The smallest functional unit of the nervous system is _________.
Neuron
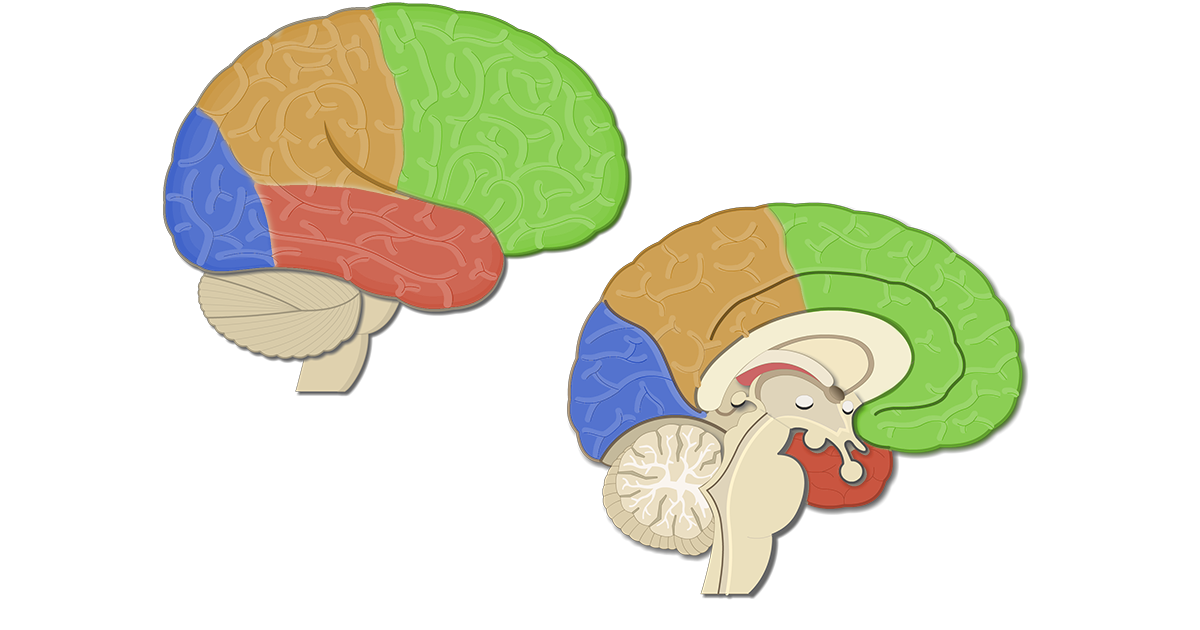
Broca's area is located in which lobe?
Frontal Lobe
What 3 structures make up the "Brain Stem?"
Pons, Medulla, and Midbrain
Cranial Nerve number "X" is also known as the "wanderer."
Vagus
Damage to the motor pathway to the tongue, can cause the tongue to deviate contralateral or ipsilateral to the site of lesion?
Ipsilateral
The "heart" of the neuron.
Soma

Wernicke's area is located in which lobe?
Temporal Lobe
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/article/en/basal-ganglia/afEchN2h98xOovuuvR5GBA_Basal_ganglia.png)
The caudate nucleus, the putamen, and the globus pallidus are the three structures of the _____________.
Basal Ganglia
Name the 7 CNs that can impact communication and swallowing.
V, VII, VIII, IX, X, XI, XII
Damage to this CN can cause decreased or limited motor control of the tongue.
VII or Hypoglossal
The cells that are considered the "glue" of the nervous system.
Glial Cells
Outfoldings of the cerebral cortex are ____________ and infoldings are ___________.
Gyri/Gyrus and Sulci/Sulcus
Name two things that the hippocampus is responsible for.
Memory function, Emotion, Attention, Navigating through Space (Proprioceptic Information)
This pathway consists of stimuli received from the VIII CN, to the cochlear nucleus, the superior olive, inferior colliculus, medial geniculate, and then received at the perspective center.
Auditory Pathway
Loss of coordination of motor movement, inability to judge distance, inability to preform rapid motor movements, intentional movement tremors, hypotonia, and slurred speech (ataxic dysarthria) are all symptoms pointing to a site of lesion in the _____________.
Cerebellum
This part of the neuron is a branch like structure that receives information.
Dendrite
The precentral gyrus is responsible for VOLUNTARY activations of muscles in the body which is represented by an image also known as the "little body or little human." This image is called_________.
Homunculus
The diencephalon consists of 4 structures, and is considered the final relay of SENSORY information directed towards the cerebral cortex. Name the 4 structures of the diencephalon.
Thalamus, Epithalamas, Hypothalamas, and the Subthalamas
The Carotid Artery supply branches off into ________ and _________.
Internal Carotid Artery and External Carotid Artery
Lesions to the __________ can cause "uncontrollable movement disorders" like: Hyperkinesia, Huntington's Disease, and Parkinson's Disease.
Basal Ganglia
In this process, the neuron is at rest, then stimulated, depolarization occurs, then repolarization, then the neuron returns to rest.
Action Potential
Important for nutrient delivery, and waste removal, the ventricles produce/contain what type of fluid for the cerebral cortex?
Cerebrospinal Fluid
The __________________ is the last stop of auditory information before being sent to the cerebral cortex. This is where all auditory fibers terminate and is part of the auditory pathway.
Medial Geniculate Body
The Anterior Cerebral Artery (ACA), Posterior Cerebral (and Communicating) Artery (PCA), and the Middle Cerebral Artery (MCA) create what is known as __________.
Circle of Willis
Damage to which branch of the Internal Carotid Artery supply will have the most impact on speech and communication?
Middle Cerebral Artery (MCA)