What are the 2 main divisions of the nervous system?
The Central Nervous System (CNS) and the Peripheral Nervouse System (PNS)
What is the function of the axon hillock?
It connects the cell body to the axon and is the site where action potentials typically begin.
What type of reflex is the patellar reflex?
A monosynaptic spinal stretch reflex.
What cells myelinate axons in the PNS?
Schwann cells.
Which part of the brain contains the primary somatosensory cortex?
The parietal lobe
What is the structural classification of neurons based on?
The number of processes extending from the cell body.
Label I, O, T, & U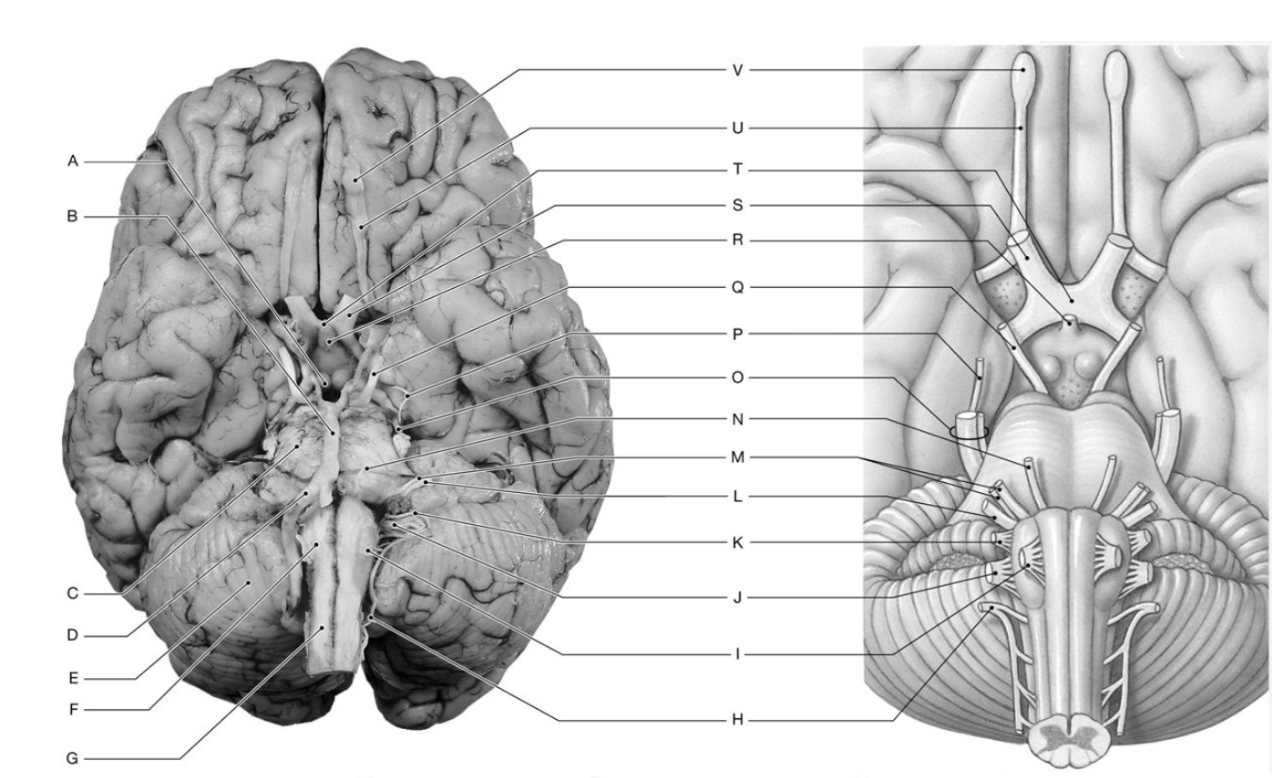
I: Hypoglossal Nerve (XII)
O: Trigeminal Nerve (V)
T: Optic Chiasm
U: Olfactory Tract
What structures are included in the CNS?
The brain and spinal cord
What is the role of myelin in the nervous system?
Myelin insulates axons and increases the speed of nerve impulse conduction.
What is a stretch reflex responsible for?
Maintaining posture and automatically regulating muscle length.
What cells myelinate axons in the CNS?
Oligodendrocytes.
Which brain structure regulates circadian rhythm by producing melatonin?
The pineal gland
What layer surrounds a single axon in a nerve?
The endoneurium.
Label A, I, Q, & X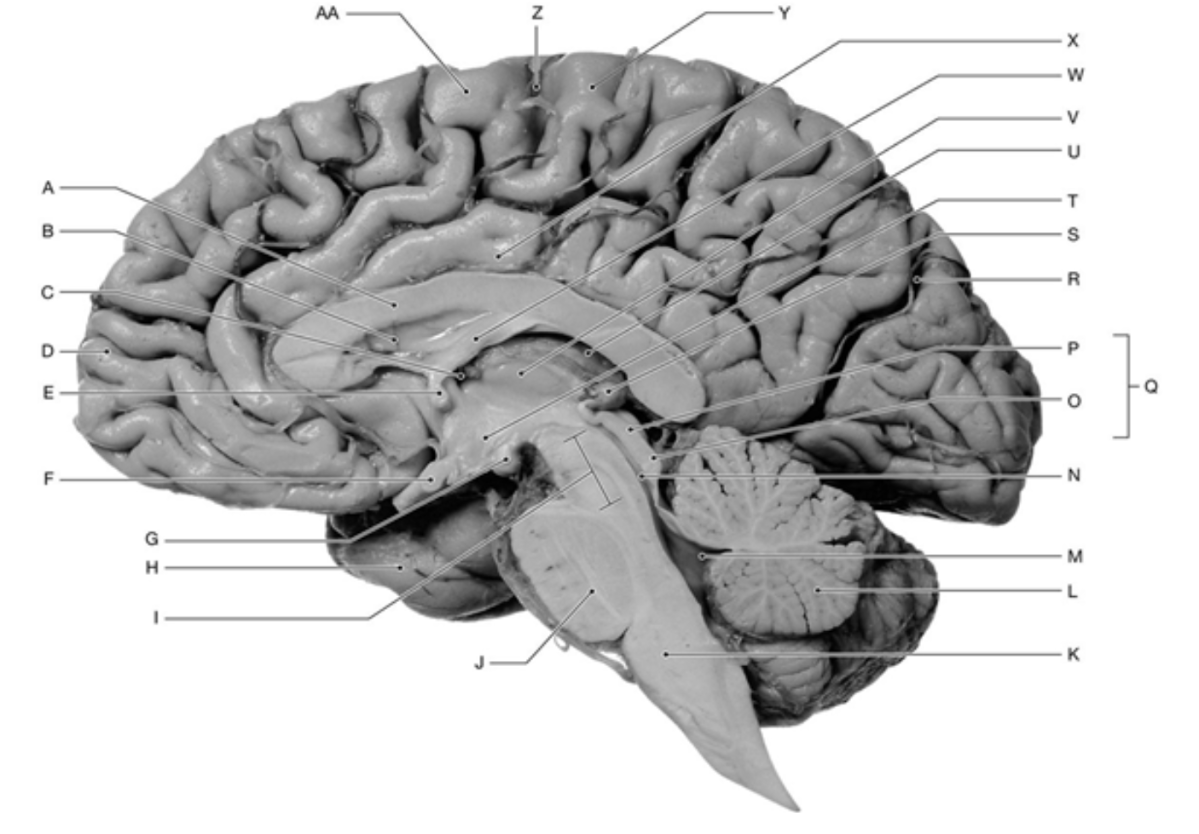
A: Corpus Callosum
I: Mesencephalon
Q: Corpora Quadrigemina
X: Cingulate Gyrus
What is the function of the Autonomic Nervous System (ANS)?
It regulates involuntary functions such as cardiac muscle, smooth muscle, and glandular activity.
What is an action potential?
It is a nerve impulse generated by the exchange of ions across a neuron's membrane.
What is a visceral (autonomic) reflex?
A polysynaptic reflex that controls actions of smooth and cardiac muscles and glands.
What is the function of microglial cells?
They perform phagocytosis of pathogens and cellular debris in the CNS.
What is the function of the reticular formation?
It maintains consciousness and alertness.
What is the fovea centralis?
A small depression in the retina with the highest visual acuity.
Label K, L, M, & N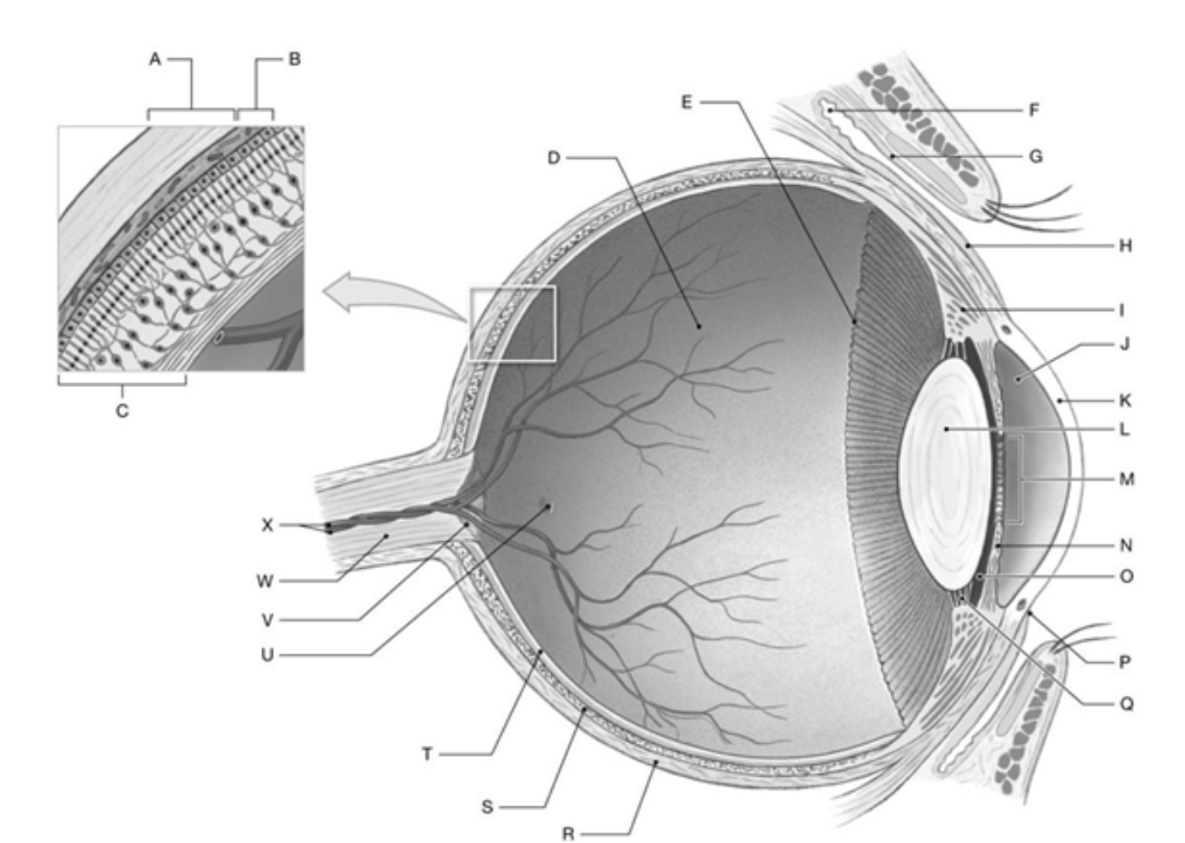
K: Cornea
L: Lens
M: Pupil
N: Iris
What are somatic receptors responsible for monitoring?
Skeletal muscle activity and external environmental stimuli such as touch, pain, pressure, and temperature.
Which ion exchange primarily generates action potentials?
The movement of sodium (Na⁺) and potassium (K⁺) ions across the neuron's membrane.
What is an acquired reflex?
A learned motor response, such as walking.
What are the three meninges that protect the brain and spinal cord?
Dura mater, arachnoid mater, and pia mater.
Where is the speech center located?
The frontal lobe.
What are rami communicantes?
Nerve branches that facilitate communication between spinal nerves and autonomic ganglia.
Label K, O, T, & W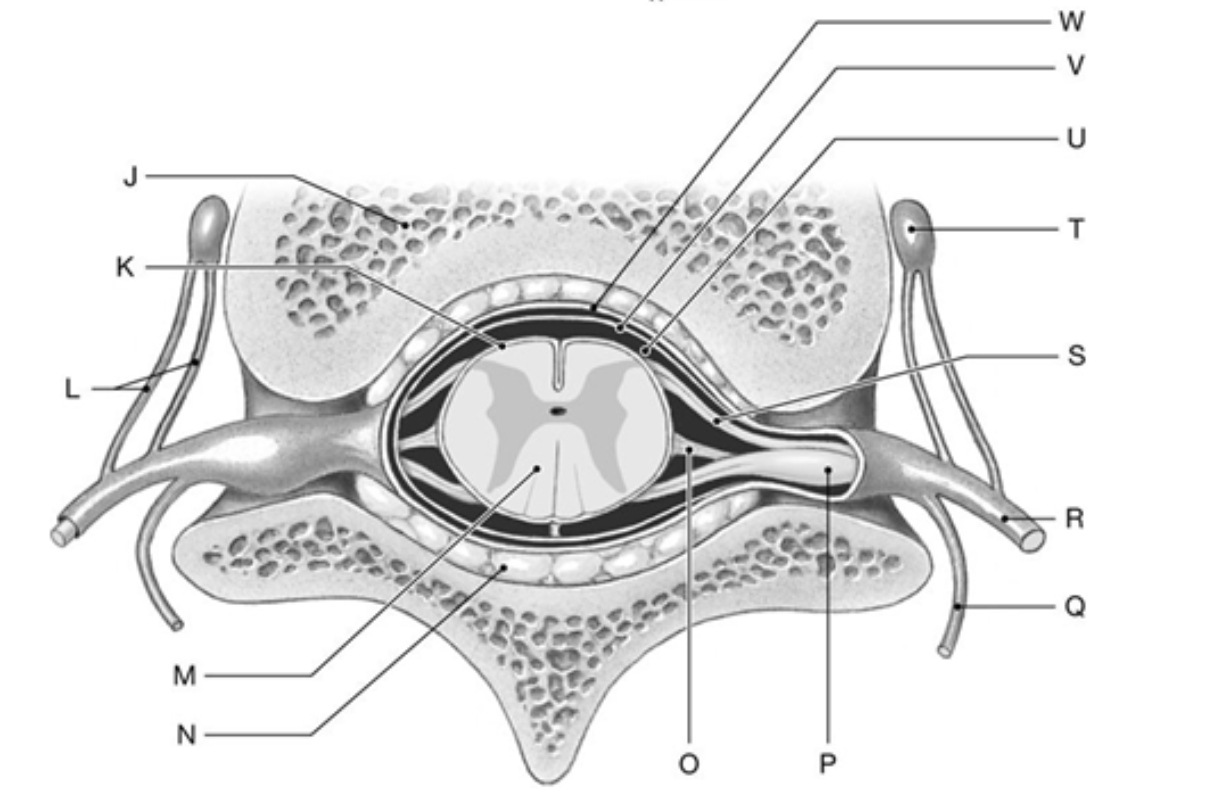
K: Pia Mater
O: Denticulate Ligament
T: Autonomic (Sympathetic) Ganglion
W: Dura Mater
What is the function of visceral receptors?
They monitor internal structures such as smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and glands.
What is excitability in neurons?
The ability of neurons to respond to a stimulus and convert it into a nerve impulse.
What pathway carries proprioceptive information to the cerebellum?
The spinocerebellar tract.
What is the Blood-Brain Barrier (BBB)?
A selective barrier that isolates CNS neural tissue from the general circulation.
What structure allows communication between the cerebral hemispheres?
The corpus callosum.
What is referred pain?
Pain perceived at a location different from the site of the stimulus, such as arm pain during a heart attack.
Label A, B, D, M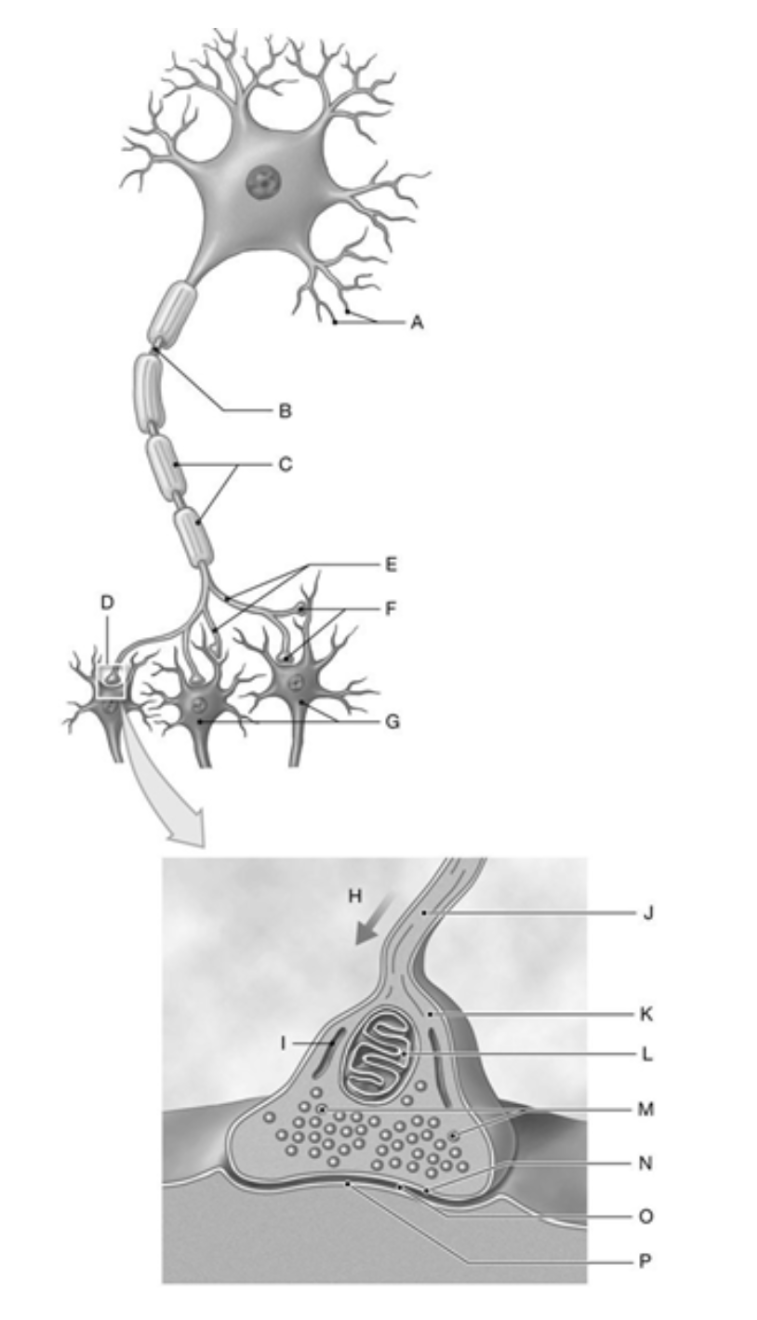
A: Dendrites
B: Axon
D: SYnapse
M: Synaptic Vesicles
What are preganglionic and postganglionic neurons?
Preganglionic - First Neuron in ANS; nerve fibers connects to the CNS to ganglia
Postganglionic - Second Neuron in ANS; fibers from ganglion to the effector
What is the most common neurotransmitter in the nervous system?
Acetylcholine (ACh).
What tract sends motor commands from the cerebral cortex to the spinal cord?
The corticospinal tract.
Which glial cell helps maintain the blood-brain barrier?
Astrocytes.
What lobe is responsible for visual processing?
The occipital lobe.
What organ secretes epinephrine and norepinephrine during sympathetic activation?
The adrenal medulla.
Label A, H, J, & Q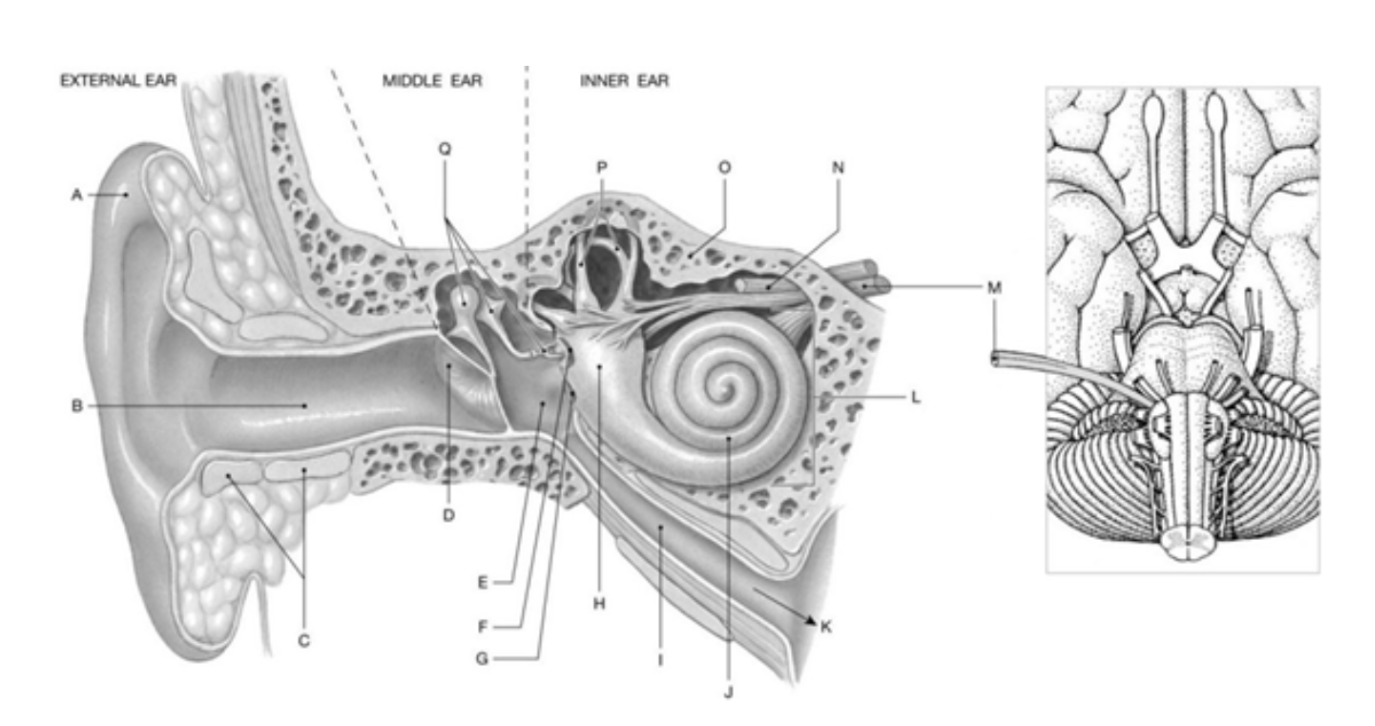
A: Auricle
H: Vestibule
J: Cochlea
Q: Auditory Ossicles