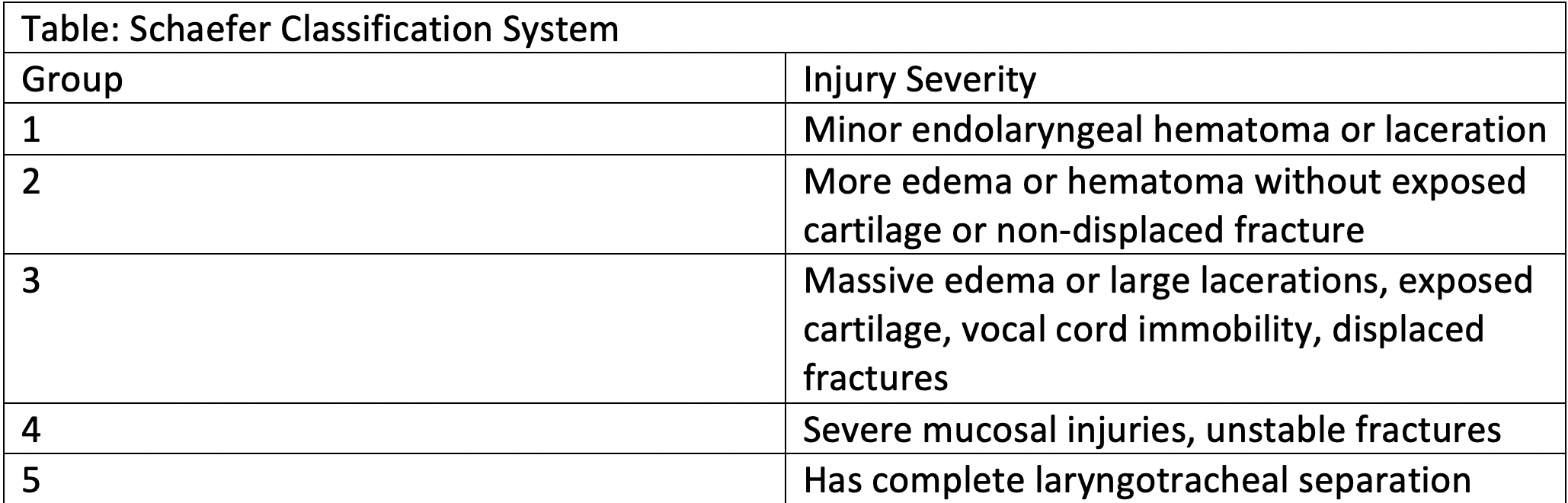
Most common site of injury to the recurrent laryngeal nerve during total thyroidectomy (true in both pediatrics and adults).
Berry's ligament = posterolateral ligament of the thyroid gland

Name the diagnosis
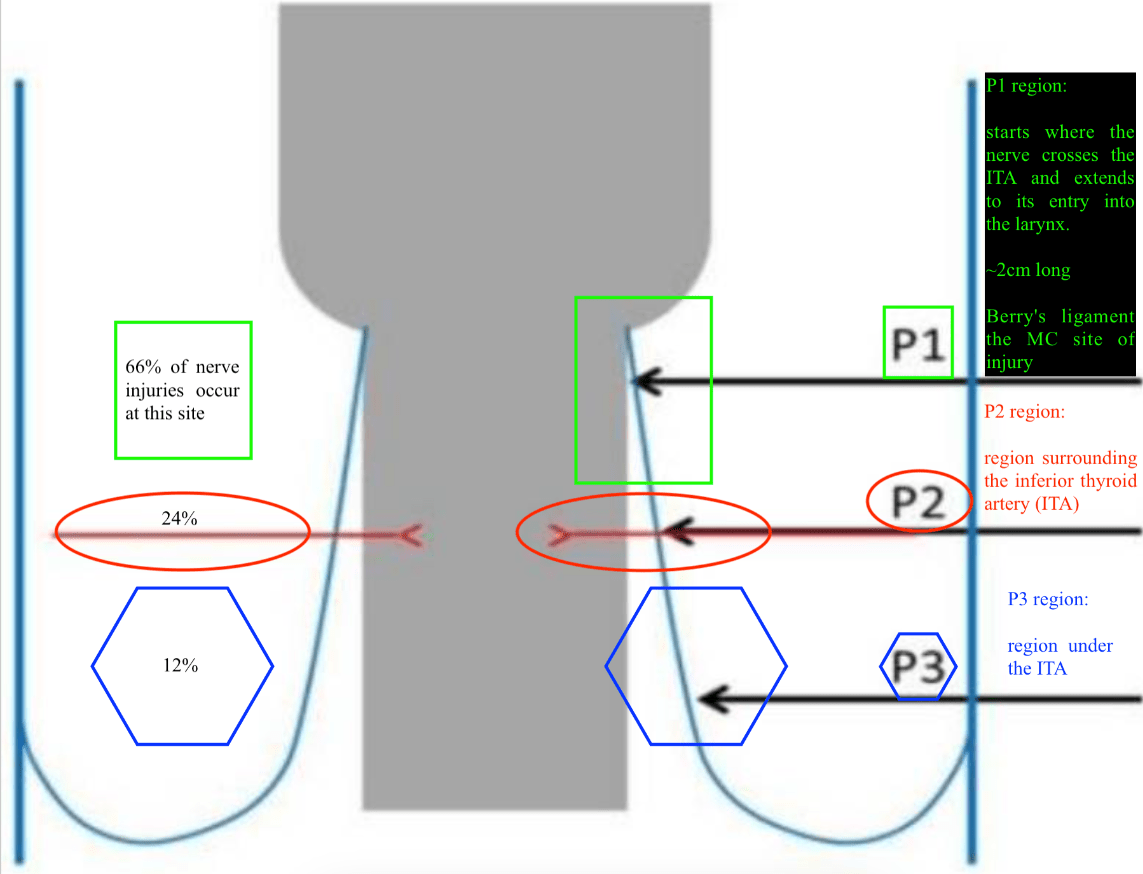
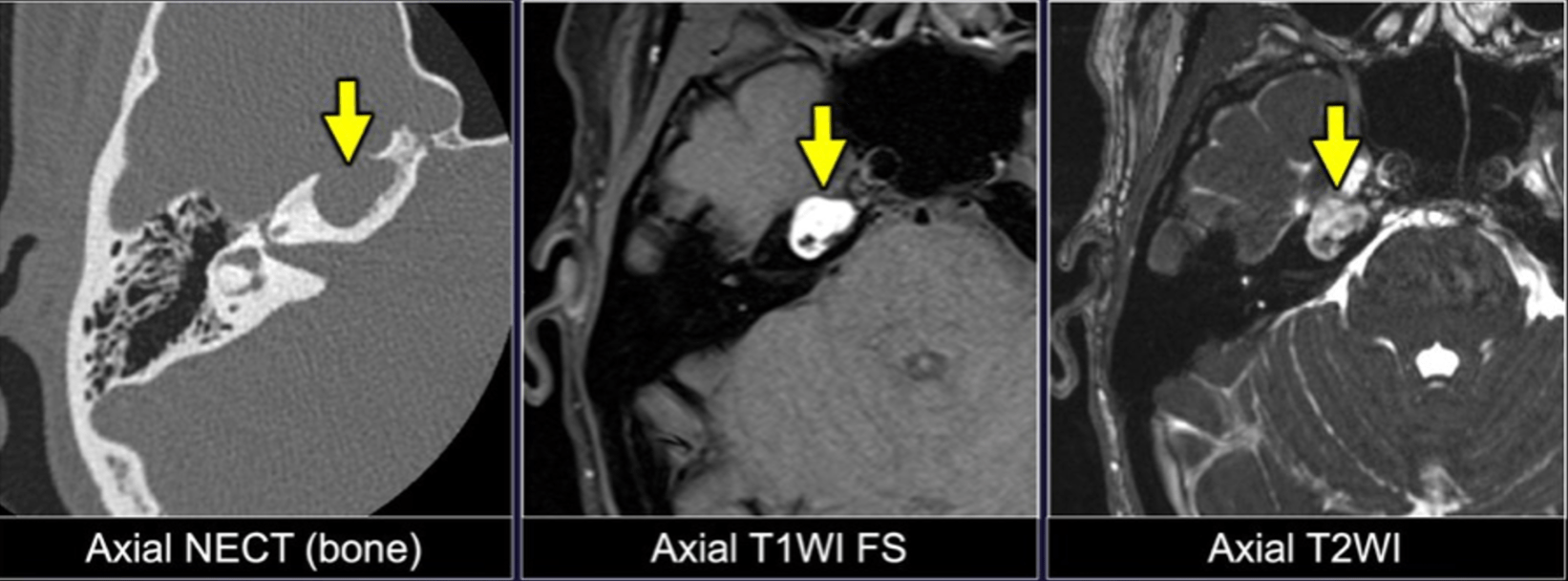
1. Destructive process in right petrous apex (Orange arrow)
2. focal collection @ petrous apex (Green arrow)
3. Mastoid effusion (Blue arrow)
4. unable to aBDuct right eye
Gradenigo’s Syndrome
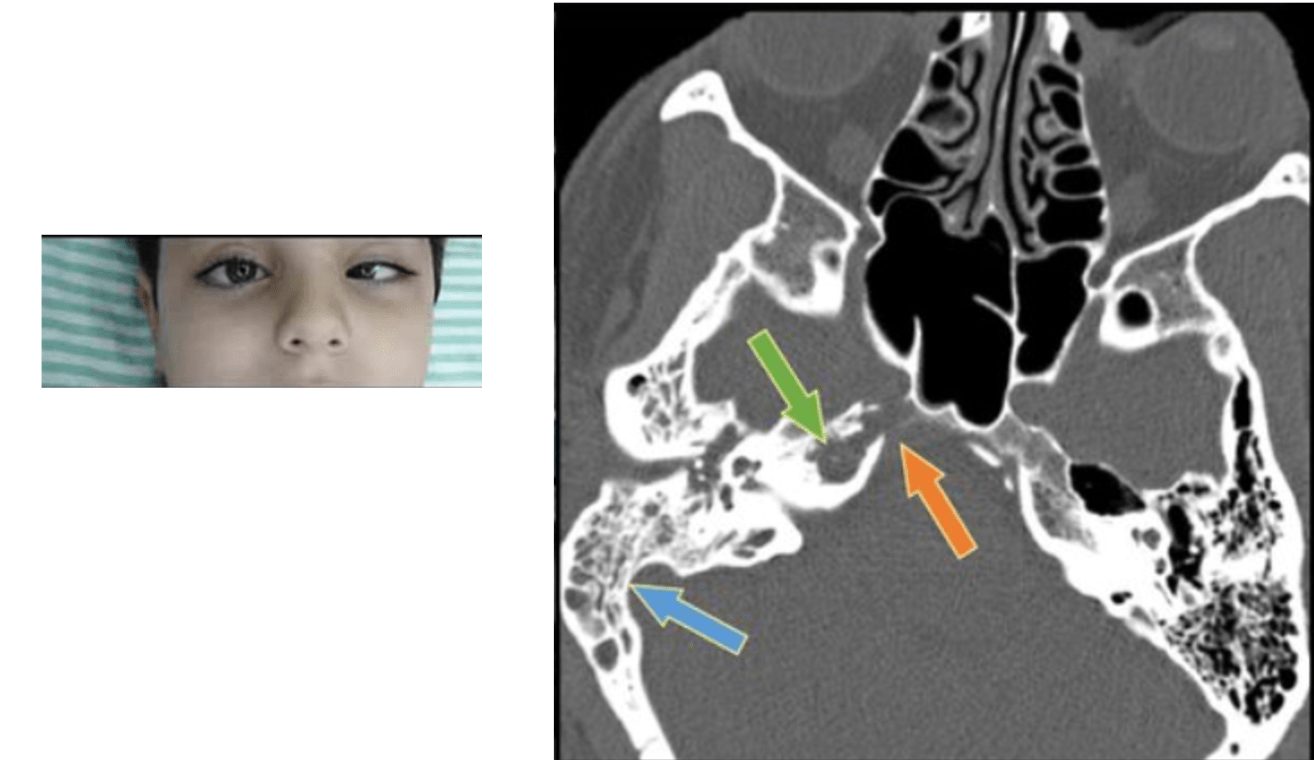
A 10 y/o M pt with acute otitis media presents to the ED due to worsening symptoms along with intractable headaches and blurry vision. On physical examination, the fundoscopic exam reveals papilledema. What potential complication do you suspect?
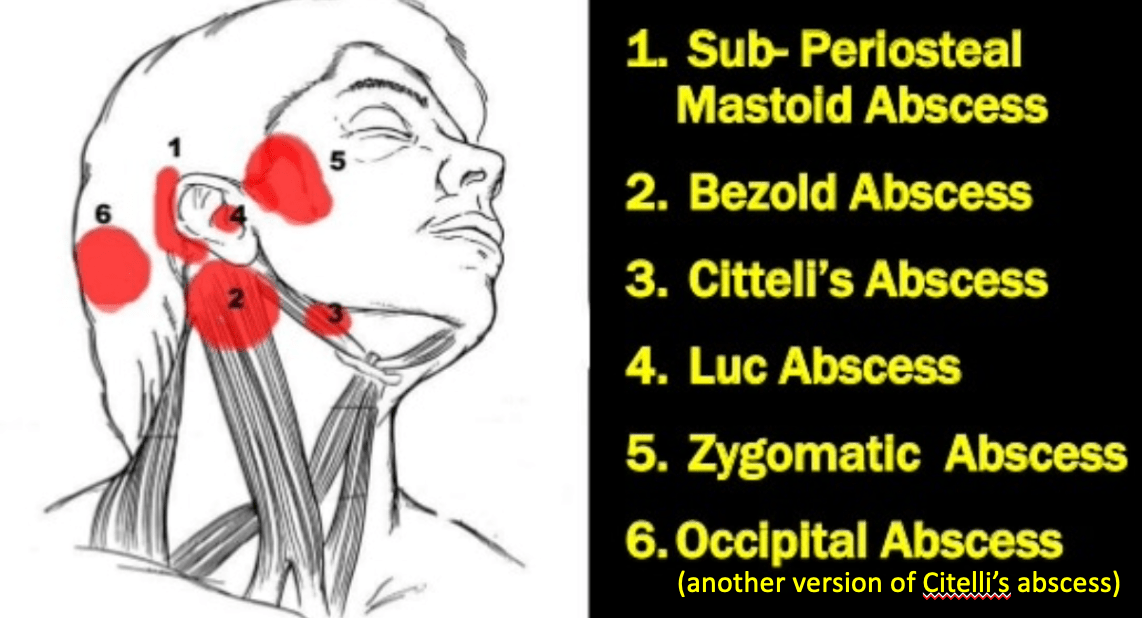
What is Citelli's abscess?

What is... the MC vascular anomaly that causes tracheomalacia?
Anomalous innominate artery
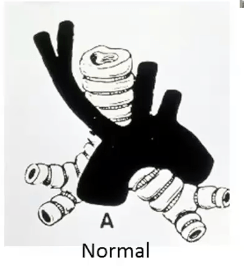

The Kiesselbach's Plexus receives its arterial blood supply of the following 4 arteries...
Kiesselbach's Plexus: site of anastomoses between ICA & ECA branches:
1. Ant ethmoid
2. SPA
3. Greater palatine
4. Superior labial
A patient with frontal bossing and mandibular keratocysts is at increased risk of developing which cutaneous malignancy?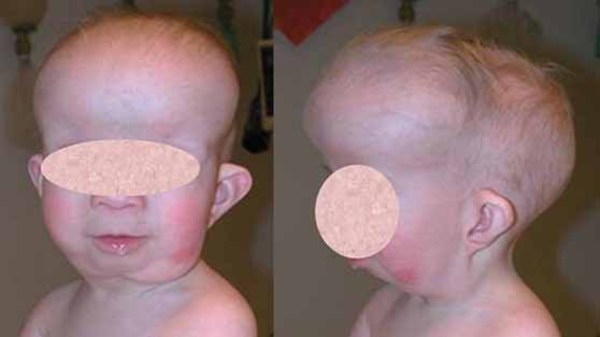
Basal Cell Carcinoma (BCCa)
Gorlin-goltz syndrome:
- AD
- mutation in the PTCH gene

Name the diagnosis
CT scan findings: Expansile lesion without bone destruction
MRI findings: Hyperintense on both T1 & T2
Cholesterol Granuloma
Patient present with congenital auricular atresia, mother would like to know if he is a surgical candidate. What criteria is used to determine surgical candidacy?
Jahrsdoerfer criteria
Tell me the ABNORMAL artery & the ABNORMAL branchial arch.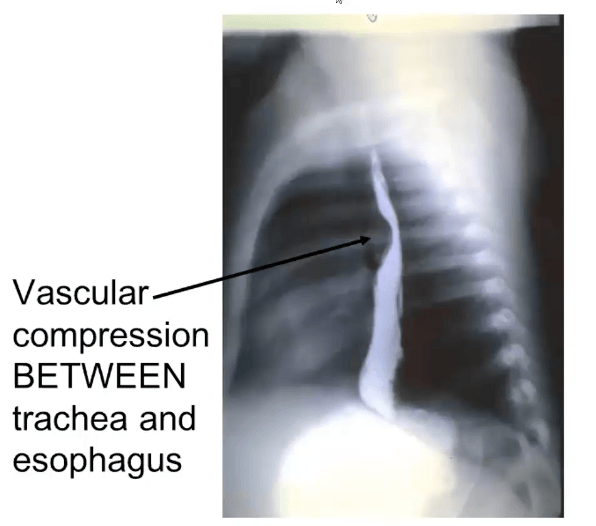
- Vascular sling = abnormal LEFT pulmonary artery (here the LEFT pulmonary artery arises from the RIGHT pulmonary artery)
- left 6 branchial arch
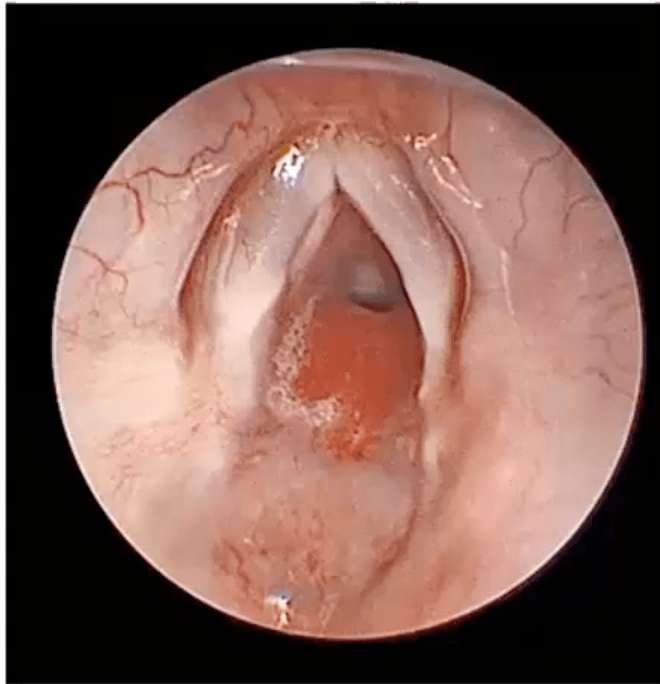
The etiology of the inspiratory stridor in this BG, is...
Subglottic hemangioma
Left posterior subglottis = #1 place to see the lesion
Proliferation phase of hemangiomas occurs during the first 3-6months of life
What is the diagnosis of this 1-day-old female with a mass arising from the maxilla?
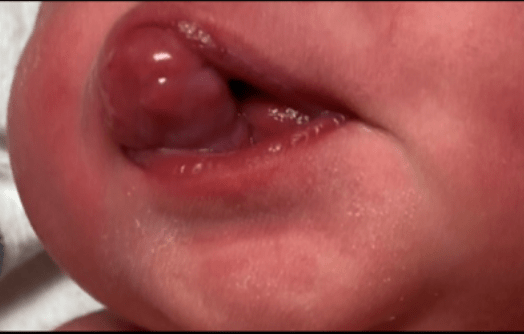
Congenital epulis.
- benign lesions that are present at birth.
- They can interfere with feeding, which is why surgical intervention is indicated within the first few days of life.
Tell me the syndrome of a child with Severe to profound SNHL, multinodulergoiter and TB-CT scan with:
PENDRED SYNDROME
- AR disorder
- Gene mutation affects pendrin, molecule involved in chloride-iodine transport
In the following CT, what is the concerning finding and in what ear?
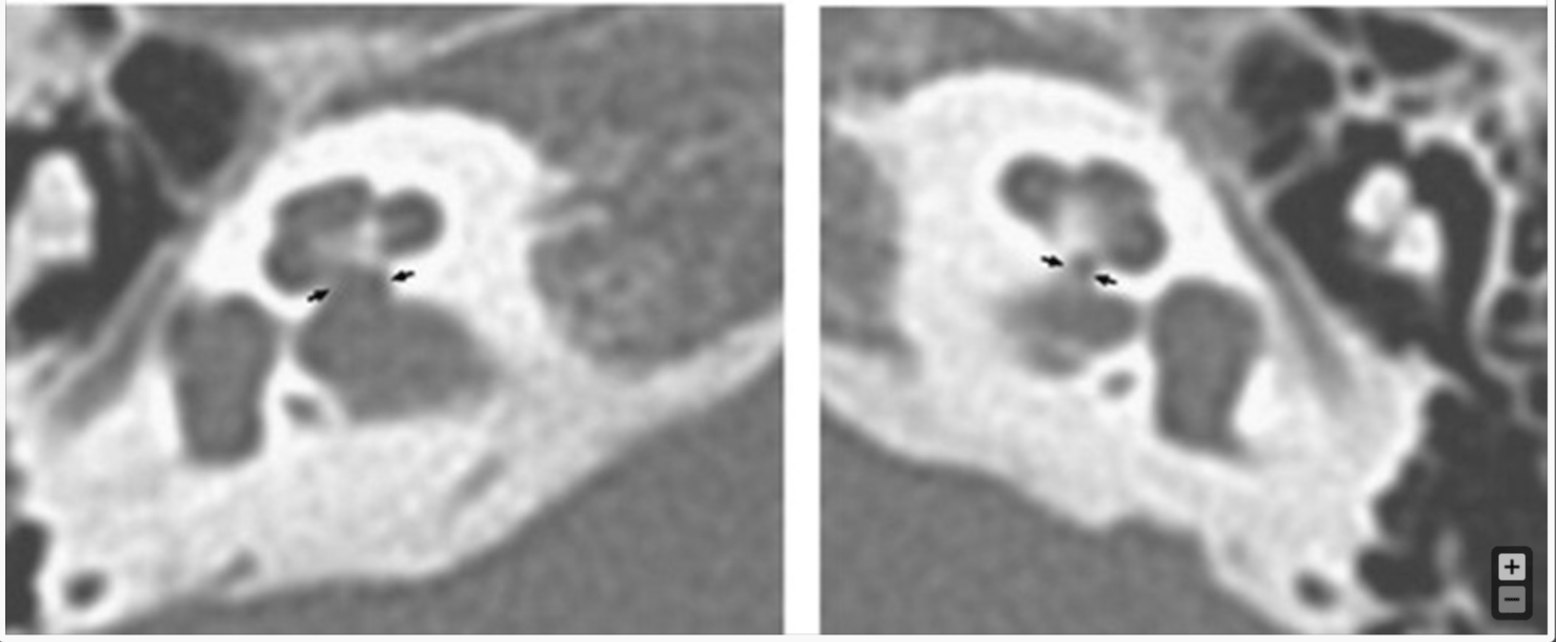
Cochlear nerve deficiency in the LEFT ear.
Cochlear nerve hypoplasia/deficiency (CND) was diagnosed by MRI or CT, with CND defined as a cochlear nerve canal (CNC) narrower than 1.5 mm.
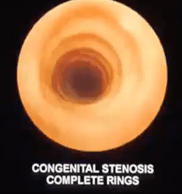
You take to OR a BG with pulmonary sling (abnormal left pulmonary artery). What additional finding would you expect to see in the Bronchoscopy?
Complete Tracheal rings.
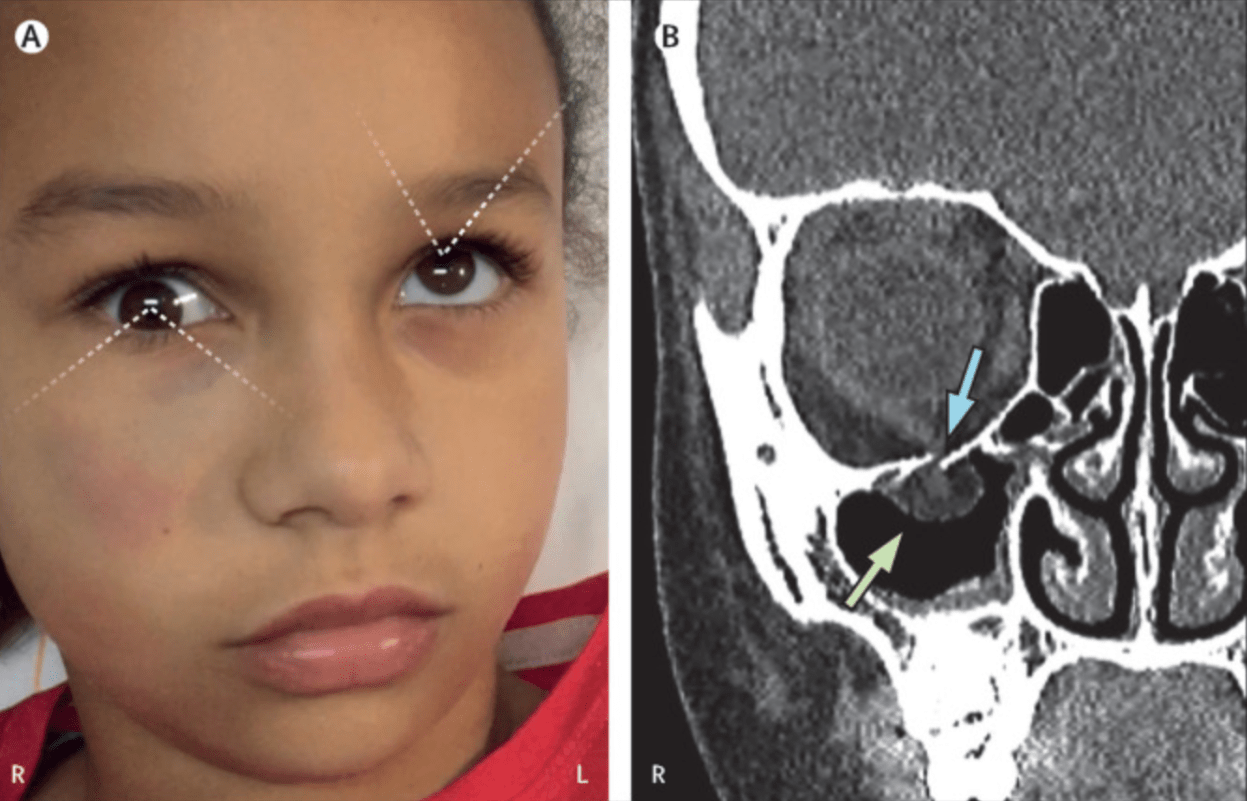
Patient with blunt trauma to the eye, hematoma around the right zygoma, inability to elevate the right eye, bradycardia, nausea, and vomiting. CT scan shows an orbital floor fracture (blue arrow) with herniation of the inferior rectus muscle and adjacent orbital soft tissue (green arrow).
What is the name of this reflex? Which nerve carries the afferent signal, and which nerve carries the efferent signal?
Bradycardia, nausea, and vomiting are due to the oculovagal reflex, also known as the oculocardiac reflex (OCR) or trigeminal–vagal reflex.
Afferent: Ophthalmic division of the trigeminal nerve (CN V)
Efferent: Vagus nerve (CN X)
Hypotension leads to bradycardia.
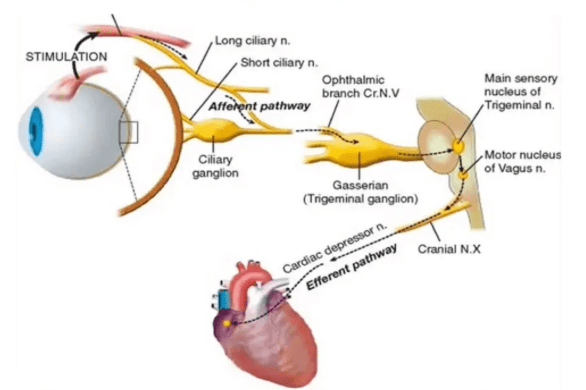
An entrapped orbital floor fracture with this reflex indicates the need for urgent reduction in the OR.
A 12-year-old with anti-TPO antibodies presents with a thyroid nodule. FNA is shown below. What is the underlying autoimmune disease? What is the diagnosis based on the FNA?
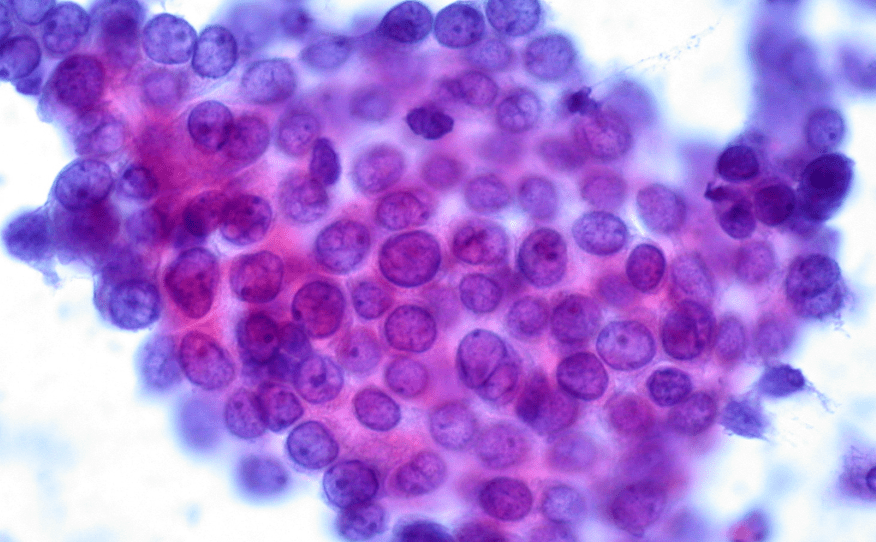
Hashimoto’s thyroiditis (HT)
Papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC)
Pediatric differentiated thyroid carcinoma (DTC) has a more aggressive behavior, characterized by:
High rate of extrathyroidal extension
High rate of locoregional metastasis
High rate of distant metastasis (most commonly to the lungs)
Children with thyroid malignancy, specifically PTC, are more likely to have HT. However, the association between HT and pediatric PTC does not appear to affect patient survival.
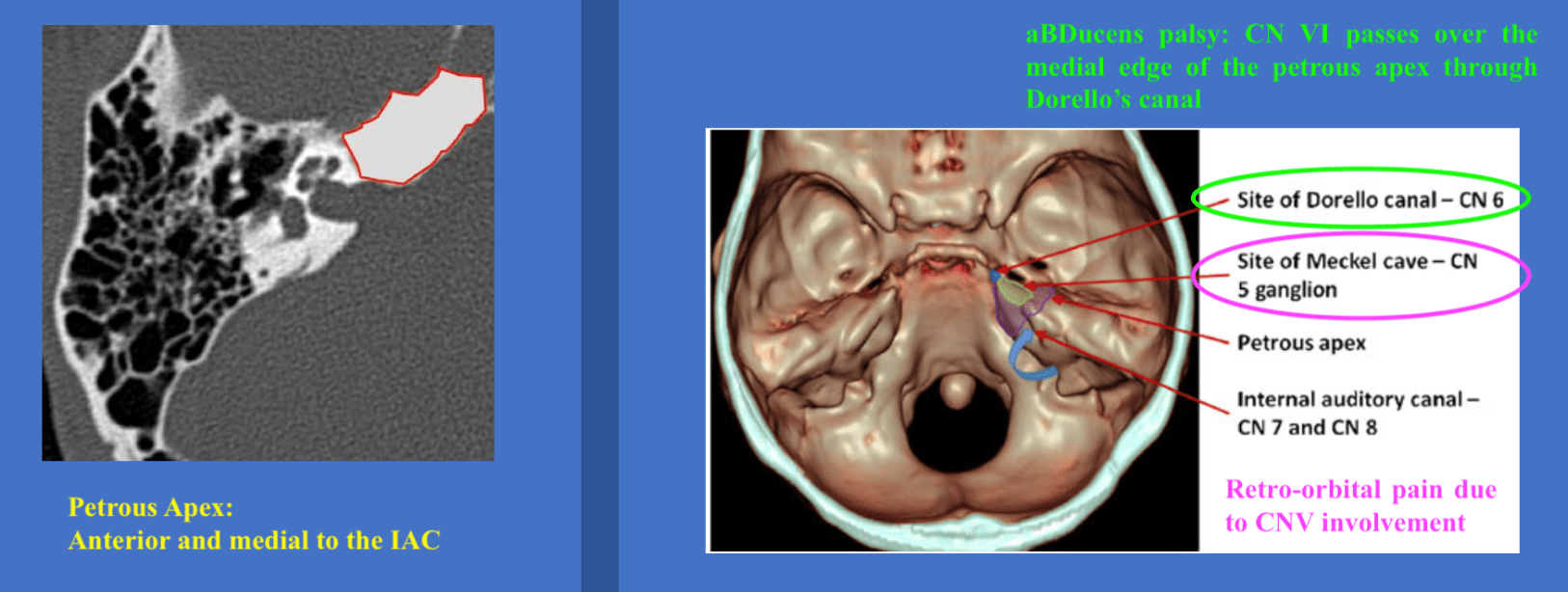
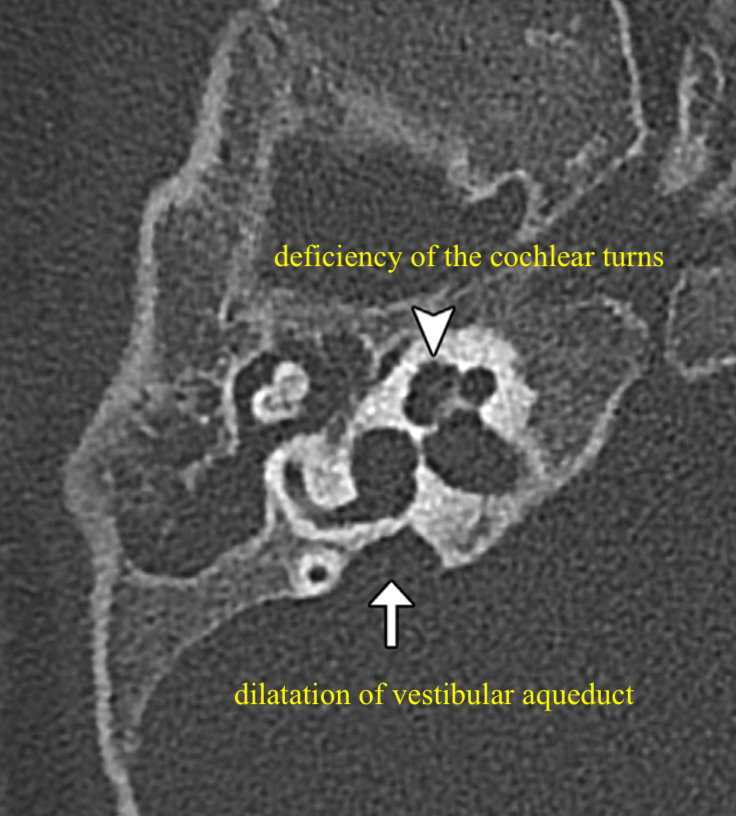
What is the most likely syndrome associated with findings on this temporal bone CT scan (B/L enlarged vestibular aqueduct) ?
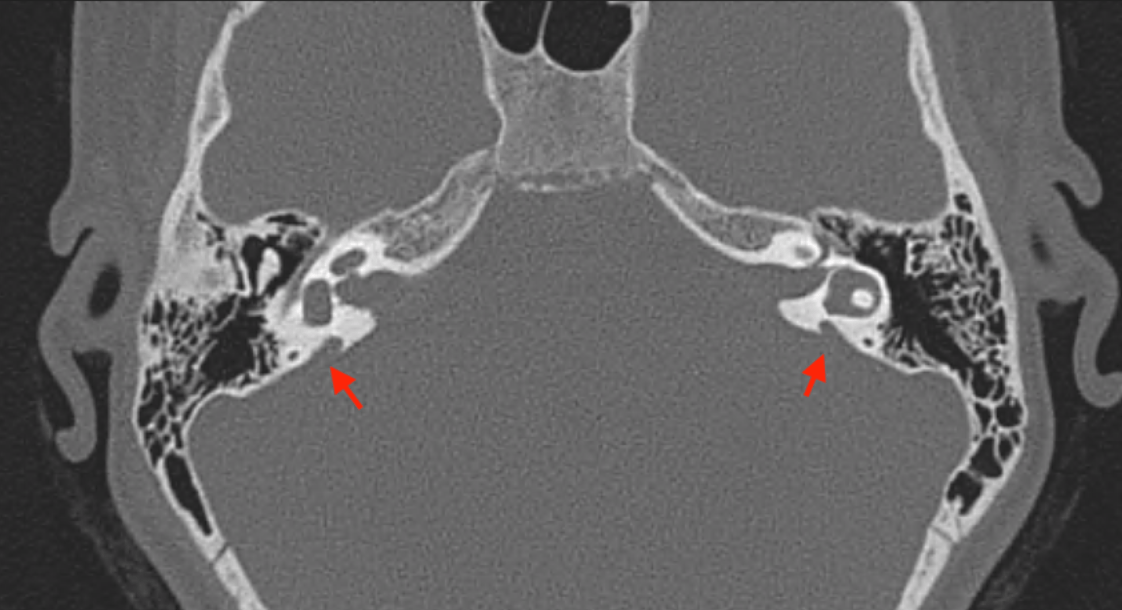
Pendred syndrome
- Sensorineural hearing loss (SNHL) that is usually congenital and often severe to profound
- Vestibular dysfunction
- Temporal bone abnormalities (bilateral enlarged vestibular aqueduct with or without cochlear hypoplasia)
- Euthyroid goiter
Congenital toxoplasmosis damages what inner structures?
What is the stria vascularis? which has been found to have calcified scars.
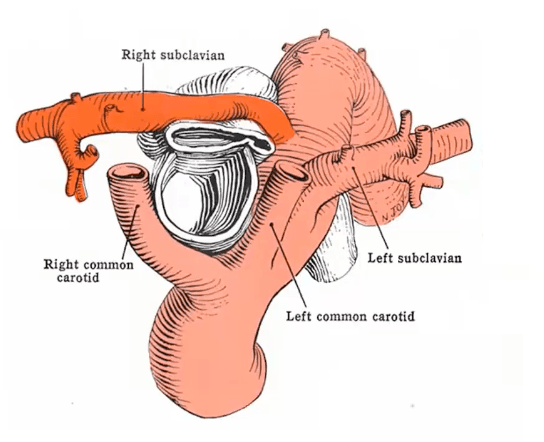
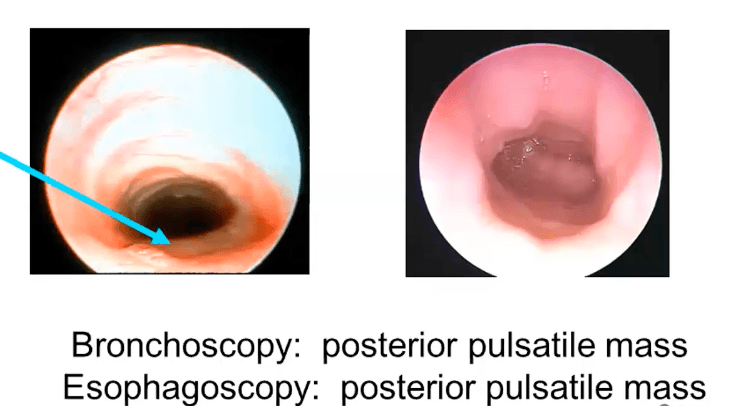
Boy with "dysphagia lusorum" & non-recurrent laryngeal nerve in the right side. Tell me the abnormal artery and what you will see in the bronchoscopy and esophagoscopy...
Retroesophageal right subclavian artery
A 10 y/o M pt with acute otitis media presents to the ED due to worsening symptoms along with intractable headaches and blurry vision. On physical examination, the fundoscopic exam reveals papilledema. What potential complication do you suspect?
Otic hydrocephalus!
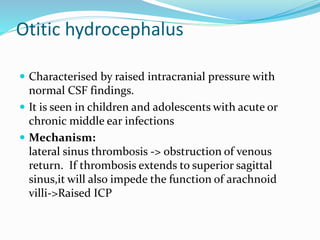
Tell me the diagnosis
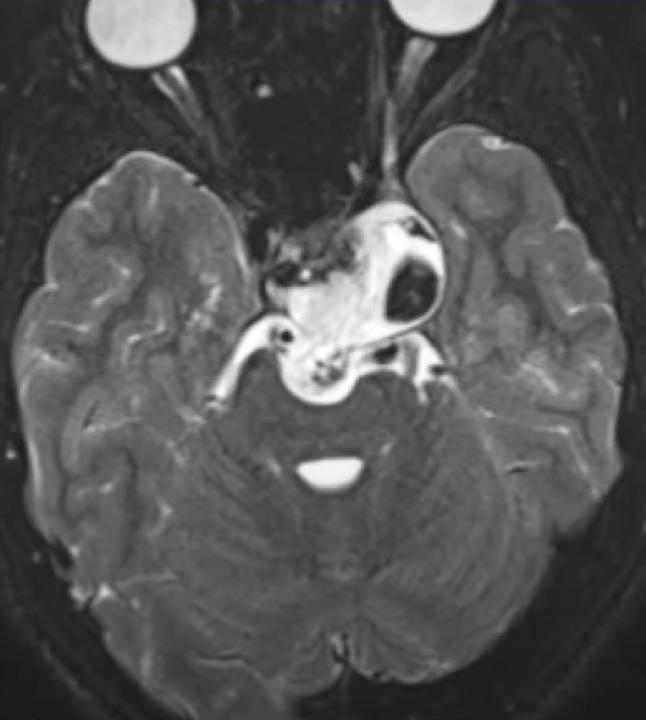
***Physaliferous cells*** = bubbly cells
Dx: Chordoma
- Midline Skull Base Lesion
- Pathology: The lesion is characterized by small, round, hyperchromatic nuclei and abundant vacuolated cytoplasm, giving a physalliferous appearance.
- Physalliferous cells: These cells resemble the fruit of Physalis plants (golden berries), with multiple clear vacuoles giving a bubbly look to the cytoplasm.


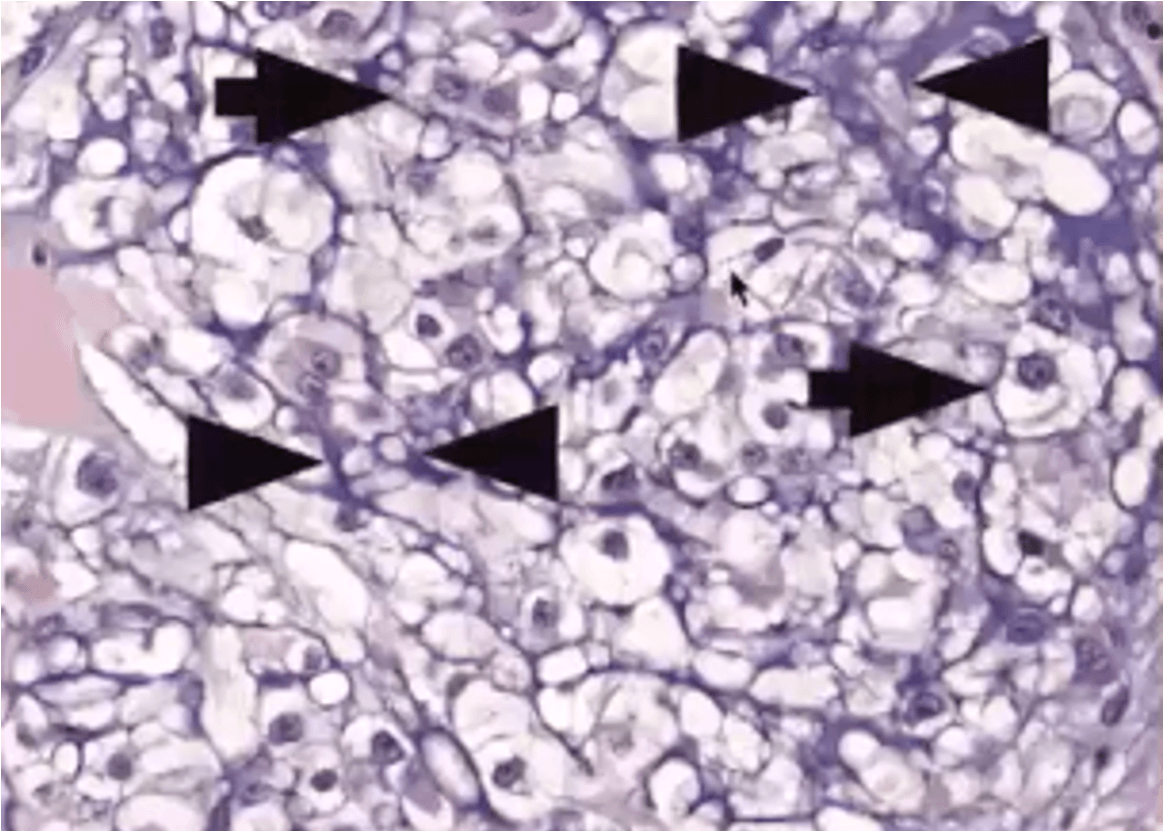
You have an MRI with finings below. You order a CT scan. Tell me the diagnosis for Pt#1 and Pt#2?
10 year old patient presents to your clinic because mother is concern of hearing loss. Patient mother states that there is family history of heart disease and use of hearing aids at early age. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Jervell Lange Neilsen
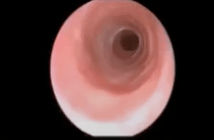
If you see this in the bronchoscopy, you think in the following vascular anomaly...
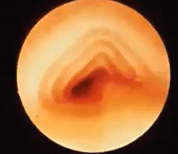
Double aortic arch (Complete vascular ring) = 2nd MCC of tracheomalacia induced by vascular compression.
- remember: MCC of vascular anomaly that causes tracheomalacia = Anomalous innominate artery
Name the Schaeffer classification grade of the following laryngeal injury.

Grade III