two or more bonded atoms with a determinate number of atomic nuclei
What is a molecule?
anything that has mass and occupies space
What is matter?
combinations of these four elements make up over 96% of the human body
What are oxygen (65%), carbon (18.5%), hydrogen (9.5%), and nitrogen (3.2%)?
particles close together in an orderly arrangement with little freedom of movement so that it retains its shape when moved from one container to the next
What is a solid?
the simplest chemical substance; all of its atoms have the same atomic number and cannot be separated into simpler substances by chemical means (e.g., iron, gold, mercury)
What is an element?
the type of chemical bonds that hold atoms of a molecule together
What are covalent bonds?
the study of matter and the changes that matter undergoes
What is chemistry?
these two elements are the only ones (besides the essential four) that make up 1% or more of the human body
What are calcium (1.5%) and phosphorus (1%)?
particles are close together, but not held rigidly so that they can flow past one another and mold to the shape of any container
What is a liquid?
two or more elements chemically combined in distinct/definite ratios of atoms that cannot be separated by physical means (e.g., salt, water, carbon dioxide)
What is a compound?
a molecule that consists of only 2 atoms
What is a diatomic molecule?
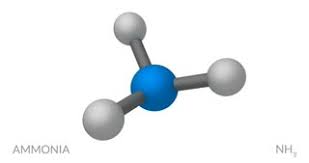
general name for this type of molecular model
What is a ball-and-stick model?
matter is classified (subdivided) into one of these two categories
What is a pure substance or a mixture?
particles have complete freedom of movement and can spread apart to fill both the shape and volume of their container
What is a gas?
physical combination of two or more substances whereby the substances retain their unique identities and can be separated by physical means (e.g., sugar water)
What is a mixture?
diatomic molecules made from atoms of different elements
What is a heteronuclear molecule?
this has a precise composition and can be either an element or a compound (e.g., NaCl, H2O, O2)
What is a pure substance?
a set of conceptual assumptions that explains data from accumulated experiments; predicts related phenomena
What is a model or theory?
general method for turning a solid into a liquid or gas
What is add heat?
the mixture composition is uniform throughout (e.g., sugar water)
What is a homogeneous mixture?
these seven elements exist as homonuclear diatomic molecules at room temperature
What are H2, N2, F2, O2, I2, Cl2, Br2 ?
two or more chemically bonded elements (any type bond)
What is a compound?
Compounds are either covalent or ionic. In this class, we define 'molecule' as the simplest form of a covalent compound. Why do we not refer to ionic compounds as molecules?
Ionic compounds do not exist as distinct molecules, so we don't call them molecules (e.g., we can't have one molecule of salt). Instead, they exist in crystal lattices composed of many, many ions.
general method for turning a gas or liquid into a solid
What is remove heat?
the composition of the mixture is not uniform throughout (e.g., oil and vinegar salad dressing)
What is a heterogeneous mixture?