What is a teratogen and what are some examples?
![]()
Any harmful agent that can affect the developing fetus
Examples can be stress, alcohol, drugs, tobacco

What is learning, according to the first page of Chapter 7? :-)
A relatively enduring change in knowledge and/or behavior resulting from specific experiences
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/learning-study-guide-2795698_FINAL-5bec544ac9e77c005185519d.png)
Memory is first encoded, then what are the next two steps of the memory process?
Storage and Retrieval
- Storage is keeping it there, and retrieval is finding it when you need it
- Memory is a reconstruction
- Is the computer analogy a good or bad example?
What is the difference between concepts and prototypes?
Concepts are mental categories into which we can place people, places, things, events, or ideas that share common characteristics.
An example of a concept or category that is thought to be typical or representative.

What is the term for the desire to reduce unpleasant arousal states resulting from basic psychological needs?
Drive
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/drive-reduction-theory-2795381_FINAL_Text-08928789d3024a859cb4f977fdb9ca2d.png)
What are some examples of basic emotions?
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/an-overview-of-the-types-of-emotions-4163976-abaafd59e7214706b7cd6326d0dd8257.png)
After fertilization, what are the other three stages of prenatal development?

1. Zygote
2. Embryo
3. Fetus
(ZEF)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/2795073-stages-of-prenatal-development-01-5a3040f6eb4d5200362d5553.png)
Give 3 examples of
1. Primary reinforcers
2. Secondary reinforcers

1. Food, water, sex, air, shelter, pleasure, romantic success
2. Money, status, college degree, paid vacations, music, holiday movies, praise, your grade in this class
Secondary reinforcers have been conditioned to be associated with a primary reinforcer

What is the difference between recall and recognition?
![]()
Example: Kahoot vs. Jeopardy, Multiple Choice vs Short Answer

Explain the following terms
1. Algorithm
2. Trial and Error
3. Heuristic
1. Step by step set of instructions
2. Solutions are eliminated one at a time
3. Mental problem solving shortcuts or "rules of thumb"
Motivations have three key characteristics (second page of this chapter)
1.
2. Causes rooted in specific mental states
3.
1. Purpose
2. Causes rooted in specific mental states
3. Intentionality
_________ is the psychological and physiological consequence of events that challenge a person's ability to cope, and which threatens their well-interferes with important goals.
Stress
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/VWH_Illustration_Behavioral-Symptoms-of-Psychological-Stress_Nez-Riaz_Final-cc72e2527af846fca78cf783818f4928.jpg)
1. Describe or give an example of a schema
2. Describe or give an example of assimilation or accommodation
1. Cognitive models that people construct of what the world is and how it works
2. Assimilation = Processing a new experience by adding it into a preexisting schema
Accommodation = Altering a schema to incorporate new information or experiences
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/what-is-assimilation-2794821-5b61db5ec9e77c005088869f.png)
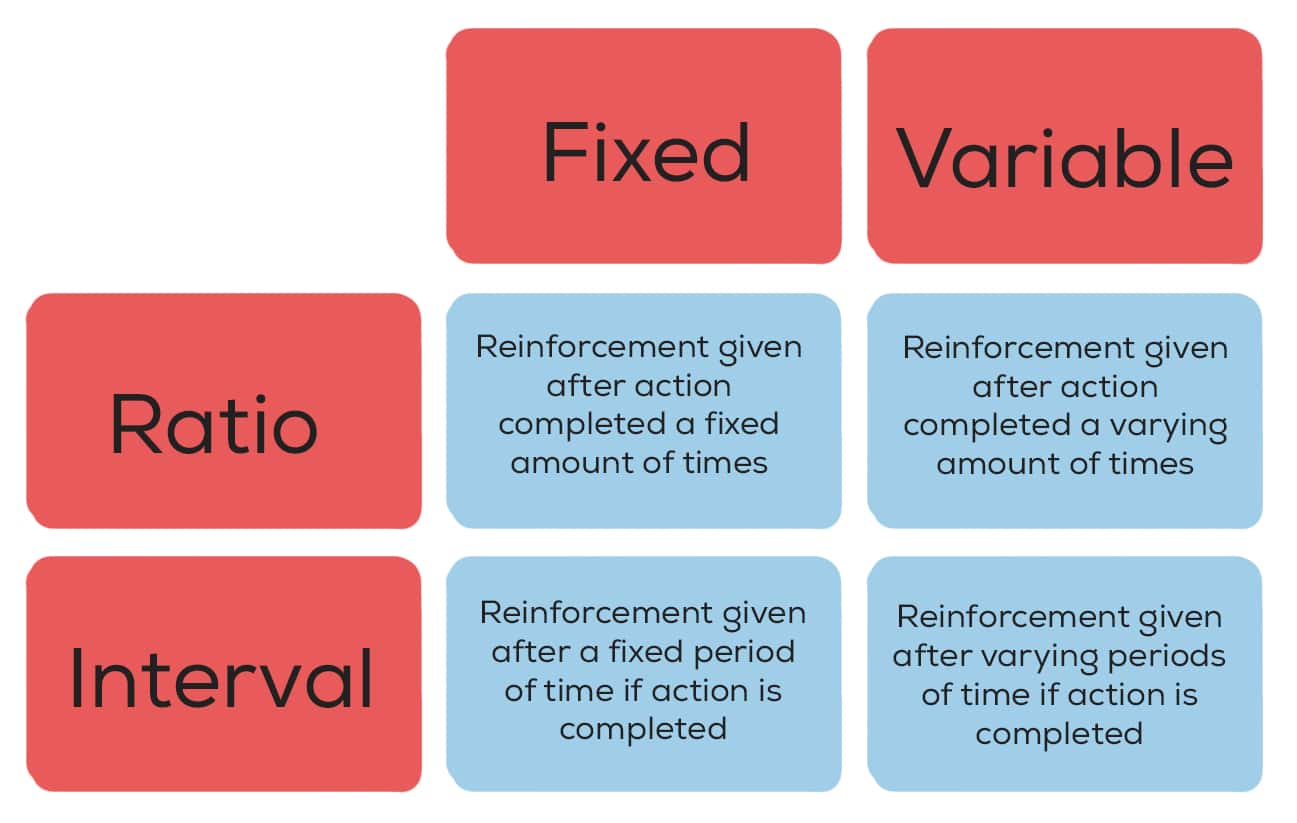
Identify the type of reinforcement schedule (fixed/variable interval/ratio)
1. When a toddler turns a page every three times, it is rewarded a piece of candy
2. At the end of each month, you are paid your salary
3. When you play a slot machine and pull down the lever, you are rewarded randomly. You could win your first try, you could win on your tenth try.
FIXED = SPECIFIC
VARIABLE = RANDOM/UNPREDICTABLE
INTERVAL = BASED ON TIME
RATIO = BASED ON BEHAVIORAL RESPONSES
1. Fixed ratio
2. Fixed interval
3. Variable ratio
BONUS EXAMPLE: A drug test is an example of a variable interval
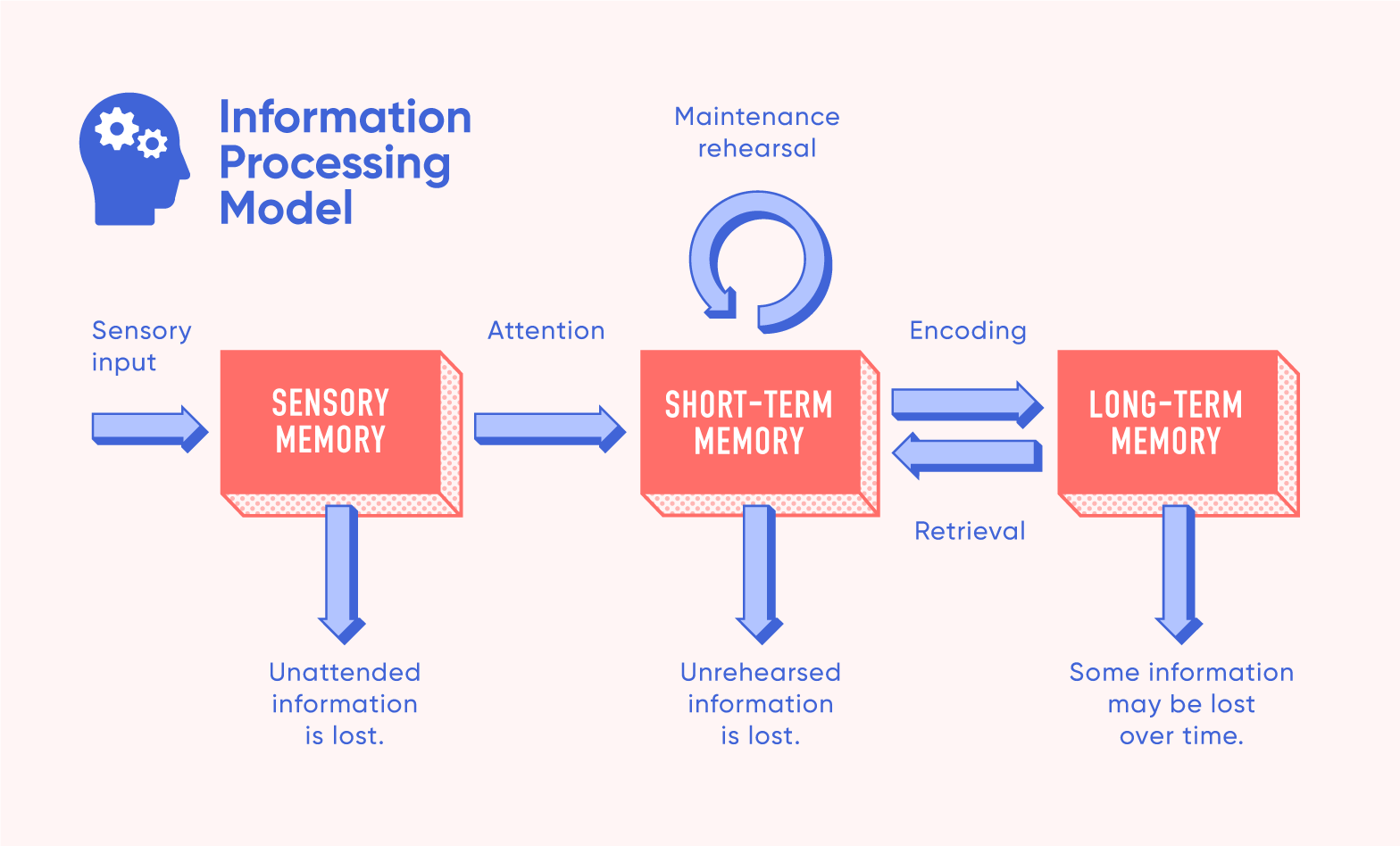
In the information-processing theory, information first goes to our _____________ memory, then our short-term memory, and finally to our ________ memory.
Sensory memory, Long-term memory
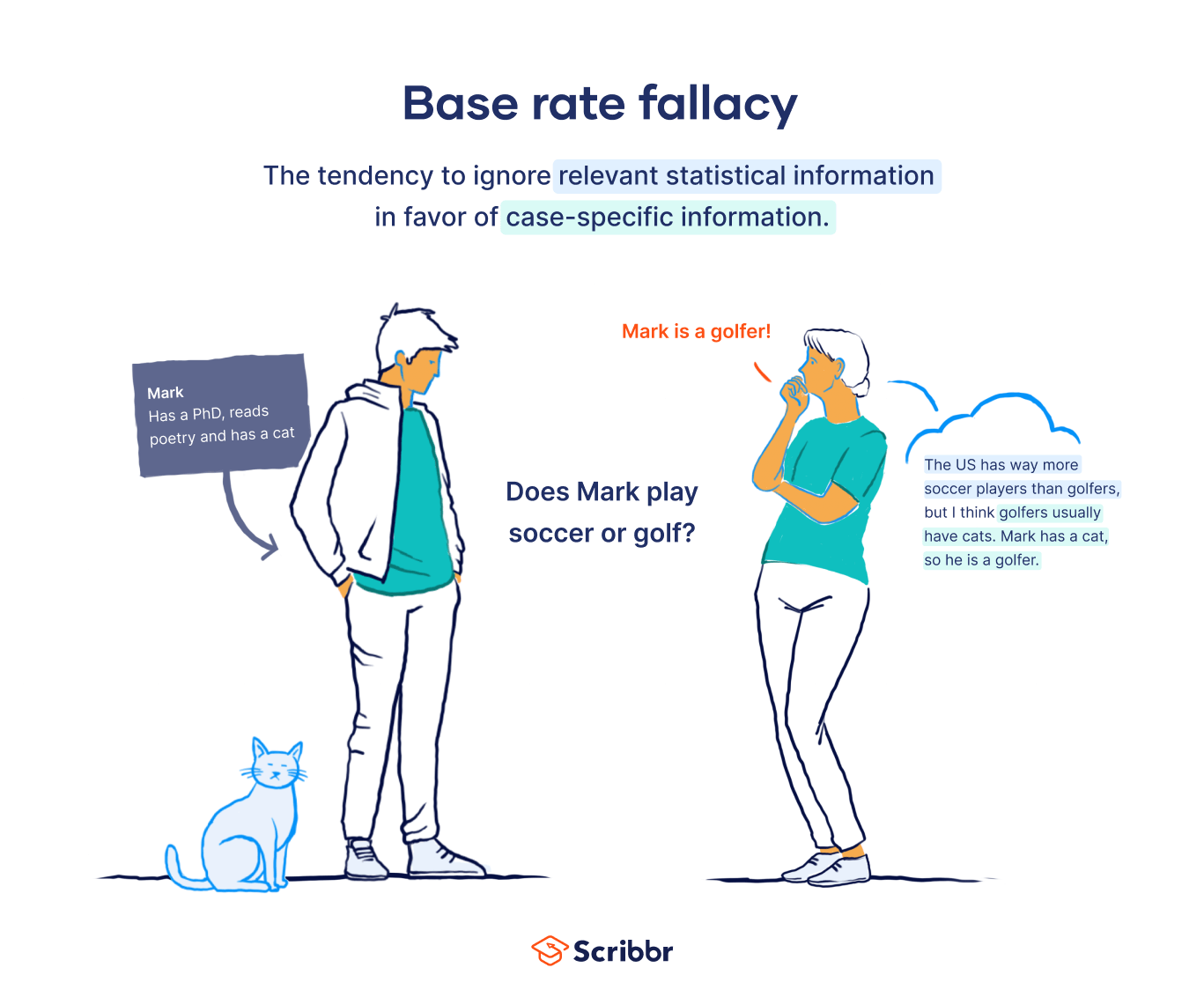
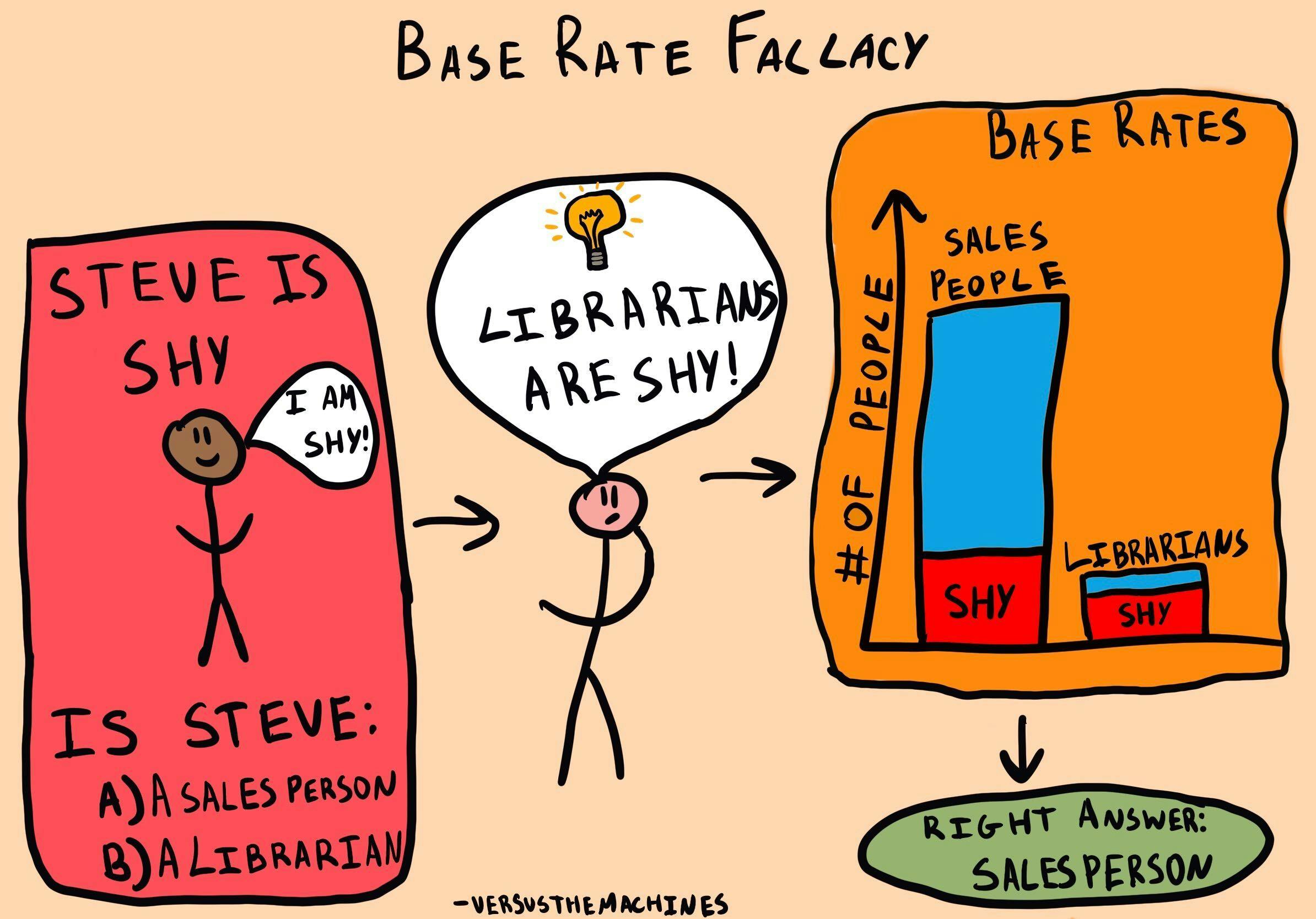
What is the largest issue when using heuristics?
Base Rates
What is the difference between extrinsic and intrinsic motivation?
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/2795164-what-is-extrinsic-motivation-5b31542404d1cf0036a91c79.png)
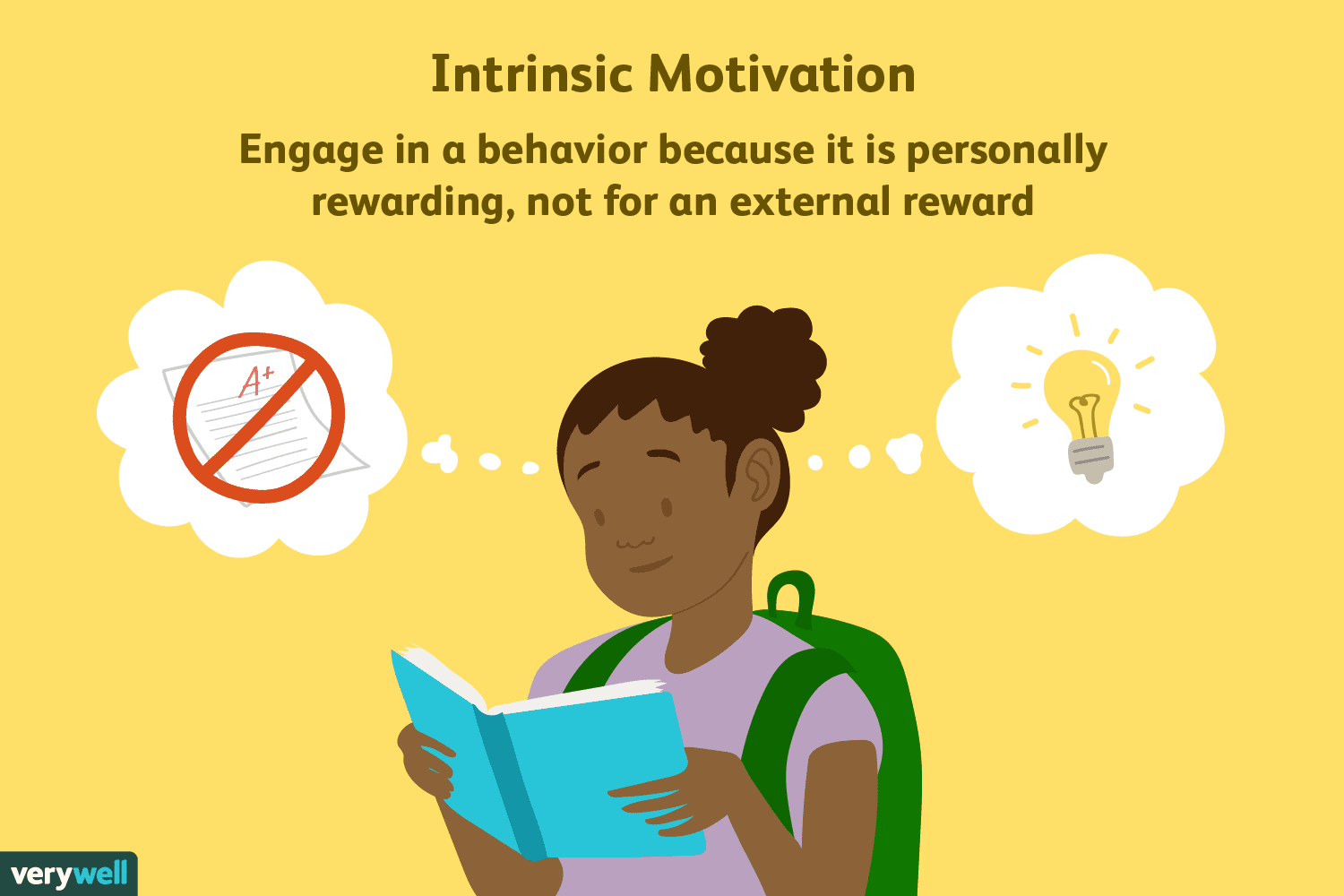
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/2795384-differences-between-extrinsic-and-intrinsic-motivation-5ae76997c5542e0039088559.png)
What are a few examples of a mood?
Being depressed (mood) on an ongoing and continuous basis
Being sad for 24 hours (emotion)
- A feeling state that is typically less intense than an emotion, but which may last for a much longer time
1. In the sensorimotor stage, what important feature(s) develop?
2. In the concrete stage, what important feature(s) develop?
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/2795457-article-piagets-stages-of-cognitive-development-5a95c43aa9d4f900370bf112.png)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/2795457-article-piagets-stages-of-cognitive-development-5a95c43aa9d4f900370bf112.png)
1. Object Permanence
2. Conservation and Theory of Mind

Identify what type of operant conditioning is below (positive/negative reinforcement/punishment)
1. After making an A+ on the second exam, you are given $1,000,000 by your parents
2. A car beeps until the seatbelt is fastened
3. For destroying a new couch, you scream at your dog

1. Positive reinforcement
2. Negative reinforcement
3. Positive punishment
BONUS EXAMPLE: A child's iPad is taken away for not doing their chores (negative punishment)
Explain what was found in Ebbinghaus's Forgetting Curve discovery
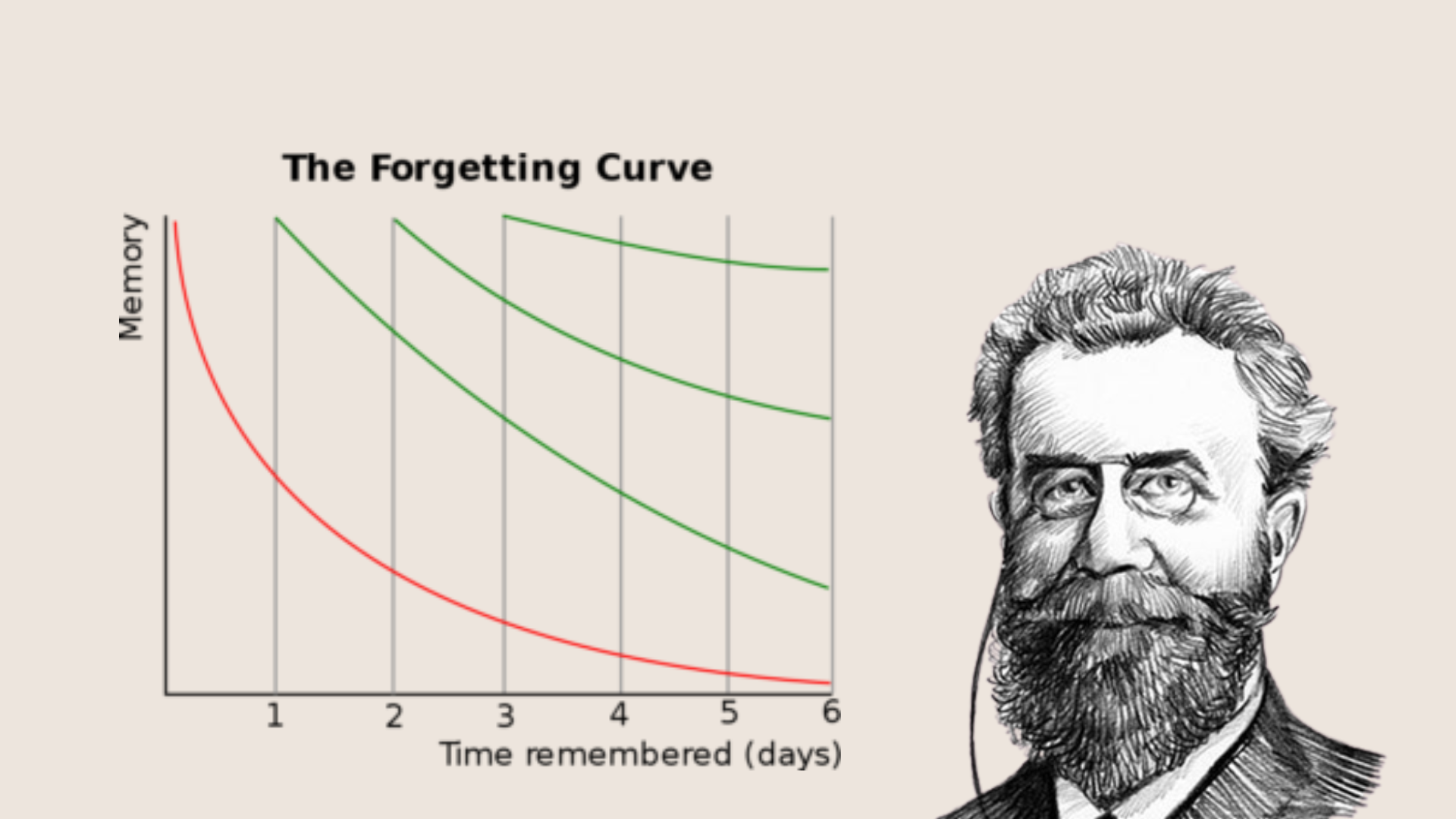
Forgetting follows a pattern according to the passage of time, with most memory according rapidly, and then at a slower pace
An alternative to g and IQ, Howard Gardner founded this view to incoporate talents that are socially valued such as athletic ability, musical ability, or the ability to understand one's own emotions and motivations. What theory is this?
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/gardners-theory-of-multiple-intelligences-2795161-5bcdfc7046e0fb0051fb2311.png)
Gardner's Theory or Multiple Intelligences

What is the difference between instrumental and hostile aggression?

Instrumental has an ultimate purpose other than causing harm to the victim and is often planned.
Hostile has an ultimate purpose of harming the victim. It is generally impulsive and accompanied by emotions, such as anger

Explain the Nature vs. Nurture debate

Debate over whether innate biology (nature) or environmental experience (nurture) is the more critical factor in the development of human development.
"Nature via Nurture" is what more scientists are leaning towards, as nature and nurture are both important
When Miah gets back to the dormitory after jogging around the campus, he likes to take a quick shower before going to class. One morning while taking a shower he hears someone flushing a nearby toilet. Suddenly, extremely hot water comes rushing out of the showerhead and Miah experiences excruciating pain. After muttering a few obscenities, he continues showering. A few minutes later, Miah hears another toilet flush, and he leaps out of the shower.
- What is unconditioned stimulus?
- What is the unconditioned response?
- What is the neutral stimulus that becomes the conditioned stimulus?
- What is the conditioned response?
1. Hot water
2. Excruciating pain
3. Sound of a toliet flushing
4. Excruciating pain is incoming (hops out of the shower)


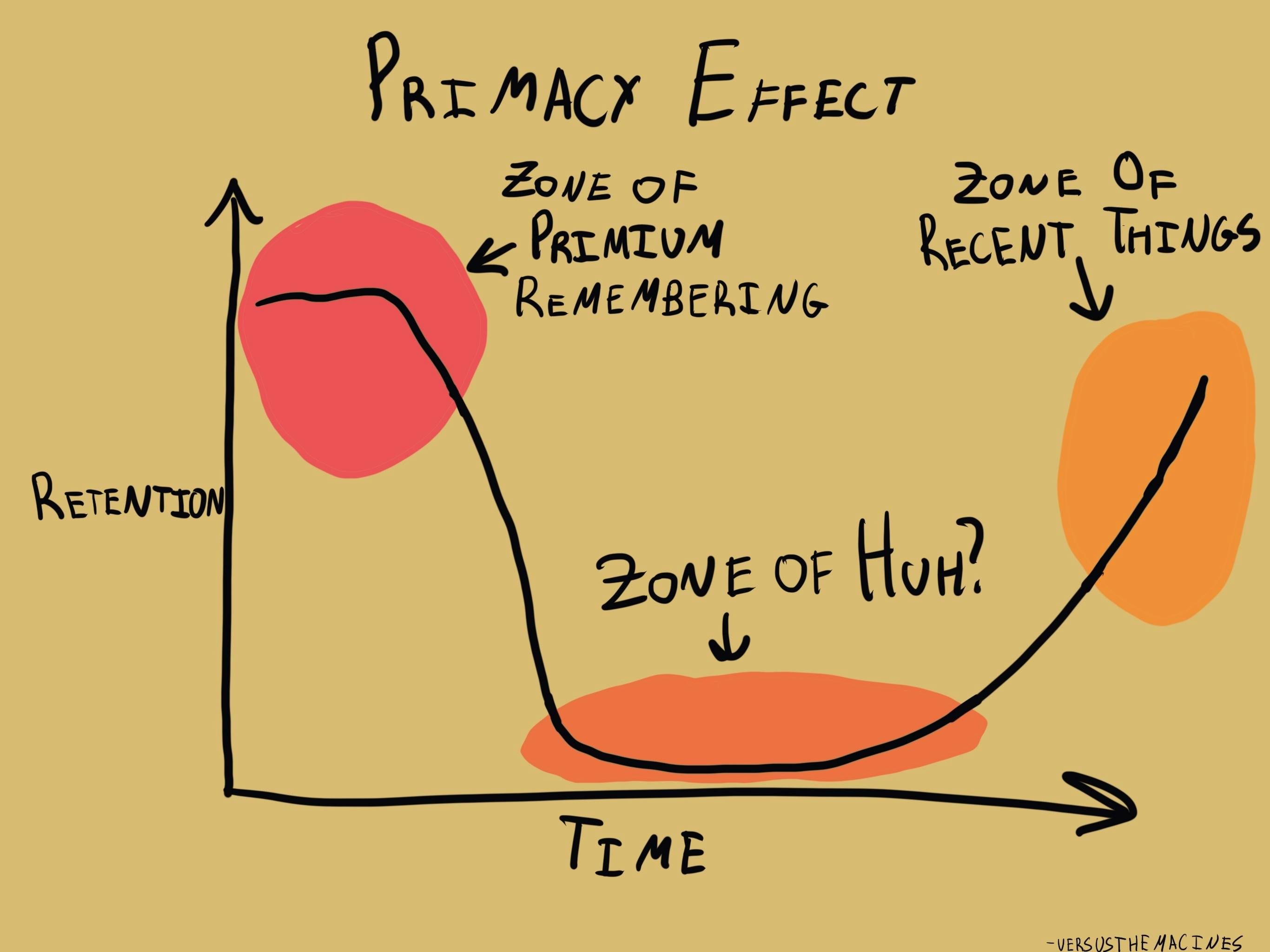
Explain what the serial-position curve found


Give an example of the availability heuristic and representativeness heuristic
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/representativeness-heuristic-2795805-5b841fdc46e0fb0025f76b56.png)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/availability-heuristic-2794824_color1-5b76d4b046e0fb00509bbb7a.png)
Fill in the blank:
Maslow's Hiarchy of Need's goes in this order (starting from the bottom)
5.
4. Safety
3.
2. Esteem
1.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/4136760-article-what-is-maslows-hierarchy-of-needs-5a97179aeb97de003668392e.png)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/maslow-s-hierarchy-of-needs--scalable-vector-illustration-655400474-5c6a47f246e0fb000165cb0a.jpg)