Which solution has the highest freezing point: 0.1 m NaCl, 0.1 M CaCl₂, or 0.1 M glucose?
NaCl
For an exothermic reaction, how does increasing the temperature affect the equilibrium?
Their concentrations don’t change during the reaction; they are considered constant.
100: What is the sign of ΔS when a solid dissolves in water?
Positive — increased disorder.
What plot gives a straight line for a first-order reaction?
ln[A] vs. time
Explain why an exothermic reaction can be non-spontaneous.
If ΔS is very negative and T is high, ΔG can still be positive.

What is osmotic pressure, and how does it relate to colligative properties?
Osmotic pressure is the pressure needed to stop solvent flow through a semipermeable membrane. It increases with the number of solute particles — a colligative property.
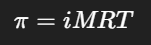

What happens to the solubility of AgCl when NaCl is added to the solution?
Solubility decreases due to the common ion effect (Cl⁻ is added, shifting equilibrium left).
What is the change in entropy of the system when 1 mol of ice melts melts at 0°C (273 K)?
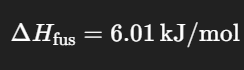
Give your answer in J/mol*K
22.0 J/mol*K
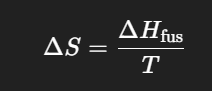
Will a precipitate form if [Ba²⁺] = 1.0 × 10⁻³ M and [SO₄²⁻] = 1.0 × 10⁻⁴ M? (Ksp of BaSO₄ = 1.1 × 10⁻¹⁰)
Q = (1.0 × 10⁻³)(1.0 × 10⁻⁴) = 1.0 × 10⁻⁷ > Ksp ⇒ Yes, a precipitate forms
The rate constant doubles when temperature increases from 298 K to 308 K.
If the reaction is 0 order, how much time in seconds does it take to go from 0.46 M of reactant to 0.1M when the frequency factor is 2 at this new temperature.
1.7 x 10^8