Image of the teeth and bones made by placing the film or cassette against the face or the head and projecting the x-rays from the opposite side.
Imaging that allows the dentist to view the entire dentition and related structures on a single image.
Panoramic
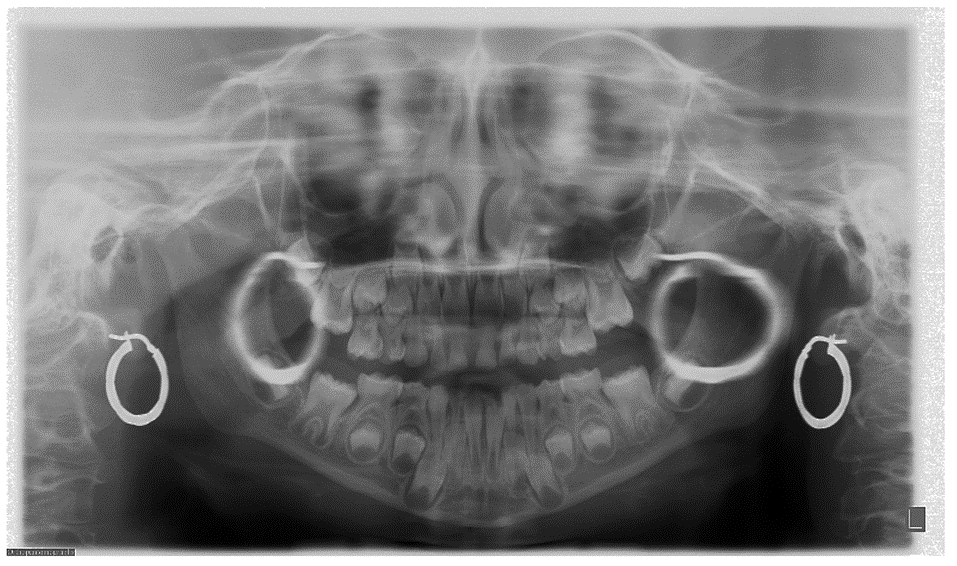
Ghost Image. Solution: Have patient remove all radiodense objects from head and neck region before being positioned. (jewelry, piercing's and glasses)
Consists of chin rest, a notched bite-block, forehead rest and lateral head supports or guides. Used to correctly position patient within the focal trough.
Head Positioner
Nasal septum
Imaginary line that divides the patient's face into right and left sides.
Midsagittal Plane
Provides 3D views of mouth, face and jaw from any direction. Used to evaluate for extraction of impacted teeth, placement of implants and exact location of mandibular nerve.
Cone Beam Computed Tomography CBCT
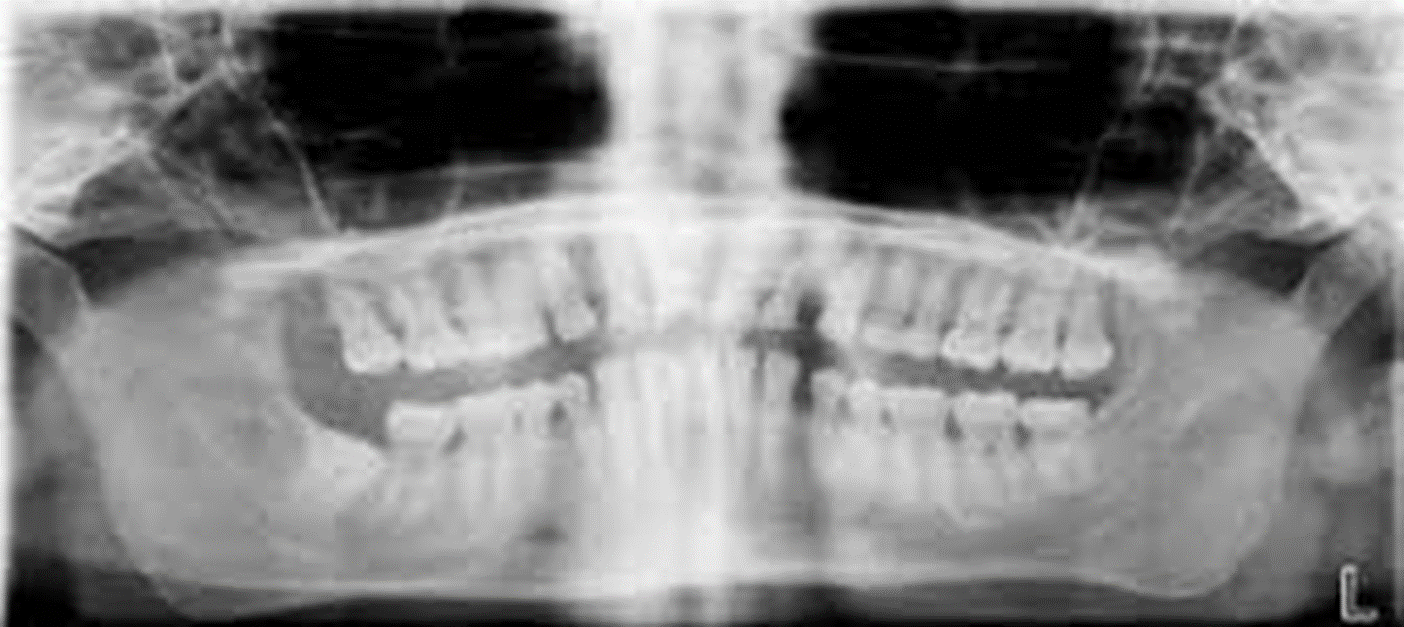
Chin too high. Solution: Position the patient so the Frankfort plane is parallel to the floor.
Allow the milliamperage and kilovoltage settings to be adjusted to accommodate patients of different sizes.
Exposure Controls
Mandibular canal/nerve
Imaginary three-dimensional horseshoe-shaped zone used to focus panoramic radiographs.
Focal Trough
Uses special imaging techniques such as arthrography and magnetic resonance imaging, to evaluate TMJ
Temporomandibular Joint Radiography
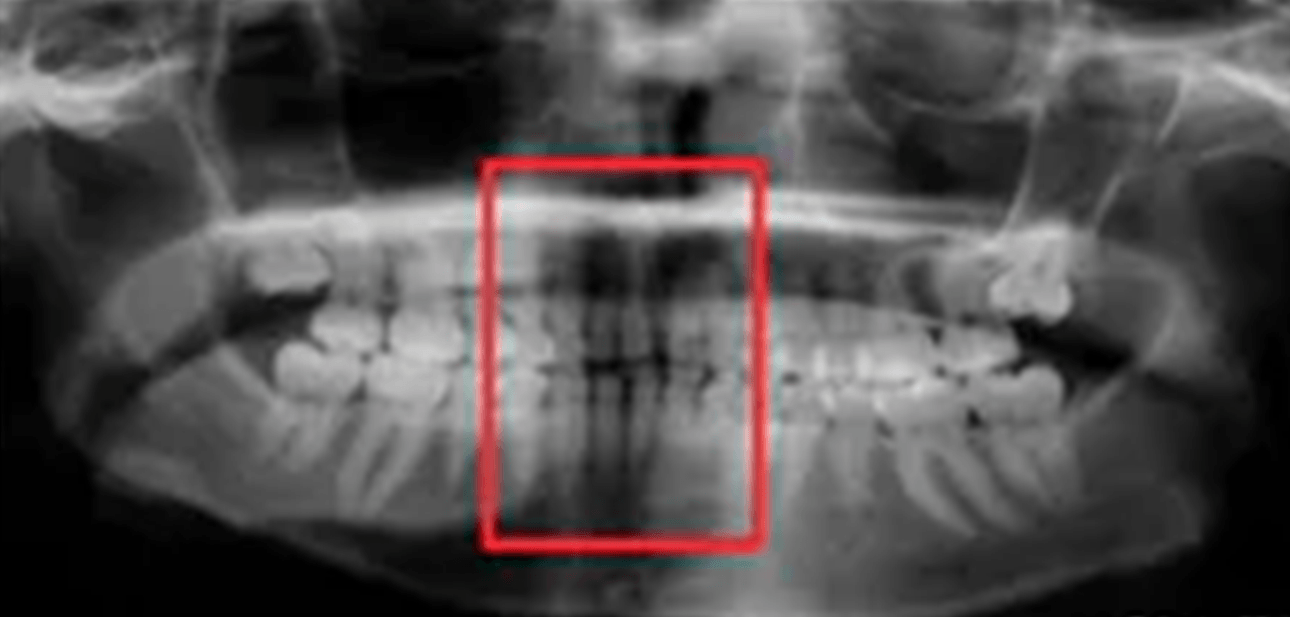
Anterior to focal trough. Solution: Position the patient so that the anterior teeth are placed in an end-to-end position in the groove on the bite-block.
Tubehead
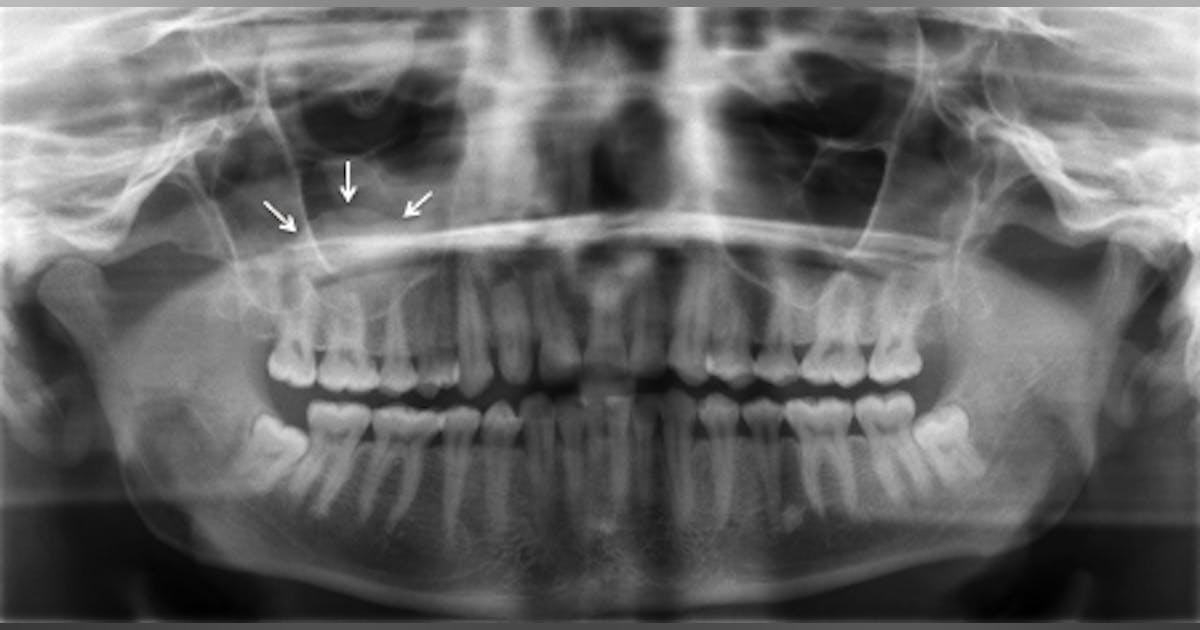
Maxillary Sinus
Imaginary plane the passes through the top of the ear canal and the bottom of the eye socket.
Frankfort Plane
Used to evaluate facial growth and development, trauma, diseases and developmental abnormalities, showing the frontal and ethmoid sinuses, the orbits and the nasal cavities.
Posteroanterior Projection
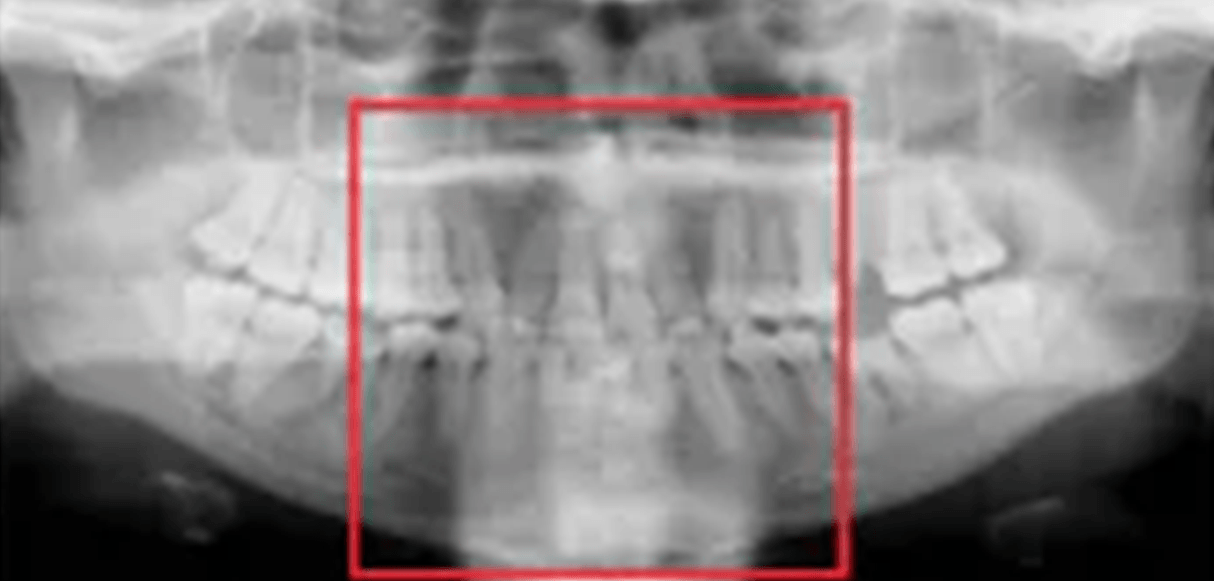
Spine not straight. Solution: The patient must be instructed to stand or sit "as tall as possible" with a straight back.
Rotates in front the patient and is sensitive to light from intensifying screens.
Film.
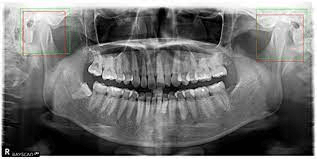
Mandibular Condyle
Special device the allows the operator to easily position both film and patient.
Cephalostat
Used to evaluate facial growth and development, trauma, diseases and developmental abnormalities. Shows the bones of the face and skull as well as the soft tissue from the profile.
Lateral Cephalometric Projection
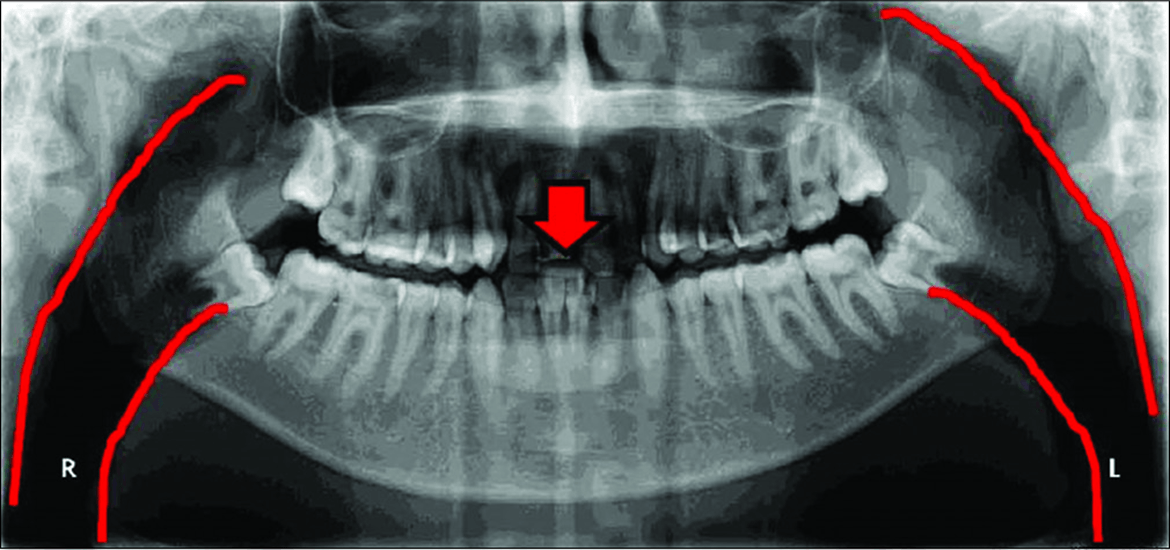
Lips are not closed and tongue is not on the roof of the mouth. Solution: Close the lips around the bite-block, swallow, and then raise the tongue up to the palate.
Device placed between the patient's head and film used to decrease scatter radiation the reaches an extraoral film during exposure.
Grid

Hyoid bone