What is diffusion?
Diffusion is the net movement of particles from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration
What is isotonic?
equal concentration of solute when compared to another solution
In the case of thermoregulation the modulator is .........
the hypothalamus
What is Homeostasis?
Homeostasis is the regulation of a relatively stable internal environment within narrow limits
What hormone is produced by the beta cells of the islets of Langerhans?
insulin
What is the independent variable in an experiment?
The variable you manipulate or vary in an experimental study to explore its effects
What is osmolality
the concentration of solute in a solution
When temperature increases and small blood vessels in the skin act as the effector, what is the response?
dilation of arterioles (vasodilation).
Could add **causing heat to be lost to the environment
Which cell is a plant cell? Justify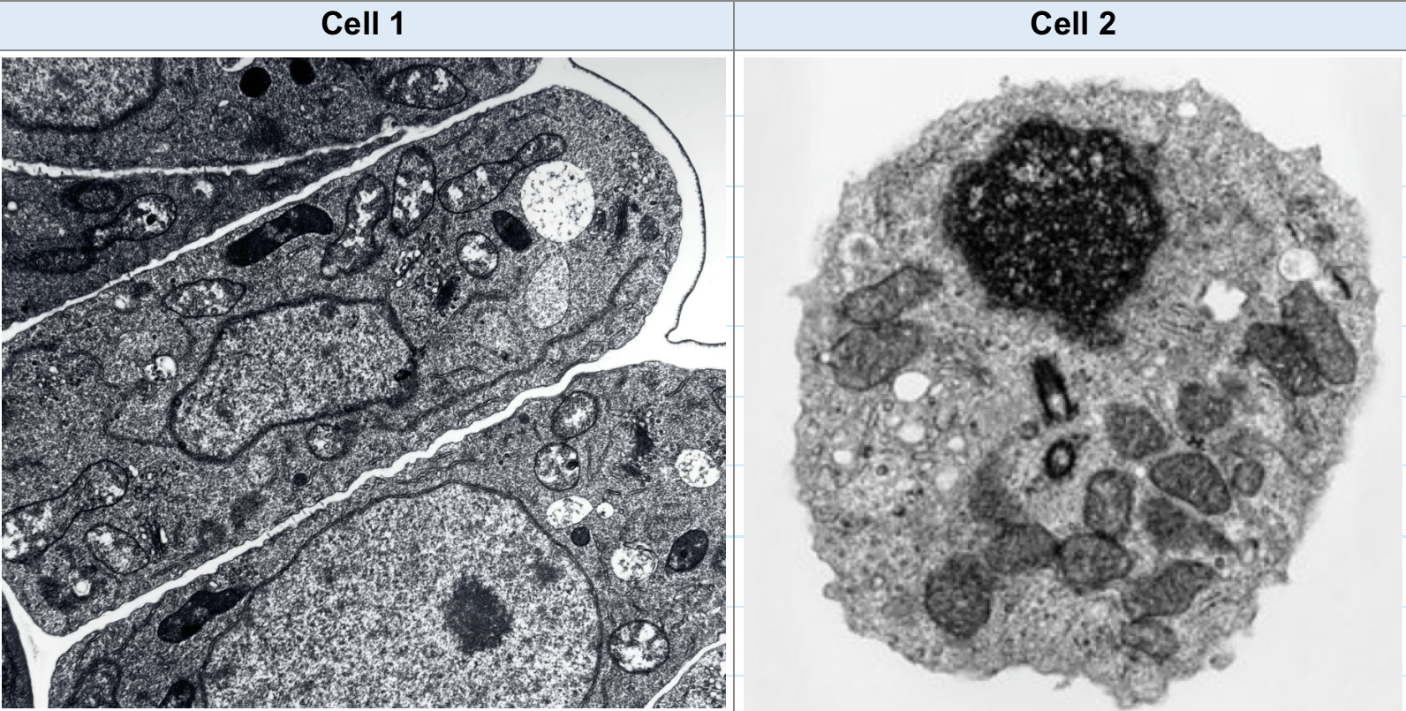
Cell 1
What is the receptor in blood glucose regulation?
the pancreas (specifically the islets of Langerhans)
Identify one difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells
- Size
- Membrane bound organelles
- Nucleus
What are the two receptor types involved in osmoregulation? and what do they detect?
- osmoreceptors detects change in osmolality
- barareceptors dectects change in blood pressure (which is affected by water concentration in the blood)
In cold temperatures when the effector is arrector pili muscles, the response is ........
raising of hair follicles/ goosebumps
Identify the organelle in the electron micrograph 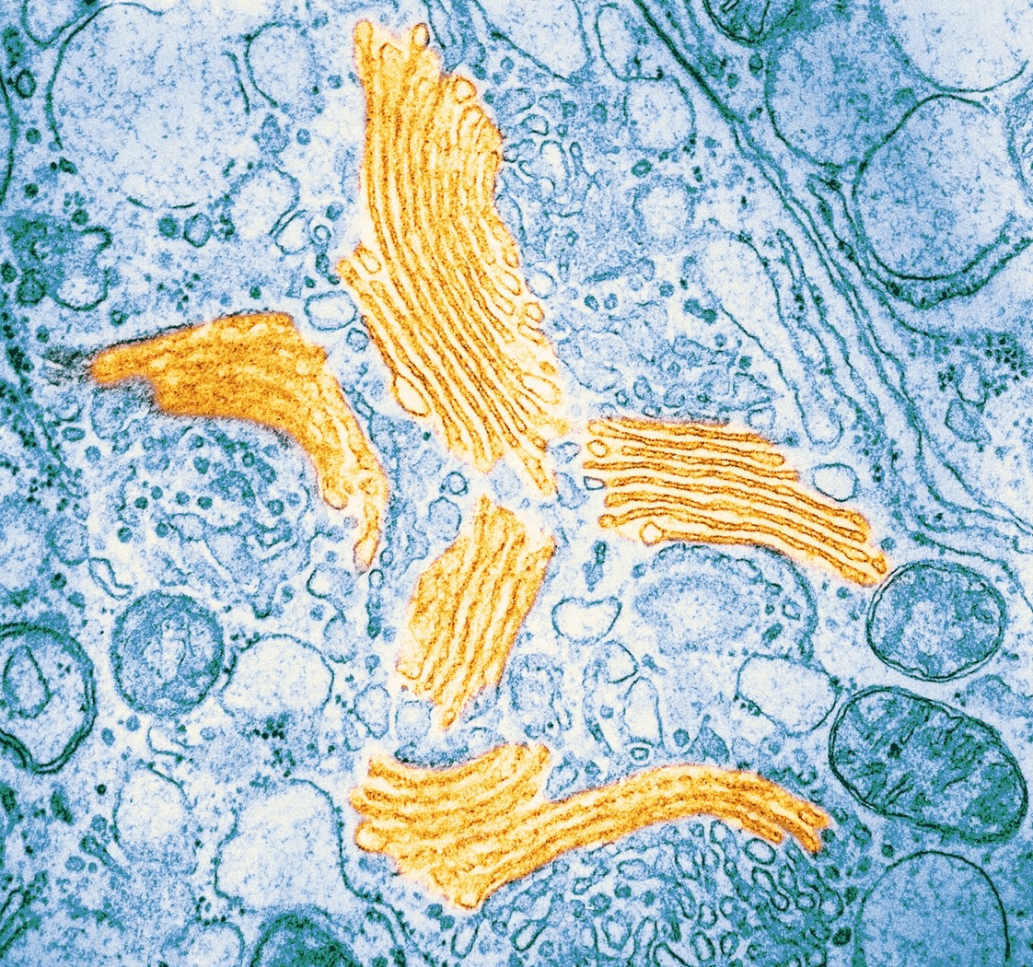
Golgi apparatus
Glycogen is formed by a process known as........ which joins glucose molecules together.
glycogenesis
Identify the organelle in the electron micrograph 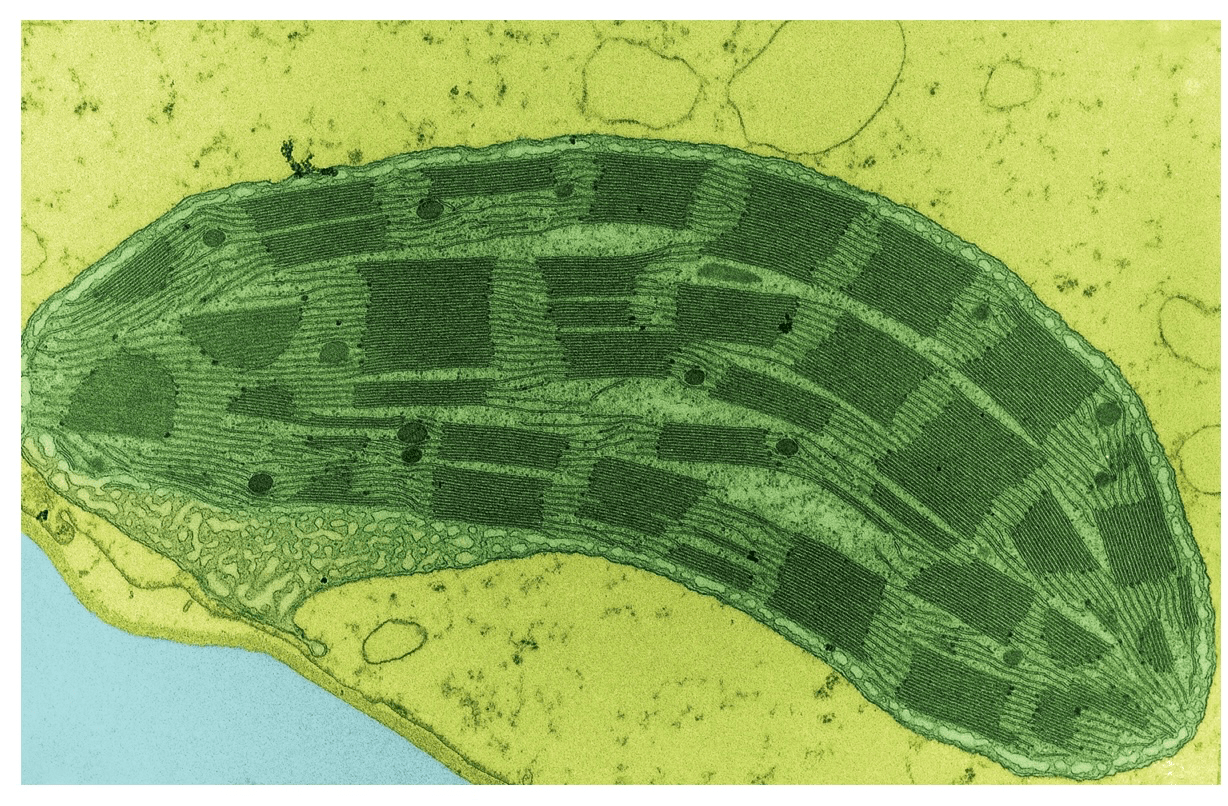
chloroplast
ADH increases water reabsorption in the distal convoluting tubules and collecting duct of the kidney by....
increasing the number of aquaporins
State the type of feedback used in thermoregulation and explain how this feedback maintains homeostasis.
Negative feedback. Acts by detecting changes in the temperature of the external environment and produces a response that counteracts this change.
Name one structural element of the small intestine that is suitable for its function.
- long and coiled
- villi
- large surface area: volume ratio
How is glucose transported around the body?
in the blood plasma
What is the general name of a signaling molecule released from endocrine glands, which acts on a specific target cell?
a hormone
What hormone does the pituitary gland secrete when the body is dehydrated (increase in osmolality)?
ADH (antidiuretic hormone)
What is conduction?
the transfer to heat through physical contact with another object
State the two pathways of apoptosis
extrinsic pathway and intrinsic pathway
When blood glucose levels fall below 5mmol/L, what hormone is secreted and which specific cells produces this hormone?
glucagon produced by the alpha cells in the islets of Langerhans.