Which acid base imbalance will hyperventilation cause?
Respiratory alkalosis
What is a normal WBC count and what is a patient with leukemia at risk for?
WBCs = 4500 to 11,000/mm3
Leukemia pts have a HIGH WBC count but these WBCs are immature & do not work so they are at an increased risk of INFECTION
What are the 3 layers of the heart?
Endocardium = inner layer
Myocardium = middle layer
Epicardium = outer layer
Pericardium = sac around heart
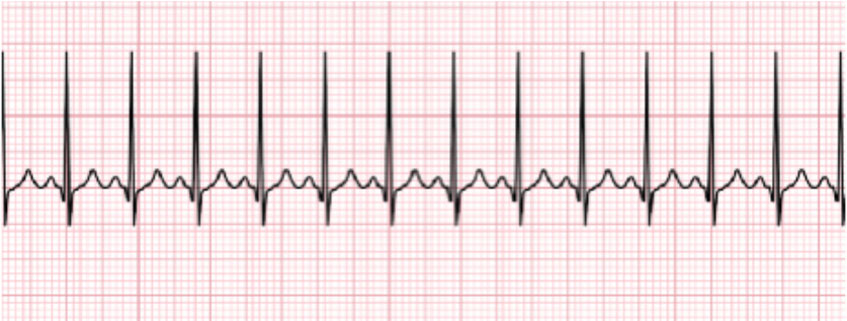
SINUS TACH
Treat underlying cause
What is the treatment for a patient with polycythemia vera?
Phelbotomy, fluids, aspirin
What will the vital signs be if the patient is in fluid volume deficit?
Low BP, High HR, high RR
What is the normal lab value for platelets?
150,000 to 400,000
What are some causes of endocarditis?
"DRUMS"
Dental work
Resistance to antibiotics
Untreated strep throat (rheumatic fever)
Major heart surgery
Stabbing self with dirty needles
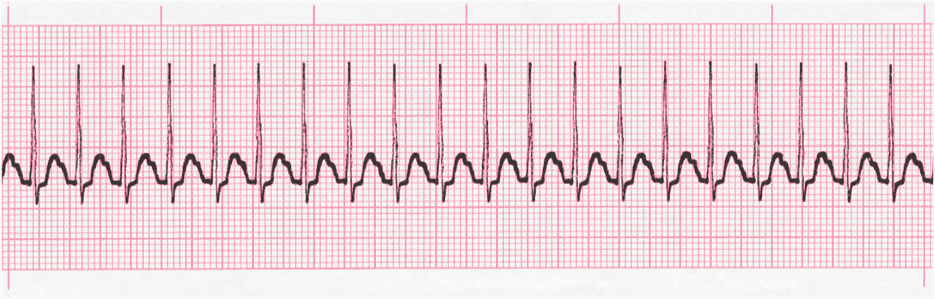
SVT
Vagal & Give Adenosine (med will stop heart for a second)
If your patient has hemophilia, they are at an increased risk for ________
Bleeding
List normal values for pH, PaCO2, HCO3
pH 7.35-7.45
PaCO2 35-45
HCO3 22-26
What electrolyte imbalance is someone with multiple myeloma at risk for?
HYPERcalcemia due to bones breaking down
What is the main difference between left & right sided heart failure?
LEFT = fluid in LUNGS
RIGHT = fluid in BODY
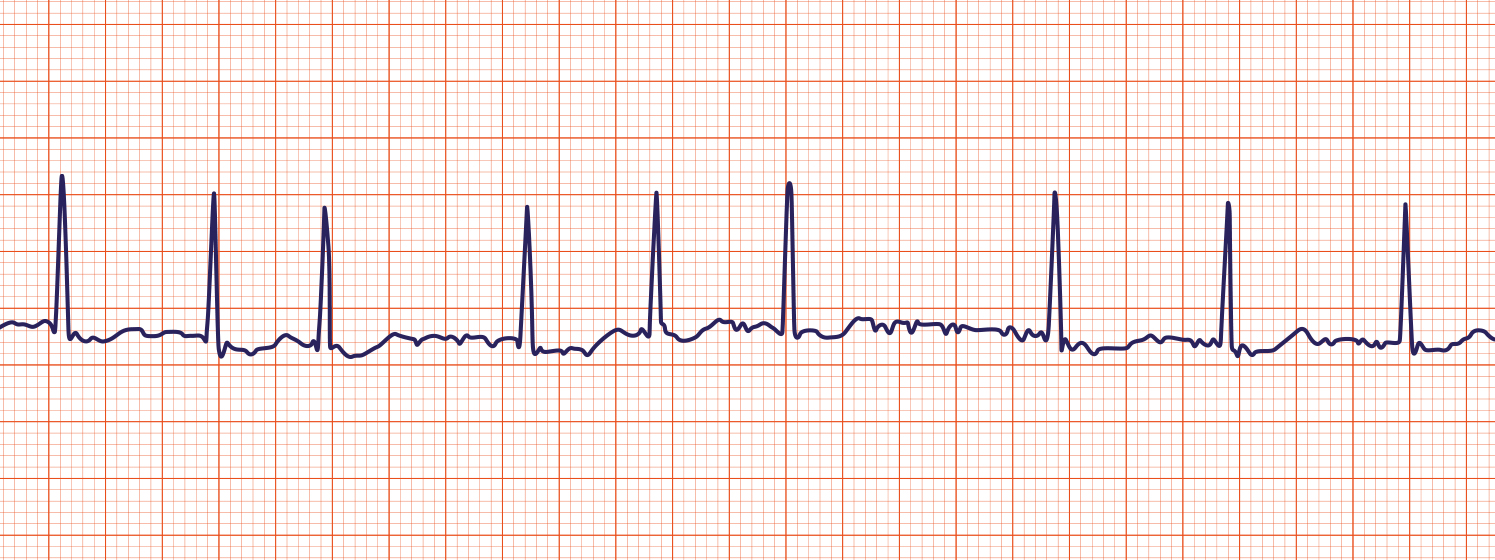
A-FIB
Give beta blocker & blood thinner. If unstable, may need to cardiovert
Interpret the ABG:
pH 7.66
PaCO2 28
HCO3 30
Respiratory Alkalosis, partially compensated
Which electrolytes will show a positive chvosteks & trousseaus sign?
HYPOmagnesemia
HYPOcalcemia
What is the inpatient treatment for sickle cell crisis? (List three)
"HOP"
hydration, oxygen, pain control
What is the treatment for an MI?
"MONA"
morphine, oxygen, nitro, aspirin
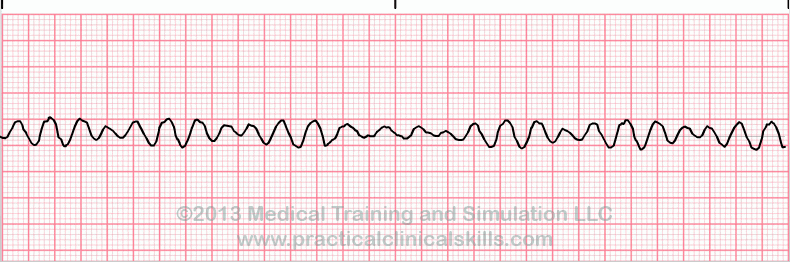
V-FIB
CPR & SHOC, Follow ACLS
(V-FIB = DEFIB)
What acid-base imbalance will a patient have who is having severe diarrhea?
Metabolic acidosis (remember "ass"idosis)
What acid base imbalance will a patient develop with severe vomiting?
Metabolic alkalosis
Less RBC means less hemoglobin to carry oxygen to the body
What should you monitor before giving digoxin?
HR over 60 bmp (listen to apical pulse for 1 min)
Potassium level

V-TACH
If pulse- Vagal, give cardiac meds, may cardiovert
If no pulse- CPR & SHOCK. Follow ACLS
What should you teach your patient to avoid taking iron tablets with? (this will decrease absorption)
Milk (should take with something acidic like orange juice)