What was the experimental problem for the toxicology lab last class?
What is the identity of the unknown pill found in Anna's stomach?
Which of the following describes the place dead bodies are kept while they await an autopsy, identification, or burial?
a. Body Farm
b. Morgue
c. Autopsy
d. Funeral Home
b. Morgue
Which systems do these describe?
During gym class, your heart beats faster to pump oxygen-rich blood to your muscles as you jog around the track.
You use your biceps to lift your backpack and your leg muscles to climb the stairs to class.
Cardiovascular, Muscular
Which of the following does NOT occur within the first 24 hours of death?
a. Livor mortis
b. Algor mortis (temperature change)
c. Rigor mortis
d. Decomposition
d. Decomposition
Name three things that are tested during a toxicology test of a drug? Ex: texture
Color, texture, reaction to water, reaction to ferric nitrate, reaction to hydrochloric acid, pH
Algor mortis, or postmortem cooling of the body, varies with ambient temperatures. Based on the results of your hot dog experiment, how does ambient temperature affect the rate of cooling of a body after death?
Depending on the ambient (environmental) temperature, dead bodies may cool down at faster or slower rates. Some may even warm up.
What does this image show?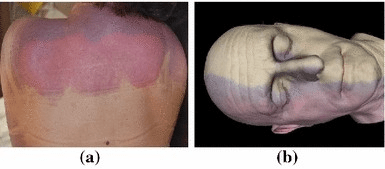
Livor mortis
Which systems do these describe?
After lunch, your stomach and intestines break down your sandwich to release energy for the rest of the school day.
Your spine keeps you standing tall while you balance a stack of books in your arms.
Digestive, Skeletal
What is the difference between algor, rigor, and livor mortis?
Algor - change in temp. after death
Rigor - stiffening of body muscles
Livor - blood settles in the part of body near the ground
Identify if the following are examples of toxins or toxicants.
Gasoline
Posion Ivy
Botulism (produced by a bacteria)
Pesticides
Gasoline - toxicant
Posion Ivy - toxin
Botulism (produced by a bacteria) - toxin
Pesticides - toxicant
What are the independent, dependent, and control variables? Students measure their resting heart rates, then perform light jogging, moderate running, and sprinting for 2 minutes each. They record their heart rate after each activity to see how exercise intensity affects pulse rate.
Independent: type of exercise
Dependent: heart rate
Control: time (2 minutes)
What section of an autopsy report includes changes to the body seen after death?
a. External Examination
b. Internal Examination
c. Postmortem Changes
d. Toxicology Results
c. Postmortem Changes
What systems do these describe?
After drinking two bottles of water at lunch, your kidneys filter the extra fluid so you need a bathroom break.
When a classmate sneezes nearby, your white blood cells jump into action to fight off any germs you inhale.
Urinary, Lymphatic
Place these in order in relation to time of death (what happens first --> last).
Livor mortis, decomposition, algor mortis, rigor mortis
1. Algor mortis (change in temp)
2. Livor mortis
3. Rigor mortis
4. Decomposition
What is the difference between a toxin and a toxicant?
Toxins are naturally occurring poisons produced by living organisms.
Toxicants are poisons manufactured by humans.
What are the independent, dependent, and control variables? To test the effect of caffeine on alertness, students drink beverages containing different amounts of caffeine. One student drinks 1 cup of coffee (60 mg of caffeine), another 1 cup of RedBull (80 mg), and another drinks 1 cup of Alani (200 mg). After 30 minutes, they complete a task that measures their reaction time.
Independent: amount of caffeine
Dependent: reaction time
Control: wait time (30 minutes), amount of drink (1 cup)
Classify each as the cause, mechanism, or manner of death.
Strangulation
Homicide
Asphyxiation
Strangulation - cause
Homicide - manner
Asphyxiation - mechanism
Following an autopsy, the medical examiner noted that the cause of death was COPD, which affects the lungs and a person's ability to breathe. What body system does COPD affect?
Respiratory System
An individual is found dead in their home. They were found at 12:30 pm, and their temperature was taken at 1 pm. The rectal temperature of the individual was 82 degrees F. Use the Glaister equation to determine time of death. Round to the nearest hour.
2 am (11 hours ago)
Toxicology is the "study of poisons." Typically, poisons such as drugs and alcohol, are ingested. Which body system would it be best to study if you were a toxicologist?
Digestive System
What are the independent, dependent, and control variables? Students test how different handwashing methods reduce bacteria. One group uses plain water, another group uses regular soap, and a final group uses antibacterial soap. After washing their hands, they all use a sterile cotton swab to collect the bacteria. After incubation, they count the number of bacterial colonies.
Independent: type of handwashing
Dependent: number of bacterial colonies
Control: type of cotton swab
During a myocardial infarction (heart attack), blood flow to the heart is blocked, and the heart cannot get enough oxygen. This can cause the heart muscle to die and lead to death of the individual.
Does this describe the cause, mechanism, or manner of death?
Mechanism (physiological change in the body that causes death).
What systems do these describe?
You quickly pull your hand away after accidentally touching a hot glue gun in art class.
You start sweating during PE, and your skin helps cool your body down.
Nervous and Integumentary
If a body is found to have a rectal temperature of 34℃ at 2:00 am in the medical examiner’s office, how long has the individual been dead?
What time (to the nearest half hour) did they die?
10:30 pm (3.5 hours ago)
The toxicology lab we performed on the pill in Anna's stomach was a ________ test because ________.
(presumptive or confirmatory)
Presumptive. We cannot be certain about the identity of the pill until a confirmatory test is performed.