Knee-chest position helps the child with this congenital heart defect
What is Tetralogy of Fallot?
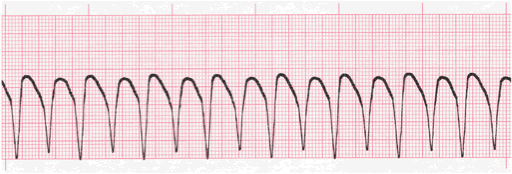
What is ventricular tachycardia (v-tach)?
Type of cardiomyopathy associated with cancer treatment
What is restrictive?
Mitral valve regurgitation leads to backflow into this heart chamber
What is left atrium?
These meds are an important first-line treatment in infective endocarditis
What are antibiotics?
This type of congenital heart defect carries a very poor prognosis
This class of medication can interact with nitroglycerin and cause irreversible hypotension
What are phosphodiesterase inhibitors (AKA ED meds)?
This type of cardiomyopathy has a strong genetic factor and is found in young athletic males
What is hypertrophic?
Pulmonary stenosis leads to higher pressure in this heart chamber
What is right ventricle?
Mitral regurgitation is associated with this type of murmur
What is a systolic murmur?
Infants are given this therapy to keep the ductus arteriosus open
What is IV prostaglandin?
Aspirin is given to patients suspected of MI. This is why.
What is aspirin is a platelet aggregate inhibitor?
(Note: ask yourself What does that mean?)
Type of cardiomyopathy that could have a high BNP
What is dilated?
This valvular disorder leads to decreased outflow to the body
What is Aortic stenosis?
S4 heart sound is associated with this valvular problem
What is aortic valve stenosis?
Typical physical examination findings include strong pulses and hypertension in the upper extremities, diminished or delayed femoral pulses, and a blood pressure (BP) gradient, with low or unobtainable arterial BP in the lower extremities.
What is coarctation of the aorta?
One possible treatment for a patient with a STEMI is PCI. This is how long after arrival at ED that the procedure must be done.
What is 90 min (door to balloon time)?
This type of cardiac infection is sometimes caused by a virus
What is myocarditis?
Problems with this valve causes blood to back up into the pulmonary bed and can lead to pulmonary hypertension
What is mitral valve?
The one that does not belong.
Pulmonic Stenosis
Overriding aorta
Ventricular septal defect
Patent ductus venosus
What is Patent ductus venosus?
(The other 3 are parts of TOF. What's the 4th?)
Typical oral dose of this inotropic med for peds from 1 month to 2 years is 10 to 15 mcg/kg
What is digoxin?
The label that corresponds to where the electrical impulse starts, AKA the pacemaker of the heart

What is SA node?
Inadequate treatment of strep infections can lead to this condition
What is rheumatic heart disease?
Valvular problems with these 2 valves may lead to atrial fibrillation
What are the mitral and tricuspid valves (AV valves)?
Often prescribed to patients with prosthetic heart valve. Teaching includes to be cognizant of green leafy vegetable consumption
What is warfarin?