What is the definition of initial position?
The starting place of an object, before it moves.
How do you find the average of a data set?
Add the values together, then divide by the number of values.
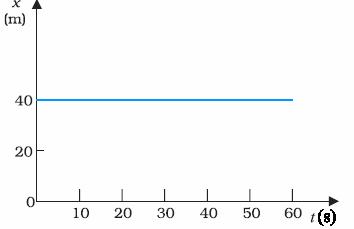
The object is stationary at 40m for 60 seconds.
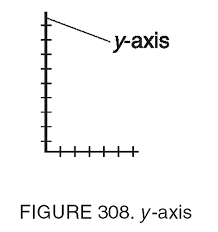
Draw an x & y axis. Label the y-axis.
What is Ms. Rapciak's favorite sport to play?
Volleyball!
What is the definition for speed?
*if you did not mention position and time, give yourself 100 points*
How many trials should you conduct if you want to have reliable data?
At least three trials. The more trials you conduct, the closer your average value is to the "true" value.
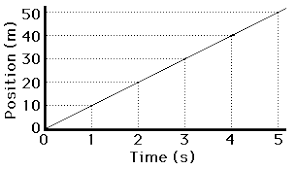
Starting at 0m, the object travels at a velocity of 10 m/s for 5 seconds.
Make a position-time graph that displays an object moving at a constant, positive velocity.
*The initial position could have been anywhere on the y-axis*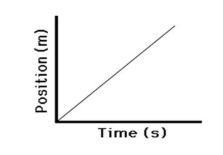
How many times per year does the Empire State Building get struck by lightning?
23 times per year
(you can get points for answering 20 - 25)
What is the difference between speed and velocity?
Velocity involves the direction an object travels in.
Velocity can be negative, speed cannot.
A group of students measured two quantities: time and position. What are the ranges of the data? (two answers)
Time (s) Position (cm)
0 0
5 25
10 50
15 75
Range of time values: 0 - 15s
Range of position values: 0 - 75cm
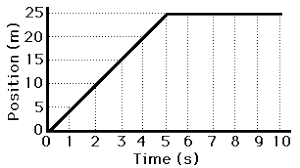
Starting at 0m, the object travels at a constant velocity of 5 m/s for 5 seconds, then stays stationary for 5 more seconds. Its final position is 25m.
What are the steps of making a position-time graph by hand?
(hint: we wrote these down in our notebooks during class)
1. Draw your x & y axes (leave space for labels!)
2. Label your axes (don't forget units!)
3. Determine the ranges of your data, then determine the scales of your axes (this is the hard part)
4. Plot your data points
5. Draw a line to connect the points
What year did the National Weather Service start naming hurricanes and tropical storms?
1953
(points for 1950 - 1955)
What is the definition of reliable data?
Data that is collected with at least three trials, and has consistent data points (small range).
Evaluate the reliability of this speed tube data. What would be your recommendation for this group?
Time (s) Position (cm)
Trial 1 Trial 2 Trial 3
2 10 15 11
4 18 25 19
6 27 32 27
8 35 38 35.5
Trials 1 & 3 are consistent with one another.
Trial 2 is inconsistent with the other trials.
I would repeat the experiment one more time and see how Trial 4 compares with the other data.
Which object traveled the farthest?
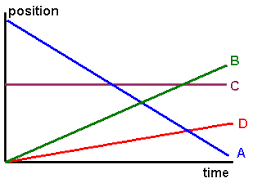
Object A.
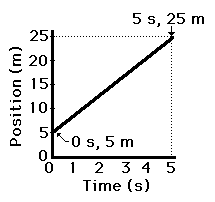
The object has an initial position of 5m. It travels at a constant velocity of 4 m/s for five seconds.
What is the fastest speed for information to travel between neurons in the human brain?
250 mph!
What is a practical test?
A supervised test that involves the application of skills. In other words, a test that is "hands-on".
After we gather data in science, we can analyze the data in order to form ____________ and we can evaluate the data's ______________.
*note: this information will not be on the assessments for this unit. just an interesting prompt to think about.*
After we gather data in science, we can analyze the data in order to form conclusions and we can evaluate the data's reliability.
Calculate the velocity of each object. (The pink line has an initial position of 30cm.)

Green: -10 cm/s
Pink: 3 cm/s
Red: 0 cm/s
Object 1 & Object 2 have the same initial position (5m). They both move at a constant, negative velocity for 5 seconds.
Object 1's speed is half as large as Object 2's speed.
(see the whiteboard)
What is the only letter in the English alphabet that does not appear in the Periodic Table of the Elements?
J