Name this relationship

Parasitic or Exploitation
What is solitary living?
Living alone, defending oneself and providing resources like food, water and shelter for oneself. With the only exception of reproduction.
Identify this response
Thigmonasty
What does endogenous mean?
Internal, controlled by a biological clock
Name THREE navigation cues

Magnetic fields, pilotage, landmarks, sun compass, solar, sonar, sound waves, wind currents, thermal/temperature, star compass, lunar/moon compass
The black walnut releases a toxic chemical into the soil that will kill any other plants nearby.
Describe the relationship between these plants

Antibiosis or Allelopathy or Amensalism, one is unaffected the other is harmed
Why are courtship rituals/displays important?

Shows sexual maturity/ready to mate. Displays characteristics that define whether or not a good mating partner. Isolates species from each other
Name at least TWO of the possible responses for the example below
** they must be responses to TWO different stimuli
Positive phototropism, negative phototropism, positive geotropisms, negative geotropism, positive hydrotropism, negative thermotropism
Name the hormone responsible for sleep

Melatonin
Give TWO benefits of migration
Resources like food, shelter, water, mates, climate
Describe FIVE different interspecific relationships
Mutualism, Ammensalism, Commensalism, Exploitation, Parasitism, Predation, Alleleopathy, Anitbiosis
Explain the importance of agonistic displays
To reduce aggressive behavior that leads to fighting. Fighting can result in injury or death of strong individuals in the group this can mean less defense against predators/invading groups.
If contests can be resolved with ritual display, fighting is not needed.
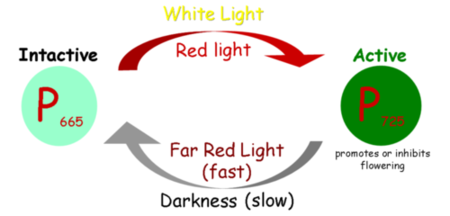
Explain this diagram
Pr is converted to Pfr during the daylight or white light or red light and Pfr is slowly converted to Pr during darkness or far-red light
Using the actogram:
Describe the activity pattern
Identify WHEN the free-running period occurs

Nocturnal, circadian,
endogenousDay 8 - 16
Give THREE risks for migration
Predation along the way, getting lost, no energy,
How do bond pairs increase the chance of survival? Give at least TWO reasons
Two adults to look after offspring
Higher chance of offspring survival
Shared energy invested to look after offspring
Less energy invested to look for mating partner
Territorial - more resources
Why would the lowest member of a social group continue to live in a social hierarchy rather than alone?
Still get some resources, food etc and access to mates. If alone would not be able to fend for self
Why would a plant need one of the following adaptations to be successful:
Wide green leaves
Higher concentrations of chloroplasts in leaf cells
Ability to ‘climb’ other plants to get higher in a forest canopy
Ability to protect leaves from predators?
Greater amount of sunlight in order to go through optimum level of photosynthesis to produce glucose in order to convert into energy to be used for growth, repair and reproduction
Name FOUR biological rhythms and the approximate length of each one
Circatidal – 12.5 hours
Circadian – 24 hours
Circalunar – 28 days
Circaannual – 365 days
Given the high risks involved in migrating – why would the gene for migration continue to survive in a population?

The benefits outweigh the costs/risks
Identify the adaptive advantage of parasitic relationship in the example below:
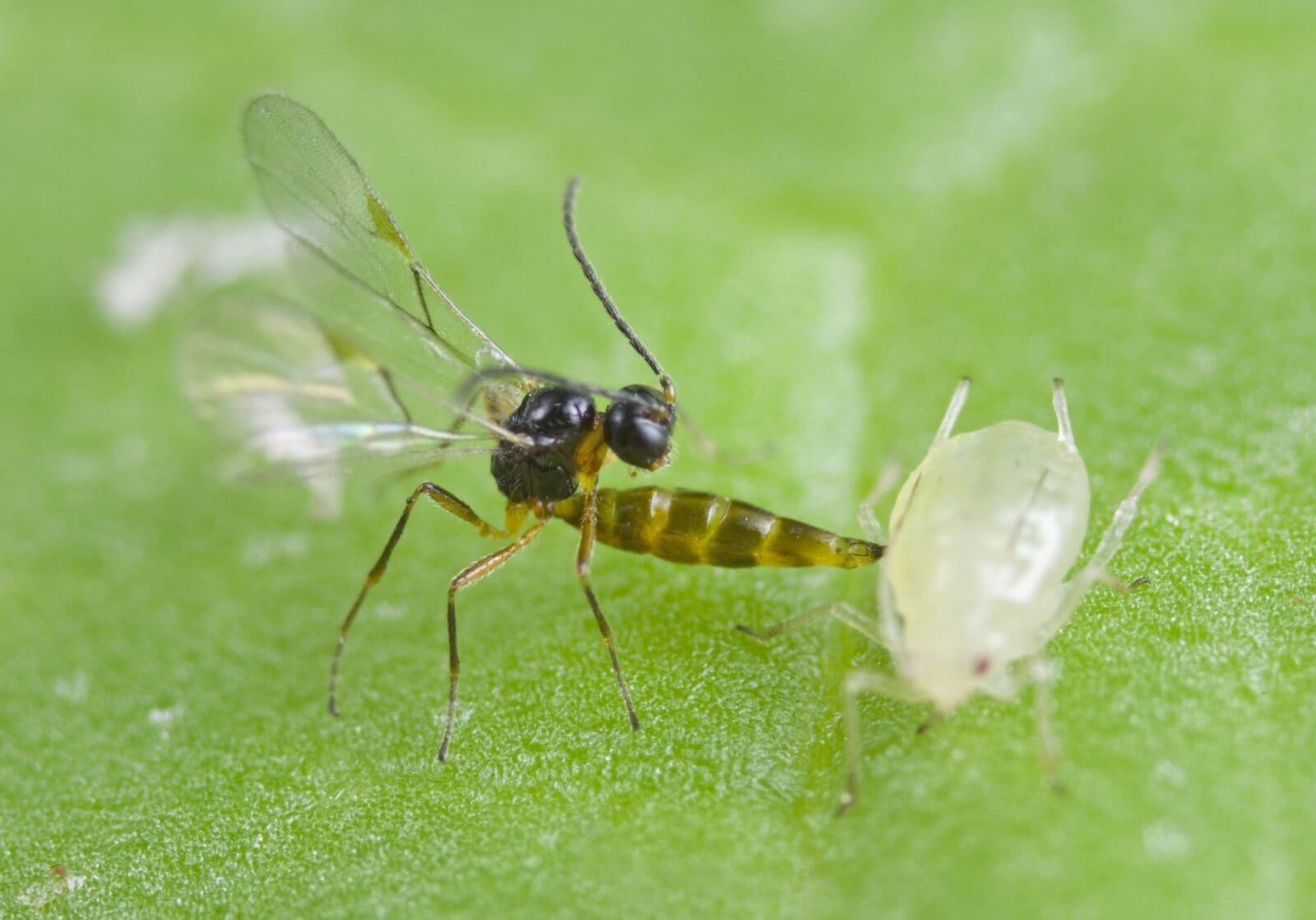

The wasp deposits an egg into the aphid body, the egg grows, hatches and the larvae eats their way out of the aphid, killing the aphid in the process.
The wasp does not use energy to care for or protect young and can instead put energy into produces more eggs to infect more aphids. This passes on the gene for this behavior onto subsequent generations ensuring it’s survival.
Compare solitary life style and co-operative and give at least ONE reason (for each) why BOTH are an advantage /disadvantage
Solitary – no sharing resources, have to defend yourself
Co-operative – sharing resources and caring for each other including defense
How does photoperiodism provide an adaptive advantage to BOTH pollinators and the plant species?
Greater amount of sunlight in order to go through optimum level of photosynthesis to produce glucose in order to convert into energy to be used for growth, repair and reproduction which is used to produce more plants
More food for the pollinators
Describe the adaptive advantage of being nocturnal for a moth

More mating partner, less predators, ecological niche (food, adaptations)
Weigh up TWO benefits and TWO costs of migration, using the example of the humpback whale.
Resources
– summer warmer waters for raising young, more food less predators
- Winter – less predators, more food