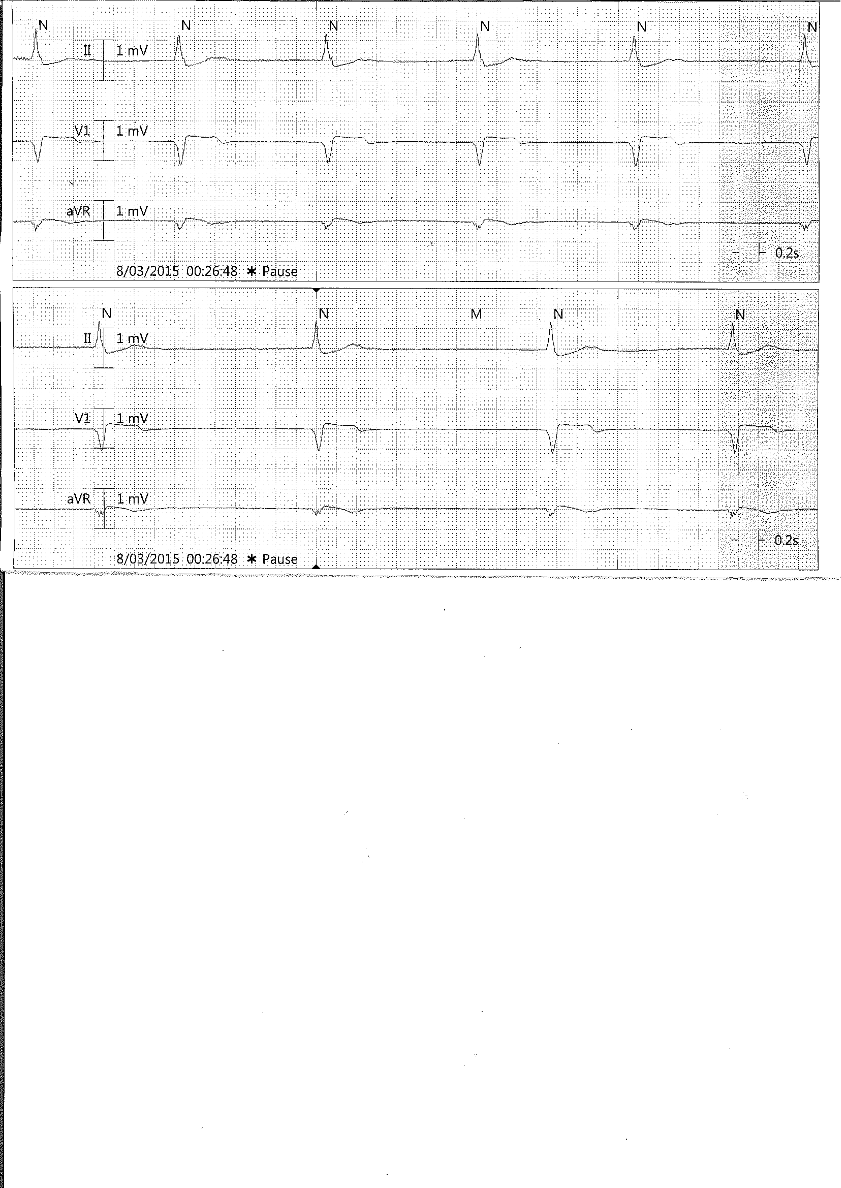
Junctional rhythm 38bpm
When and Who reported the first ECG?
1903 by Willem Einthoven
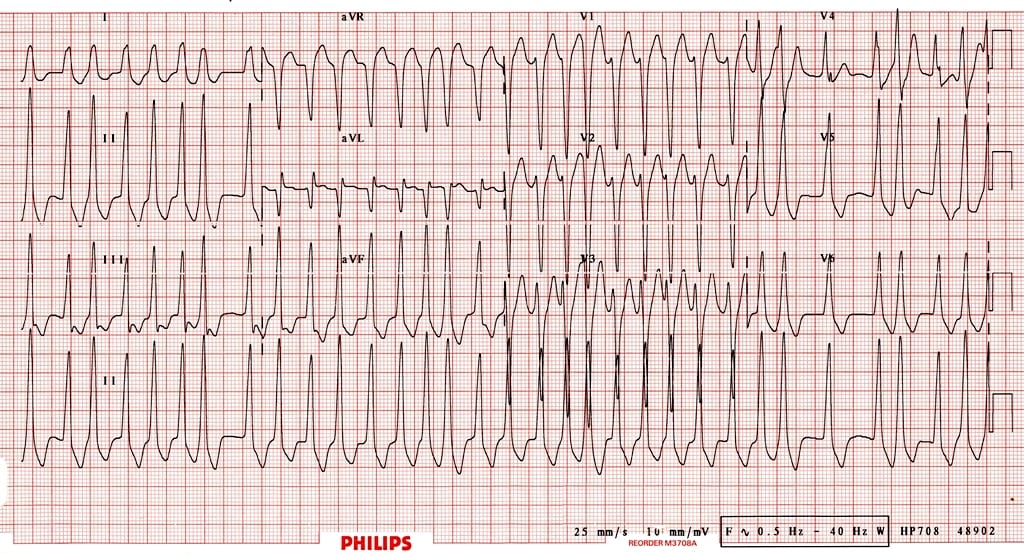
Atrial fibrillation in a patient with WPW (pre-excitation).
Rates up to 300bpm.
Explain the clinical significance of a patient with pre-excited atrial fibrillation
The presence of an accessory pathway allows for rapid conduction to the ventricles, bypassing the AV node - rapid ventricular rates may result in degeneration to VT or VF.

Anterolateral STEMI
STE anterior leads (V2-V4) and lateral leads (1, aVL, V5-6)
Reciprocal STD in inferior leads.
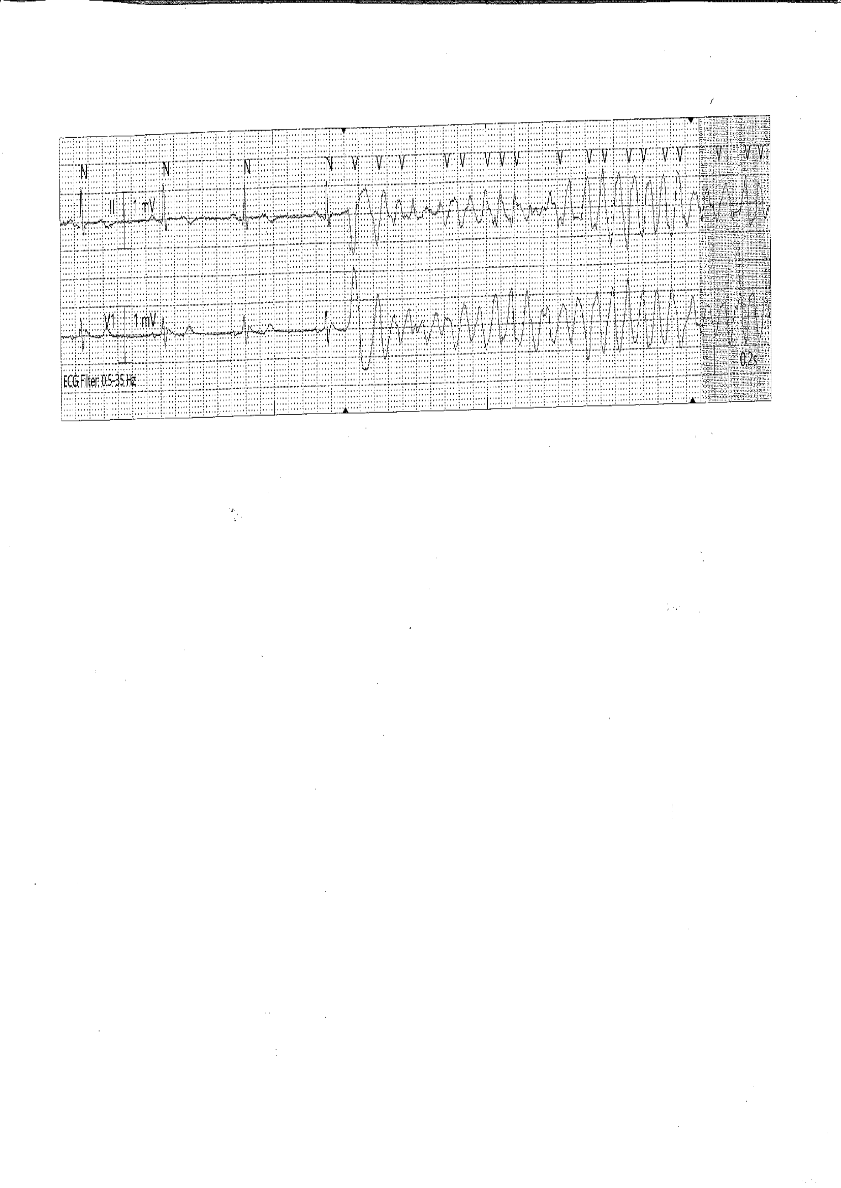
PVC on T wave (R on T) causing Torsades de Pointes
Demonstrate and describe the placement of a 12 Lead ECG using correct anatomic terms.


Sinus rhythm with AV dissociation.
What mechanisms may cause a wide complex during an SVT?
Pre-excitation (accessory pathway)
Rate related bundle branch block

Inferior STEMI
Hyper-acute T waves and STE in II, II and aVF
Reciprocal changes in anterior leads.
Hint: 18 Y/O presenting with 1/7 chest pain
Sinus rhythm with global STE, STD in V1
Myopericarditis
How long is a prolonged QT interval and what arrhythmia are people with a long QT at risk of developing?
Prolonged if >440ms in men and >460ms in women. Torsades de pointes.

Atrial fibrillation with RBBB, 92bpm
Describe the regions of an ECG in relation to localising acute coronary syndrome.


Inferolateral STEMI
STE in inferior (II, III and aVF) and lateral (I, V5-6)
STD in V1-V3 suggesting posterior extension.

Artifact
What ECG findings would you see associated with sinus node dysfunction?
Hint: there is 8
Sinus bradycardia
Sinus arrhythmia
Sinus pause or arrest
Sino-atrial exit block
Chronotropic incompetence
Tachy/brady syndrome
Wandering Atrial Pacemaker
Atrial fibrillation

Monomorphic VT, shock on T wave causing VF, shock reverting to sinus rhythm.
What is the lead on the top right of Einthoven's triangle?
Right arm
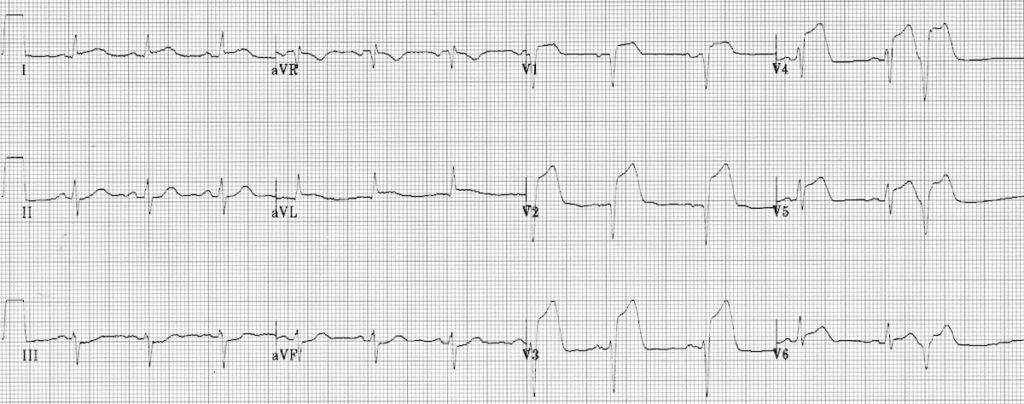
Anterior STEMI
STE V1-6
Reciprocal changes III and aVF