Name 2 items that increase membrane fluidity
Cholesterol and unsaturated fatty acids
Explain the 1st law of thermodynamics
Energy can be transferred, but NOT created or destroyed
Write the formula for cellular respiration. Label what's oxidized and what's reduced
C6H12O6 + 6O2 --> 6CO2 + 6H2O + ATP + heat
Glucose is oxidized to make carbon dioxide
Oxygen is reduced to make water
Write the formula for photosynthesis. Label what's oxidized and what's reduced
6CO2 + 6H20 + light energy -> C6H12O6 + 6O2
Carbon dioxide gets reduced to form glucose
Water is oxidized to form oxygen
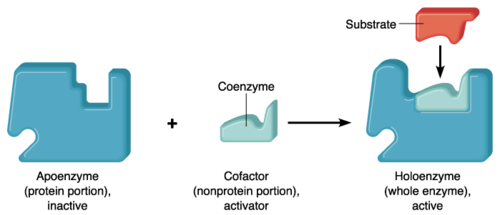
What are cofactors?
REQUIRED, non-protein enzyme helpers.
Also called coenzymes if organic
Name the 2 proteins that are used in facilitated diffusion
Channel and carrier
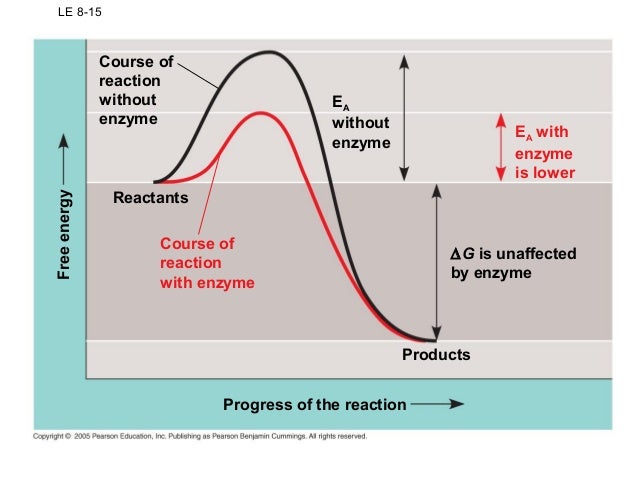
Which (color) reaction uses an enzyme? Which does not? How do you know?

*Red: has enzyme
*Black: no enzyme
Letter A represents Activation energy. It is lower in the red reaction
What are the 2 types of fermentation and their outputs?
Alcohol - ethanol
Lactic Acid - lactic acid/lactate
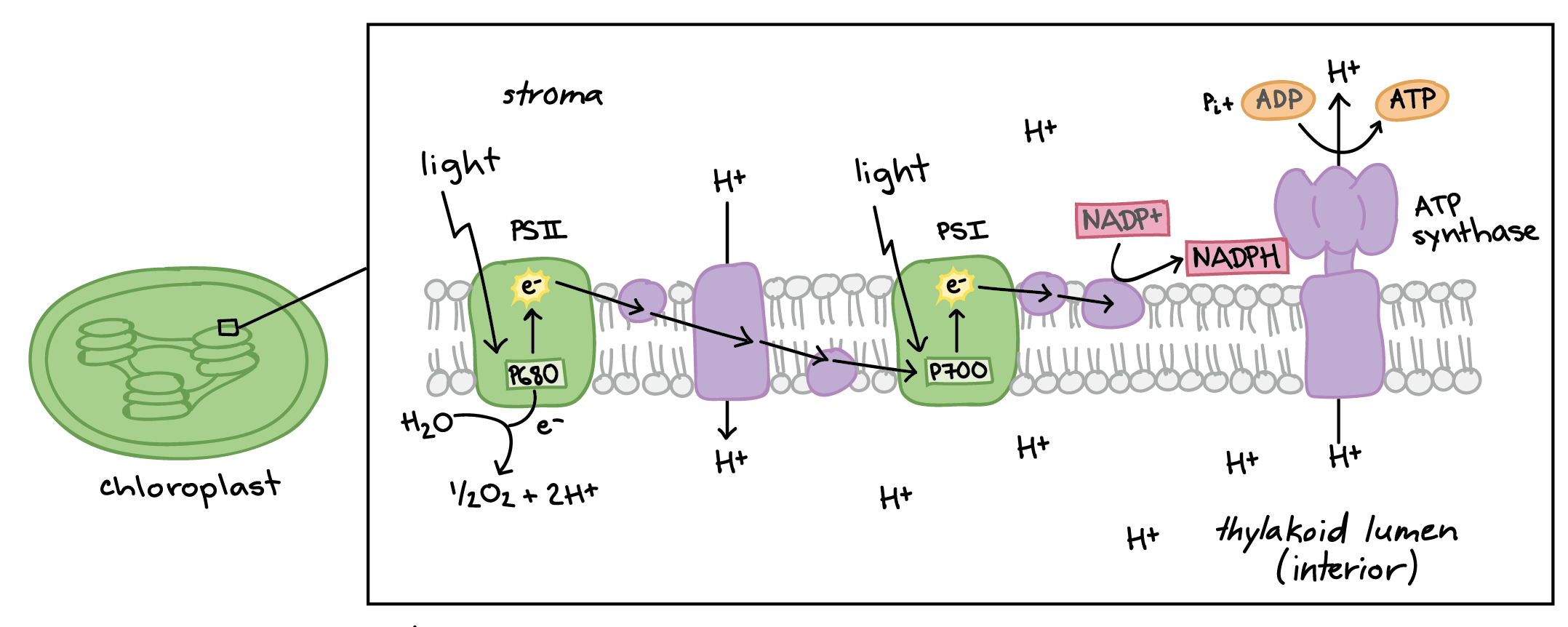
Explain the Light Reactions. Inputs? Outputs? Location?
PSII captures sunlight to make ATP, PS I generates NADPH using electron transport chains.
Inputs: water and sunlight
Outputs: ATP, NADPH,
Location: thylakoid membranes
Explain how active and passive transport differ. Give an example of each
Active:requires energy, move things from low to high concentration. Ex: sodium potassium pump
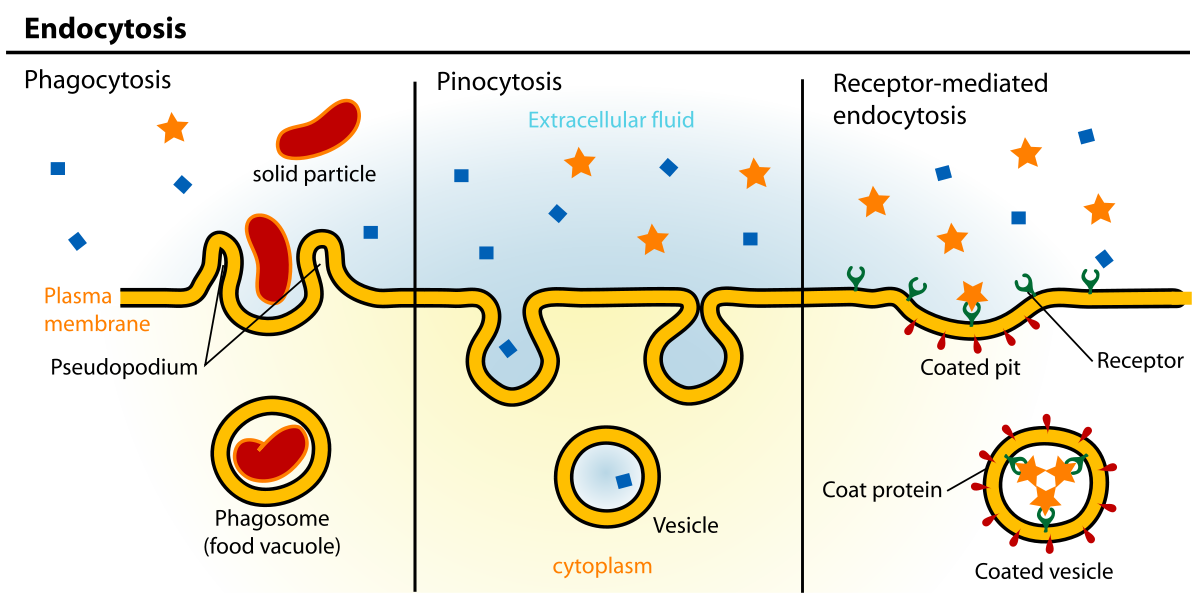
Name and explain the 3 types of endocytosis
Phagocytosis - Cellular eating
Pinocytosis - Cellular drinking
Receptor mediated - specific molecules pulled in by receptors (ex: neurons)
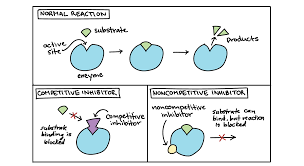
Name and explain the 2 types of enzyme inhibitors
Competitive: inhibitor binds to the active site
Non-Competitive: inhibitor binds to the allosteric site (anywhere thats not active site)
Name each step of cellular respiration and where it occurs
Glycolysis - cytoplasm/cytosol
Pyruvate oxidation: mitochondrial matrix
Kerbs/Citric Acid Cycle: mitochondrial matrix
Oxidative phosphorylation: ETC - inner membrane; CO - inter membrane space
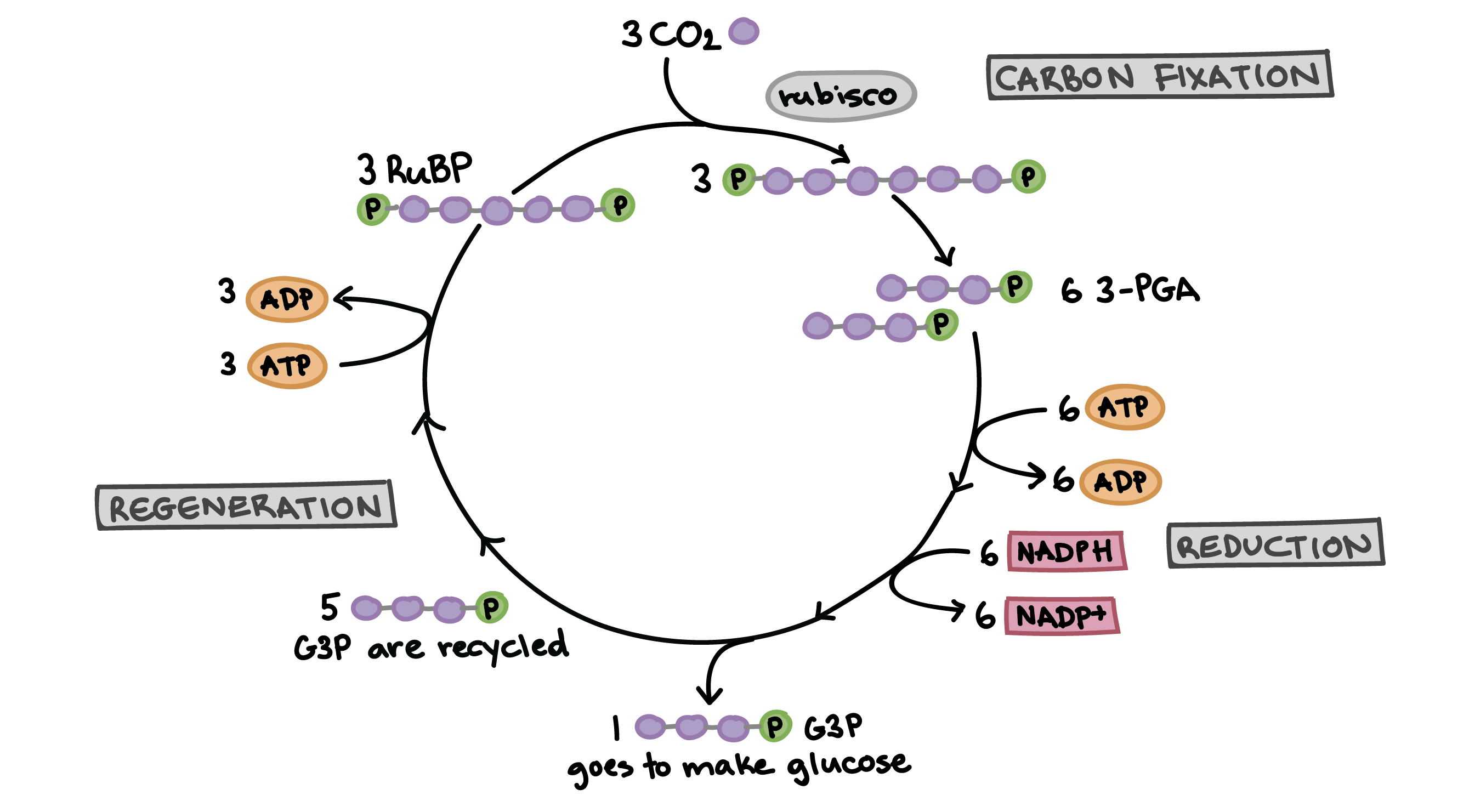
Explain the Calvin Cycle. Inputs? Outputs? Location?
Inputs: Carbon dioxide, ATP, NADPH
Outputs: Sugar (G3P, which makes glucose), ADP, NADP.
Location: Stroma
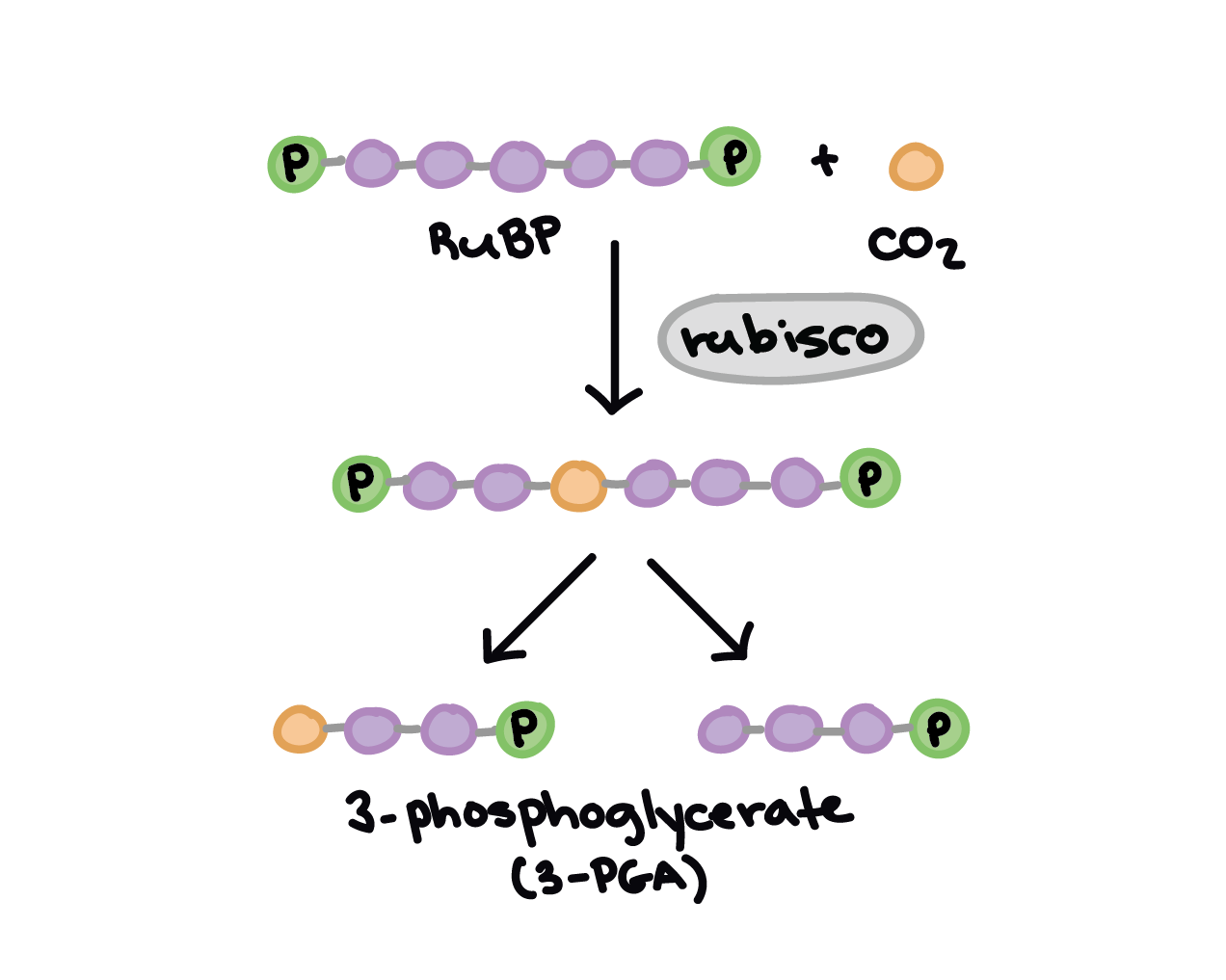
What is rubisco?
The enzyme used in the Calvin Cycle. It "fixes" carbon from the air.
Come up to the board. Name 3 components of the membrane below, and explain their function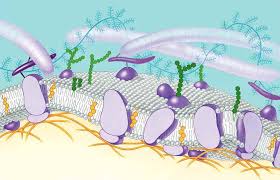
Items found include:
Transmembrane proteins
Integral proteins
Peripheral proteins
Cholesterol
Glycolipids and Glycoproteins
What type of reaction is this?

Exergonic (catabolic)
Come up to the board and point out the various components of the mitochondria. State where each step of cellular respiration occurs

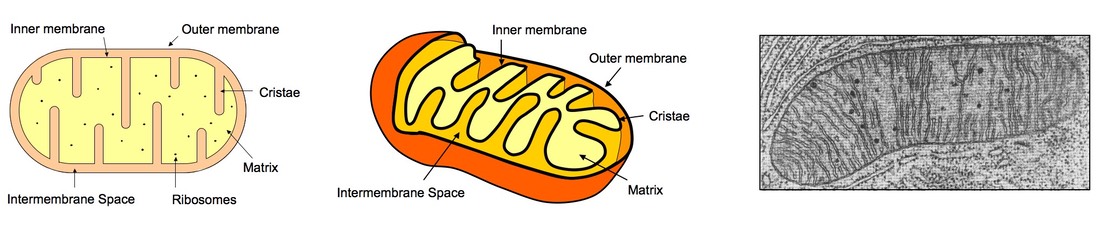
Come up to the board and point out the various components of the chloroplast. State where each step of photosynthesis occurs
![]()
Thylakoid space = lumen
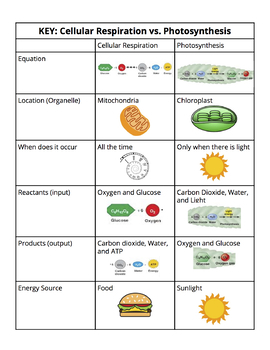
Name and explain 2 similarities and 2 differences between cellular respiration and photosynthesis
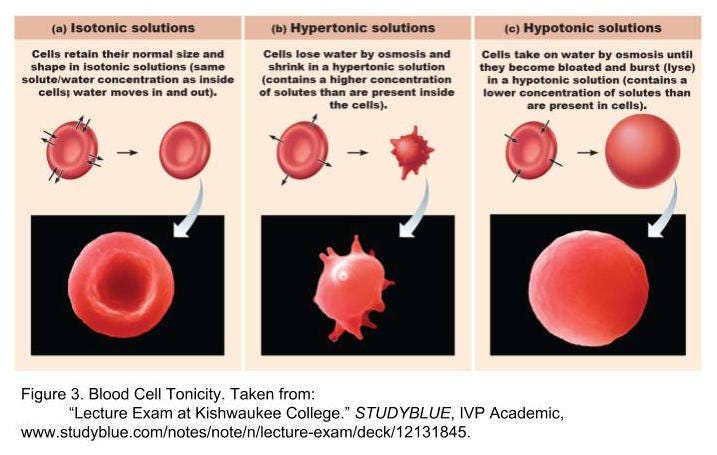
Name and explain the 3 types of osmotic solutions
Hypertonic - more solute less water
Hypotonic - more water less solute
Isotonic - equal solute and water
What are 2 environmental factors that can denature proteins (like enzymes)?
Temperature, pH
State the inputs and outputs of the Citric Acid/Krebs cycle
Inputs: 2 Acetyl CoA, NAD+, ADP, Pi, FAD+
Outputs: 2ATP, 6NADH, 2FADH2, 4CO2

Name the 3 steps of the Calvin Cycle
1) carbon fixation
2) reduction
3) RuBP regeneration

Explain what happens in Oxidative phosphorylation. Start with the electron transport chain, then go to chemiosmosis.
ETC: electrons pumped (active transport) through the inner membrane so protons can "pile up" in the inter membrane space. Water is released because oxygen is the terminal electron acceptor.
CO: Protons flow (diffuse) back through the inter membrane space into the matrix through ATP synthase enzyme. This enzyme puts ADP and Pi together to form ATP.