(antimicrobial treatment)
EPA stands for _____________________.

Environmental Protection Agency

What does PROPHYLAXIS mean?

Prevention of a disease
Sum of ALL microbes in & on humans. These COLONIZE our bodies, not causing disease.
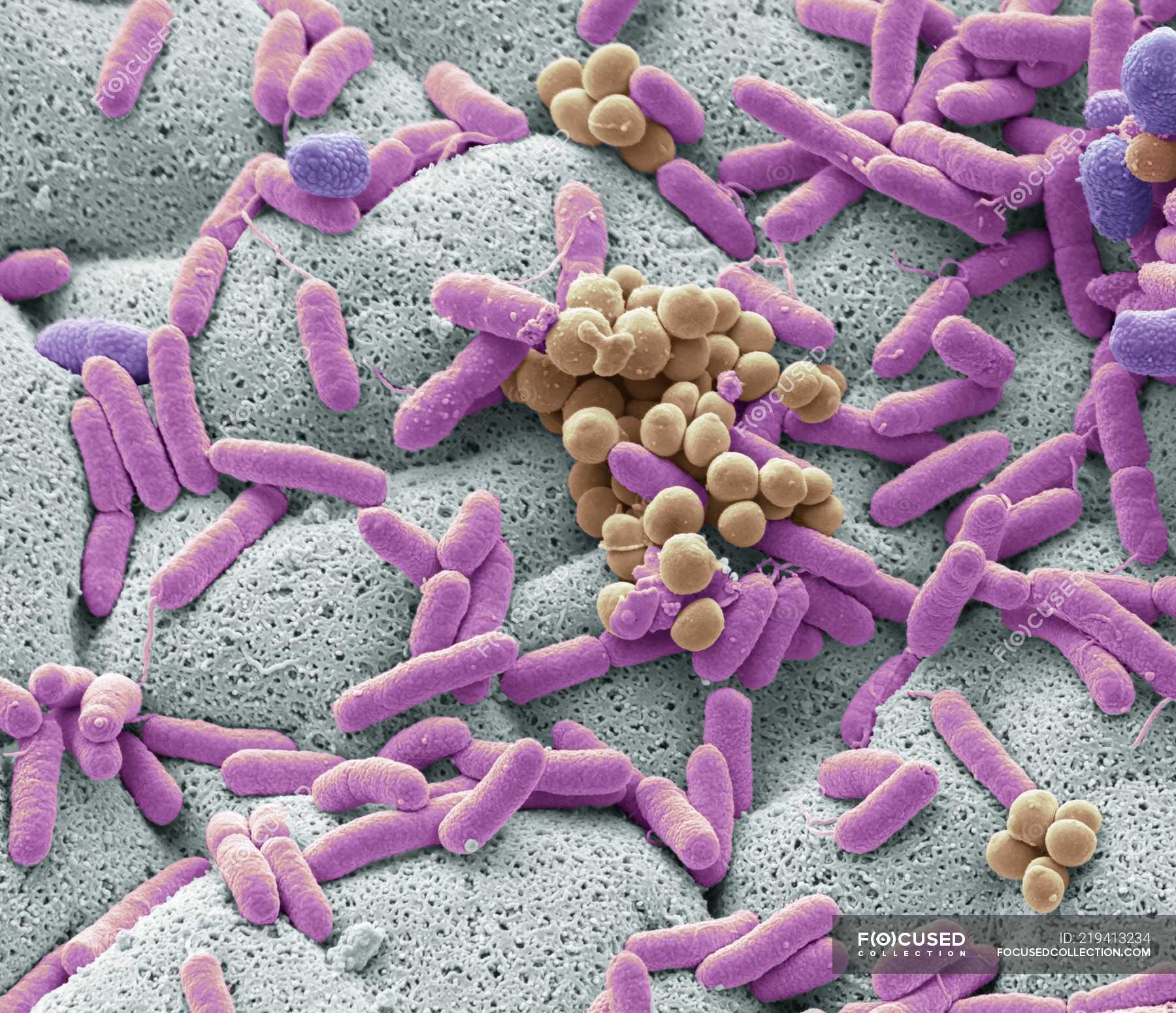
Human Microbiome (normal biota)
How many lines of defenses (against microbes) do we have?
Three
1st line of defense
2nd line of defense
3rd line of defense
What does the term "ubiquitous" mean?
Literally everywhere
(in microbiology: microbes are ubiquitous)
What is the dormant state of a bacteria called?
The bacteria is extremely resistant to chemical, mechanical and physical control methods when in that state.
Bacterial endospore
An antimicrobial medication that KILLS fungi:
fungicidal drug
or simply: fungicide
-cidal or -cide = destroys/kills
What is a disease-causing microbe called?
(Most microbes are NOT disease-causing, most are beneficial to humans)
Pathogen
Which line of host defense is SPECIFIC (against a very specific microbe)?
The third line of defense is SPECIFIC

Which microbes do NOT consist of cells?
viruses and prions
Process of complete destruction of ALL microbes, including all forms, such as bacterial endospores on inanimate (non-living) objects.
Sterilization:
Antimicrobial medication that stops reproduction of bacteria is called:

bacteriostatic drug
-static
What causes infections and infectious diseases?
(This is the ONLY means of what causes infections, NOTHING else does)
Microbes
(bacteria, viruses, microscopic fungi, protozoa, prions)
(helminths [parasitic worms] cause infectious-like diseases and are therefore included in a microbiology class)
What is "achieved" by the third line of defense?
Immunity
What is the cell of some microbes called that is simpler, does not have organelles (except a few ribosomes) and has their nucleic acid loosely swimming in the cells (not surrounded by a membrane)? This cell type also has a cell wall in addition to the cell membrane.
Prokaryotic cell
The use of physical or chemical methods/processes to destroy VEGETATIVE states of pathogens. Can not destroy bacterial endospores and prions
- Can remove toxins
- Generally, NOT USED on living tissue. Used on non-living objects and surfaces.

Disinfection
Antimicrobials that are effective against a wide variety of microbial types are called ______________. (these can treat infections caused by different microbes)
Broad-spectrum drugs
______________ ___________awaits an opportunity to cause disease. They do NOT cause disease under normal circumstances but do so when the opportunity arises.
(example E. coli in the intestines)
Opportunistic pathogen
Which line of defense includes physical barriers such as the skin and mucous membranes, but also includes out microbiota?
1st line of defense
(non-specific, trying to protect us against ALL microbes, not only against one specific one)
Which microbes consist of prokaryotic cells?
BACTERIA
(both, eubacteria and archaebacteria)
- Eubacteria: bacteria as we know
- Archaebacteria: ancient bacteria, first organisms on earth, extremophiles
The use of chemical agents directly on exposed body surfaces. It destroys or inhibits the growths of vegetative microbes.
- Removal of microbes on skin (scrubbing)
Antisepsis
What do narrow-spectrum drugs/medication do?
They can only treat a limited spectrum of microbial infections (caused by more specific microbes).
Which of the following is/are common portal-of-entry/ies:
- Mucous membranes
- Skin
- Respiratory system
- Gastrointestinal system
- Urinary system
- Urogenital tract
Everyone is a common portal-of-entry
Which 2 cell types play the major part in our immunity?
B lymphocytes (B-cells) and T lymphocytes (T-cells)
What is a helminth?
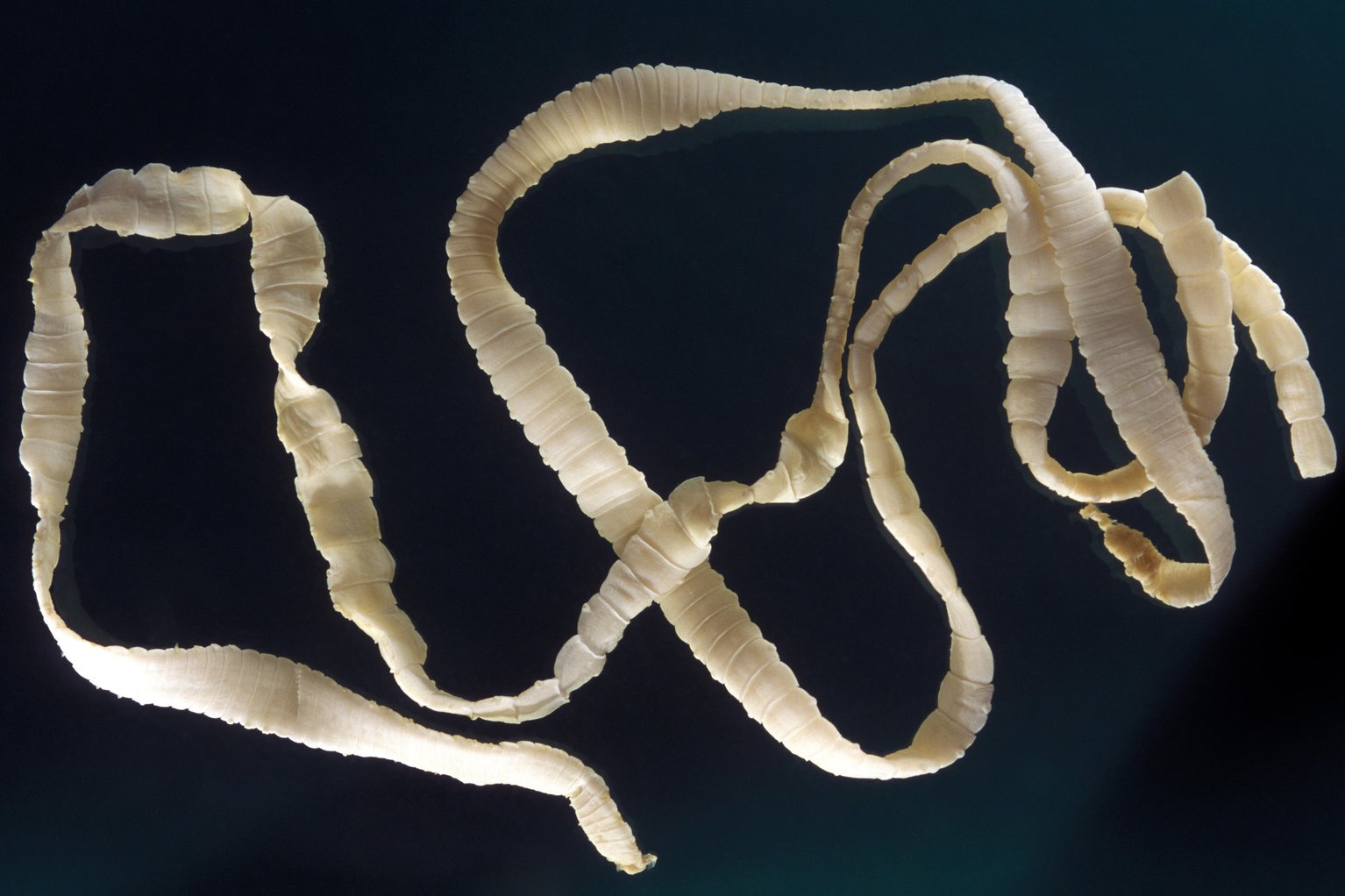
Parasitic worm (example: tape worm)
- macroscopic
- causes infectious-like illnesses
- goes through some microscopic life stages in its life cycle (egg, larva)

