want
Enzyme used in DNA replication to sequence DNA or RNA strands it also fixes errors.
DNA polymerase
Basophils
Name that hypersensitivity:
Mediated by production of IgE.
reactions may include hives, eczema, allergic asthma, food allergy, anaphylaxis
Immediate hypersensitivity (type 1)
What factors are NOT synthesized in the liver and where are they synthesized?
IV Calcium synthesized in diet
vWF Von Willebrand factor Synthesized in endothelial cells
This lipid metabolite of arachidonic acid promotes platelet aggregation vasoconstriction in the area
Thromboxane A2
What are the three components of Virchow's Triad?
- hypercoaguability
- venous stasis
- endothelial injury
List the base pairings in DNA? In RNA?
RNA: AU, GC
Macrophages types in Lung, Liver, and Brain
Lung- Alveolar macrophage
Liver- Kupffer cell
Brain- Microglia
Two elements required for DNA synthesis
Vitamin B12 and folate
-Can result in hyperuricemia, increased potassium, increased phosphate, decreased calcium
- may also lead to arrhythmias, acute renal failure, or seizures
Tumor lysis syndrome
Name the hypersensitivity:
- Response mediated by CD4 or CD8 T cells
- delayed due to occurring several days after exposure
- most commonly manifests as a blistering skin rash
Ex: Reactions to metals in jewelry or poison ivy
T cell -mediated hypersensitivity (type 4; delayed)
What inactivates cofactors VIII and V?
This antimicrobial enzyme is a chemical barrier found in tears and mucus. It causes bacterial lysis by disrupting bacterial cell walls.
Lysozyme
Three pathways for complement activation
- Classical (bacteria coated with antibodies)
- Lectin (MBL protein in liver attaches to bacteria then activates compliment cascade)
- Alternative (compliment binds to bacterial wall initiating cascade)
Type of malignancy arising from glandular epithelial cells
Adenocarcinoma
host cell surfaces becomes unrecognizable, immune system sees host as "non-self". B cells make IgM or IgG against host then bind to host leading to inflammation and cell death.
Antibody-mediated hypersensitivity (Type 2)
1) Intrinsic pathway factors include:
2) Assessed by what test?
3) Intrinsic pathway is influenced by what drug?
1) XII, XI, X, IX, VIII, V, II
2) aPTT
3) Heparin
Biophysics of vascular wall tension
Law of LaPlace
Lymph fluid returns to the blood via the
Thoracic duct
(largest lymphatic vessel)
Utilized as a marker for B cell maturation, may assist in mucosal immunity
IgD
Target of many anti-fungal drugs
ergosterol
neoplasm
Name this hypersensitivity:
-IgM or IgG is produced against a foreign protein
-leads to an immune complex formation
-activates the complement cascade leading to inflammation
Examples: post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis and RA
Immune complex mediated hypersensitivity (Type 3)
T/F In Moderate CAD the diameter of the vessel and the lumen increase in size.
False. diameter of the vessel remains constant in Minimal/Moderate CAD as the lumen size expands. This changes in severe CAD.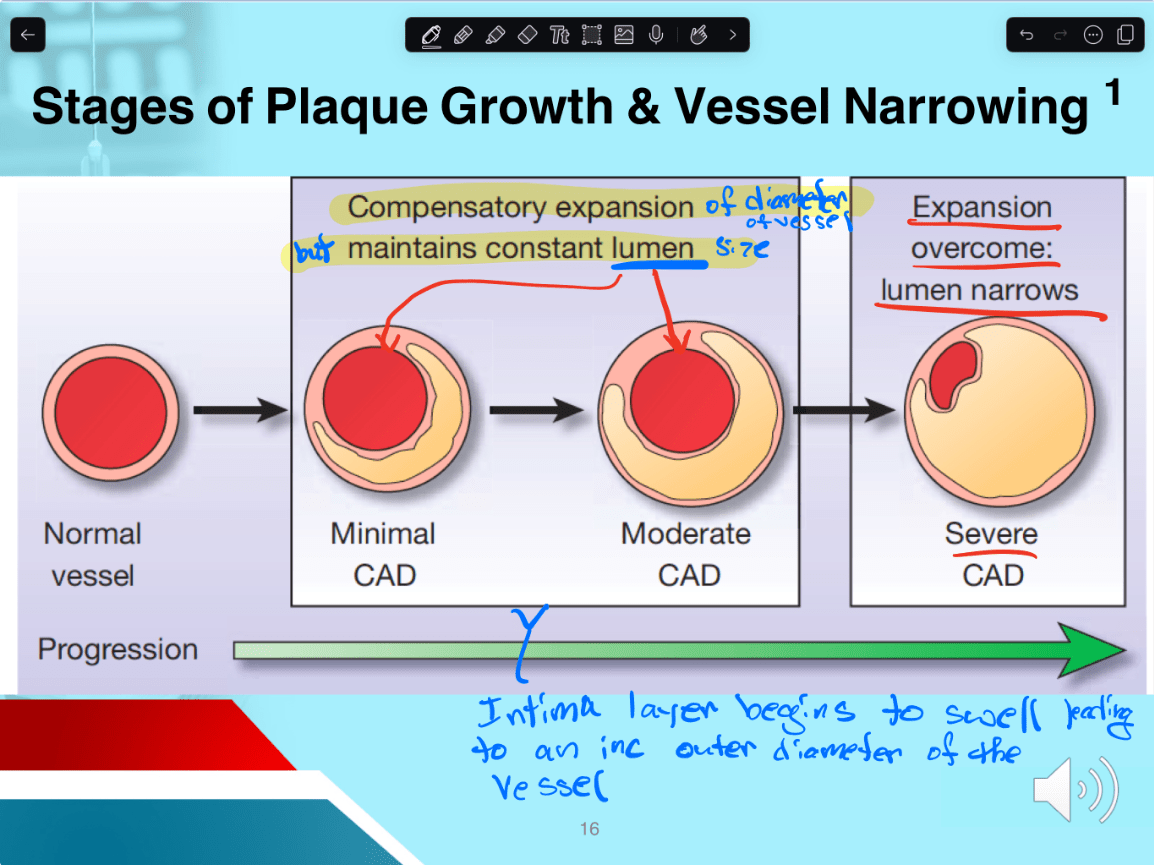
GALT consists of 3 secondary lymphoid tissues types:
- Peyer pathces
- Isolated lymphoid follicles
- Mesenteric lymph nodes
In the primary immune response what antibody peaks first then what antibody peaks second?
Is this the same in a secondary response?
Secondary: no response is different. IgG peaks way higher, and faster at the same time as IgM
Genetic disorder producing abnormal alpha or beta chains.
1) Epstein-Barr can lead to:
2) Hep B can lead to:
3) HPV can lead to:
1) Burkitt lymphoma
2) Hepatocellular carcinoma
3) head/neck & anogenital
Endothelial cells release this inhibitor of platelet activation and aggregation.
Nitric Oxide
Calculate the MAP for someone with a SBP of 120 and a DBP of 60.
MAP= 80
MAP= DBP + (SBP-DBP)/3
What physiologic components play a large role in inspiration and expiration?
diaphragm, intercostal muscles, and chest wall
Breathing is generated by a network of neurons located near the upper end of the medullary respiratory center.
Pre-Brontzinger complex which display pacemaker activity.
Surfactant is a phospholipid protein liquid secreted by what
Type 2 alveolar epithelial cells (AEC)
What stage in slow response action potentials do calcium channels switch from T-type to L-type channels?
Phase 0 - upstroke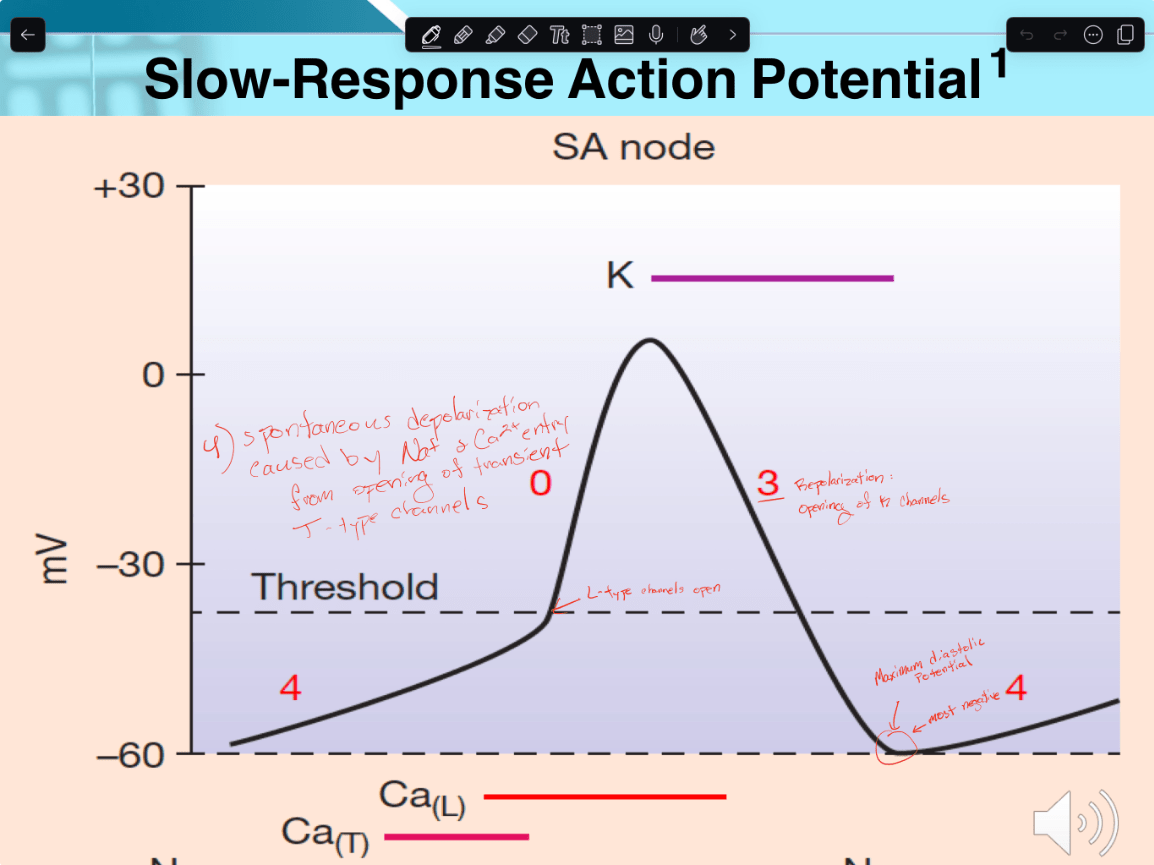
What is the HR if the CO= 6L/min and SV= 75mL?
80 bpm
CO=HR x SV
*be mindful of units*
Fun fact:
we are NOW 1000 days out from graduation.