Tapping and Icing to get motor responce
What is the Reflexive Theory?
Resistance to movement on both sides of the joint.
Rigidity
This is an objective method of measuring progress for seated balance when someone cannot sit unsupported.
What is time?
This is an EB intervention you could use early on after stroke to increase repetitions of reaching.
What is UE robotics?
This system is important for knowing where your joint is in space.
What is the sensory system?
Pusher Syndrome is considered a mismatch between these two systems.
What are the visual and postural vertical systems?
If a patient draws this from memory. This is what type of neglect?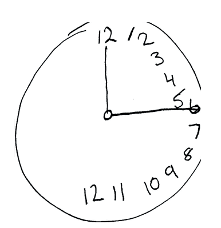
What is representational neglect?
What is inferior?
Motivation is Key to learning
What is the Optimal Theory of Motor learningl?
This modality can be added to agonist or antagonist to decrease spasticity.
What is Estim?
According to the evidence for ataxia this intervention could make error greater when removed?
What is using distal weights?
This is the requirement for patients when using CIMT or mCIMT.
What is active wrist and finger extension?
What is an Ankle Reaction?
Someone who has pusher syndrome often pushes toward this side.
What is toward the weak side?
This picture identifies what type of neglect?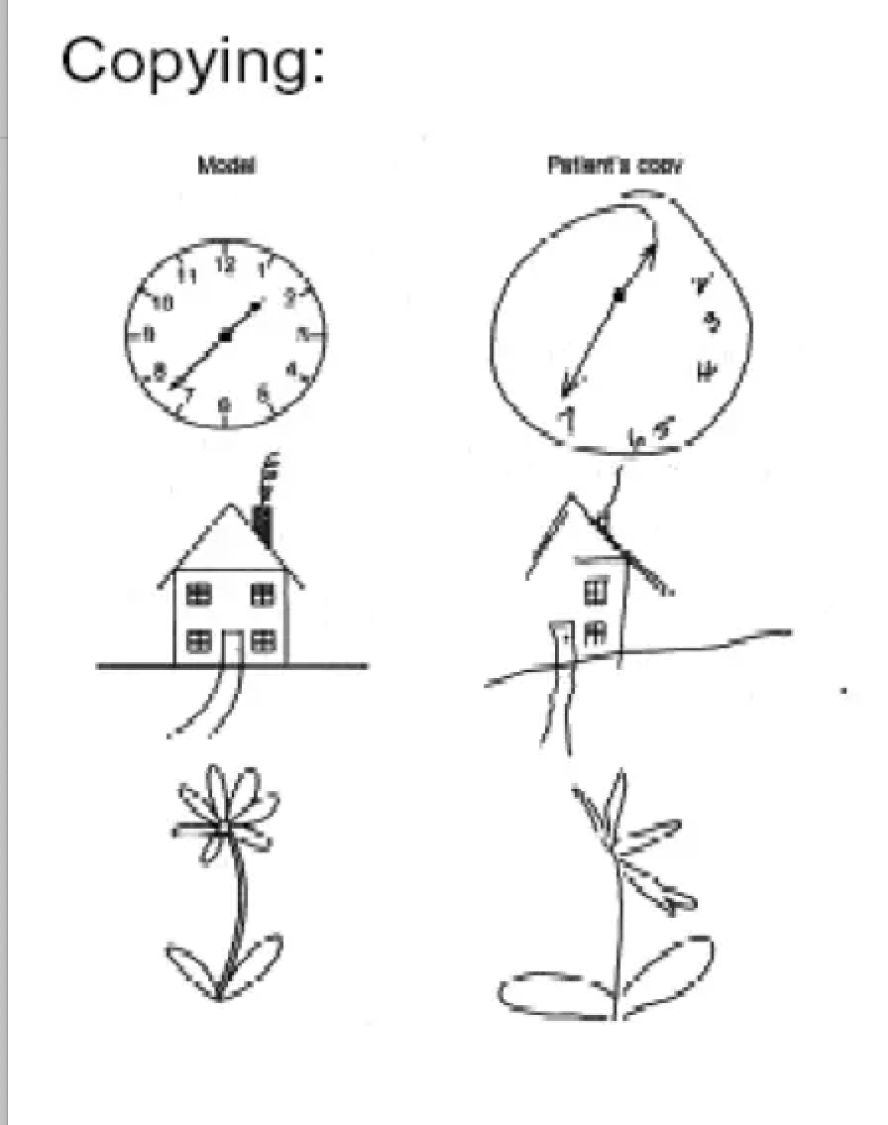
What is visual neglect?
This can be used early after stroke to support the shoulder and prevent subluxation.
What is shoulder strapping?
What is Roods?
This medication is best for focal spasticity.
What is Botox?
According to the TWIST algorithm this is the cut off for the trunk control test to predict walking at 6 weeks.
What is greater or equal to 40?
According to the PREP algorithm, this SAFE score at 72 hours indicates a complete recovery.
What is 8?
This is an automatic reaction to help a person maintain balance when their center of mass is displaced.
What is an equilibrium reaction?
This scale that is most sensitive to change in pushing behavior.
What is the Burke Lateralpulsion Scale?
This is a scale that looks at both pen and paper testing and behavioral testing for neglect.
What is the Behavior Inattention Test (BIT)?
This is a muscle that is commonly spastic that can contribute to trunk lateral bending and shoulder IR, ADD spastic pattern.
What is the latissimus dorsi?
Allowing Compensatory Strategies early is what Neuroplasitic Principle?
What is Interference?
This is a secondary consequence associated with Spasticity.
What is contracture?
Which is missing for stability techniques: Place and Hold, Rhythmic stabilization and ...
What is alternating isometrics?
According to Chedoke McMasters, this is the cut-off score to focus therapy on compensatory strategies.
What is <4?
These 3 types of training can improve functional ambulation.
What is balance exercises with strength and resistance training, standing practice, or balance exercises with biofeedback?
This is the first step when treating someone with pushing syndrome.
What is overleaning them to the strong side to diminish the push.
These are the two interventions that are most supported AND feasible in the clinic for neglect.
What are sensory stimulation and visual scanning?
This is an exercise that should NOT BE done in rehab with stroke patients with shoulder pain.
What are pulleys?
What is Autonomous Stage?
Of the two ataxia scales, this is the most efficient one.
What is the Sara Scale for Ataxia?
According to the literature, these are the 5 R's necessary for effective task-specific training of the upper limb.
A patient has the following deficits in the left LE:
Strength grossly 2/5
Sensation intact
BERG balance 25
Normal Vestibular exam
ROM Normal
What would be the best intervention to improve this patient's balance?
What is strength training?
This is the first step in treatment when treating someone with backwards disequilibrium.
What is standing with their heels and back against the wall.
When testing sensation in a stroke patient this is the first test to perform to determine if more testing is necessary.
What is sharp/dull discrimination?
This is the most common cause of shoulder PAIN.
What is impingement.