When were X-rays discovered? And by who?
November, 8 1895
Wilhelm Roentgen
The 2 most commonly used systems of measurement in radiologic science are the _______ and ___________ or __________.
The 3 parts of the X-ray imaging system
HIGH VOLTAGE GENERATOR
X-RAY TUBE
The 3 primary parts of the high-voltage generator.
HIGH-VOLTAGE TRANSFORMER
FILAMENT TRANSFORMER
RECTIFIERS
Generally radiographic equipment may be classified as __________ or __________.
MOBILE, PERMANENTLY INSTALLED
1. ______ = Anything that occupies space and has mass
2. ______ = quantity of matter as describe by its energy equivalence
3. ______ = mass of object via force exerted on a body due to gravity
1. MATTER
2. MASS
3. WEIGHT
The British System uses the _____ for mass, _____, for length, and _____ for time.
POUND (lb), FOOT (ft), SECOND (s)
Provides for control of kVp, mA, exposure time, and line compensation
OPERATING CONSOLE/CONTROL PANEL
The high-voltage transformer is also known as ____________.
STEP-UP TRANSFORMER
Permanently installed type radiographic equipment can be divided into these 6 parts.
TUBE
COLLIMATOR
CONTROL CONSOLE
TABLE
TUBE STAND
WALL UNIT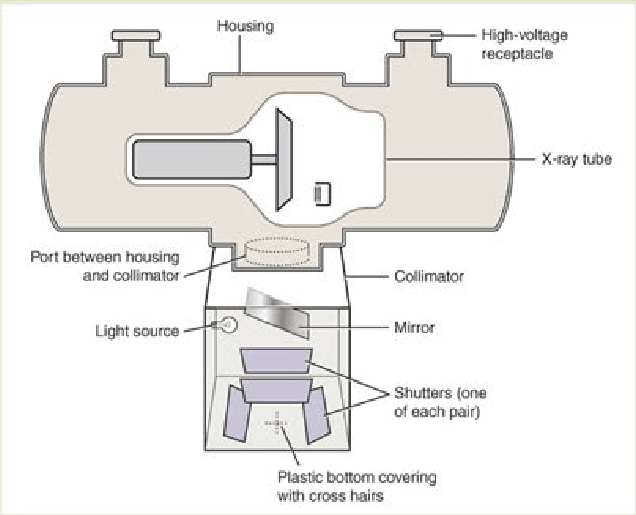
1. ______ = ability to do work
2. ______ = transfer of energy
ENERGY
RADIATION
The SI uses ______ for mass, ______ for length, and ______ for time.
KILOGRAM (kg), METER (m), SECOND (s)
The two most important photographic image qualities.
DENSITY, CONTRAST
The process of converting AC to DC. Ensures that e- flow from cathode -> anode only.
VOLTAGE RECTIFICATION
The tube head assembly consists of these 3 parts.
X-RAY TUBE
COLLIMATOR
TUBE STAND
Name the 2 types of ionizing radiation. Provide examples.
NATURAL/ENVIRONMENTAL RADIATION:
Cosmic rays, terrestrial radiation, radon (largest)
HUMAN-MADE RADIATION:
- Diagnostic x-rays
2. SI equivalent = _______
1. CURIE (Ci)
2. BECQUEREL (Bq)
1. Adjustment of ____ determines the quality of the x-ray beam.
2. _______ is also known as the electrostatic charge (C).
1. kVp
2. mA
Rectifiers are located in the _________ section.
HIGH-VOLTAGE
The external structure of the x-ray tube consists of these 3 parts.
SUPPORTIVE STRUCTURE
PROTECTIVE HOUSING
GLASS/METAL ENCLOSURE
X-rays are (⬆️/⬇️) penetrating, invisible rays that are a form of __________ radiation.
⬆️, ELECTROMAGNETIC
Accredits radiologic science educational programs
JRCERT
The 4 technical factors.
mA: quantity, instensity, amount
TIME: seconds (mAs)
kVp: quality, penetration, wavelength
DISTANCE: inverse sq law
FALSE, CUT IN HALF
The 3 basic configurations of the tube stand.
FLOOR MOUNT
FLOOR/CEILING (FLOOR/WALL) MOUNT
OVERHEAD TUBE ASSEMBLY
T/F: X-rays travel in circular waves.
FALSE, X-rays travel in straight lines.
1. The _______ is used to quantify radiation intensity.
2. The SI equivalent is ________.
1. ROENTGEN (R)
2. AIR KERMA (Gya)
The autotransformer has ______ winding and is designed to supply a precise voltage to the _______ circuit and _______ circuit of the x-ray circuit
SINGLE
FILAMENT
HIGH-VOLTAGE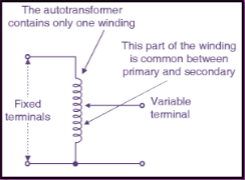
The three types of generators.
SINGLE-PHASE POWER GENERATOR
THREE-PHASE POWER GENERATOR
HIGH-FREQUENCY GENERATOR
1. The ______ is the negative side of the tube. Is made up of 2 primary parts: _________ and ________.
2. The x-ray tube current is adjusted by controlling the _________ current.
1. CATHODE, FILAMENT, FOCUSING CUP
2. FILAMENT
T/F: X-rays travel at the speed of sound in a vacuum.
FALSE, SPEED OF LIGHT
Published the national certification examination for radiographers
ARRT
THERMIONIC EMISSION
 Power fluctuates from zero to maximum potential 120 times each second (under full-wave rectification)
Power fluctuates from zero to maximum potential 120 times each second (under full-wave rectification)
SINGLE-PHASE POWER GENERATOR
1. The _______ is the positive side of the tube. There are 2 types: _________ and ________.
2. General purpose x-ray tubes use _______ anodes b/c they must be capable of producing ⬆️intensity beams in ⬇️time.
1. ANODE, STATIONARY. ROTATING
2. ROTATING
The first x-ray fatality in the US occurred in ______.
1904
1. The _____ is used to quantify occupational exposure or dose equivalent.
2. SI equivalent = _______
1. REM
2. SIEVERT (Sv)
Measures the quantity of radiation that reaches the IR via ionization chambers/cells.
AUTOMATIC EXPOSURE CONTROL (AEC)
 Voltage applied to the x-ray tube is ________
Voltage applied to the x-ray tube is ________
THREE-PHASE POWER GENERATOR
NEARLY CONSTANT
1. The anode electricity and radiates heat/x-rays from the ________.
2. _____% of kinetic energy is converted to ______.
3. The ________ is the actual x-ray source.
2. 99, HEAT
3. FOCAL SPOT
With the introduction of the ______ tube and the ______ transformer, significant injuries to soft tissues ⬇️.
CROOKES tube, SNOOK transformer
Publishes the Radiography Practice Standards
ASRT
1. _______ timers:
Old technology, not common now.
2. _______ timers:
Most exposure timers are ______ and are controlled by a ________.
3. _______ timers:
Used on falling load and capacitor discharge imaging systems.
SYNCHRONOUS
ELECTRONIC, ELECTRONIC, MICROPROCESSOR
mAs
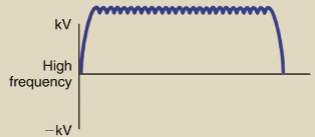 used in almost all station x-ray imaging systems
used in almost all station x-ray imaging systems
FULL-WAVE RECTIFICATION or HIGH-FREQUENCY VOLTAGE GENERATION
ANODE HEEL EFFECT
What are the 3 basic radiation safety techniques?
TIME: ⬆️exp time=⬆️dose, keep fluoro time⬇️
DISTANCE: ⬆️distance=⬇️dose (inverse sq law)
SHIELDING: Use lead for protection
1. The ______ is used to quantify the biological effects of radiation on humans and animals.
2. SI equivalent = _________
1. RAD
2. GRAY (Gyt)
1. ⬆️heat results in (⬆️/⬇️) x-ray tube life.
2. Maximum radiographic techniques should never be applied to a ______ anode.
3. The most frequent case of abrupt tube failure is e- arcing from the _________ to the enclosure b/c of vaporized _________.
1. ⬇️ DECREASED
2. ❄️ COLD
3. FILAMENT, TUNGSTEN