This New England colony was founded by Puritans seeking religious freedom for themselves but had little tolerance for other religions.
Massachusetts (Bay Colony)
This economic system aimed to increase a nation’s wealth through a favorable balance of trade and colonial resources.
mercantilism
The cultivation of this crop in present-day Mexico and the American Southwest allowed for the growth of settled communities.
maize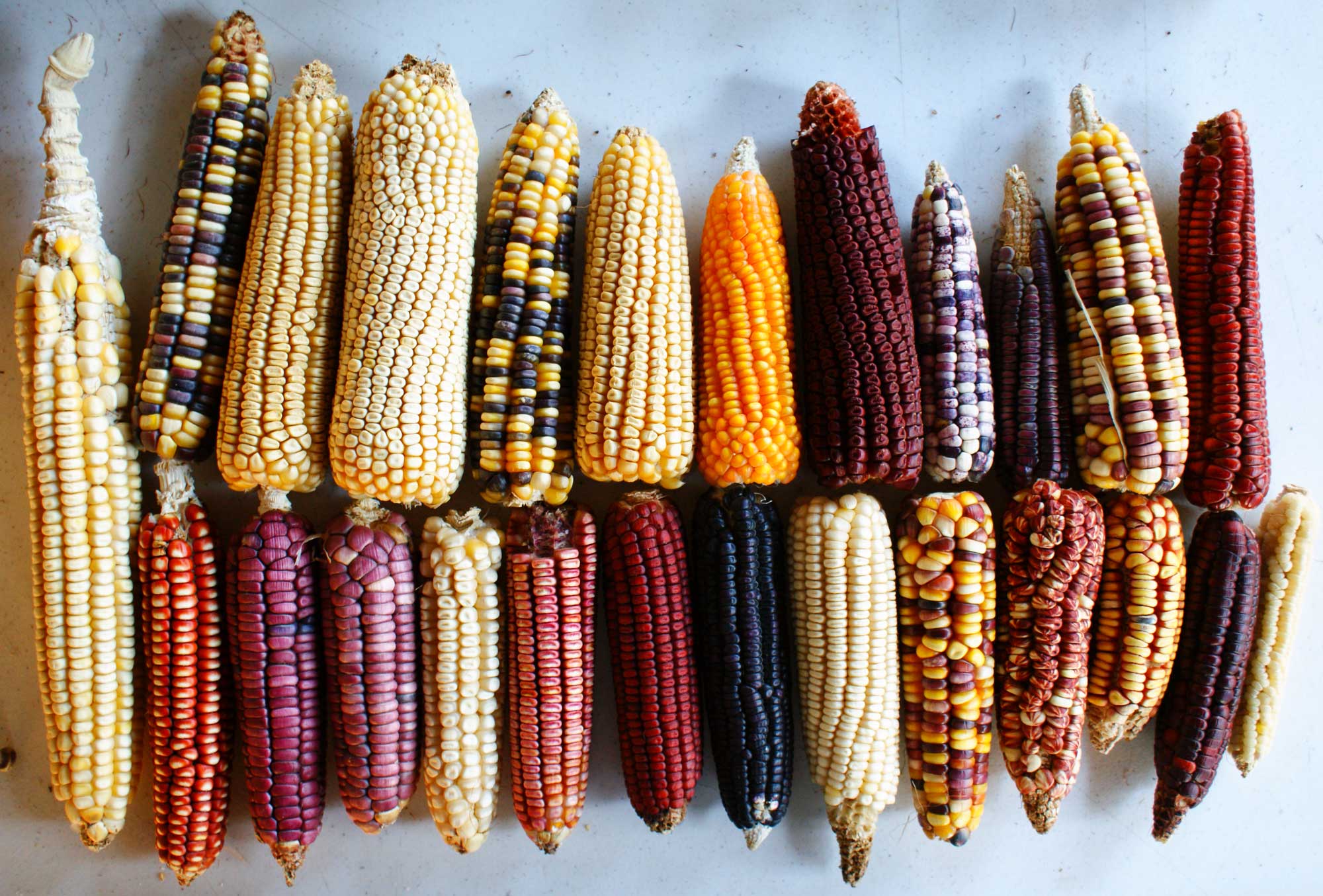
This system in Spanish America forced Native Americans to labor in agriculture and mining.
Encomienda system

Event that resulted in the deaths of 24 innocent men and women in Massachusetts
Salem Witch Trials

Colonists in the Chesapeake region primarily grew this cash crop, which later relied on enslaved African labor.
tobacco
Three words to describe the Middle Passage
examples: inhumane, unsanitary, deathly, exploitation, etc.
The “Three Sisters” agricultural system combined maize with these two other crops.
beans and squash

By the late 1600s, indentured servitude in the Chesapeake gave way to this labor system across the south.
African chattel slavery

One new law in response to slave rebellions
Enslavement as a permanent, hereditary condition
Legality of the physical punishment of enslaved people
Limited the ability of enslaved people to gather or testify
Punishments for white people who harbored fugitives
Ban on interracial marriage
The Middle Colonies were known for producing this staple crop, which gave them the nickname the “breadbasket colonies.”
wheat (cereal crops)

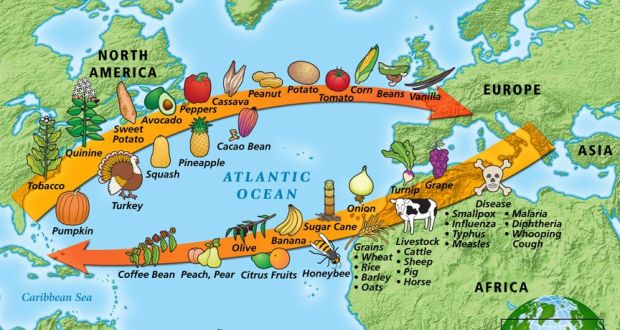
The transfer of plants, animals, people, diseases, technology, ideas, etc. between the New World and the Old World
The Columbian Exchange
Native groups in the Great Plains and Great Basin developed this kind of lifestyle in response to their dry environment
a nomadic/mobile lifestyle

Major fear caused by Bacon's Rebellion
Possibility of an interracial alliance between white indentured servants and Black slaves

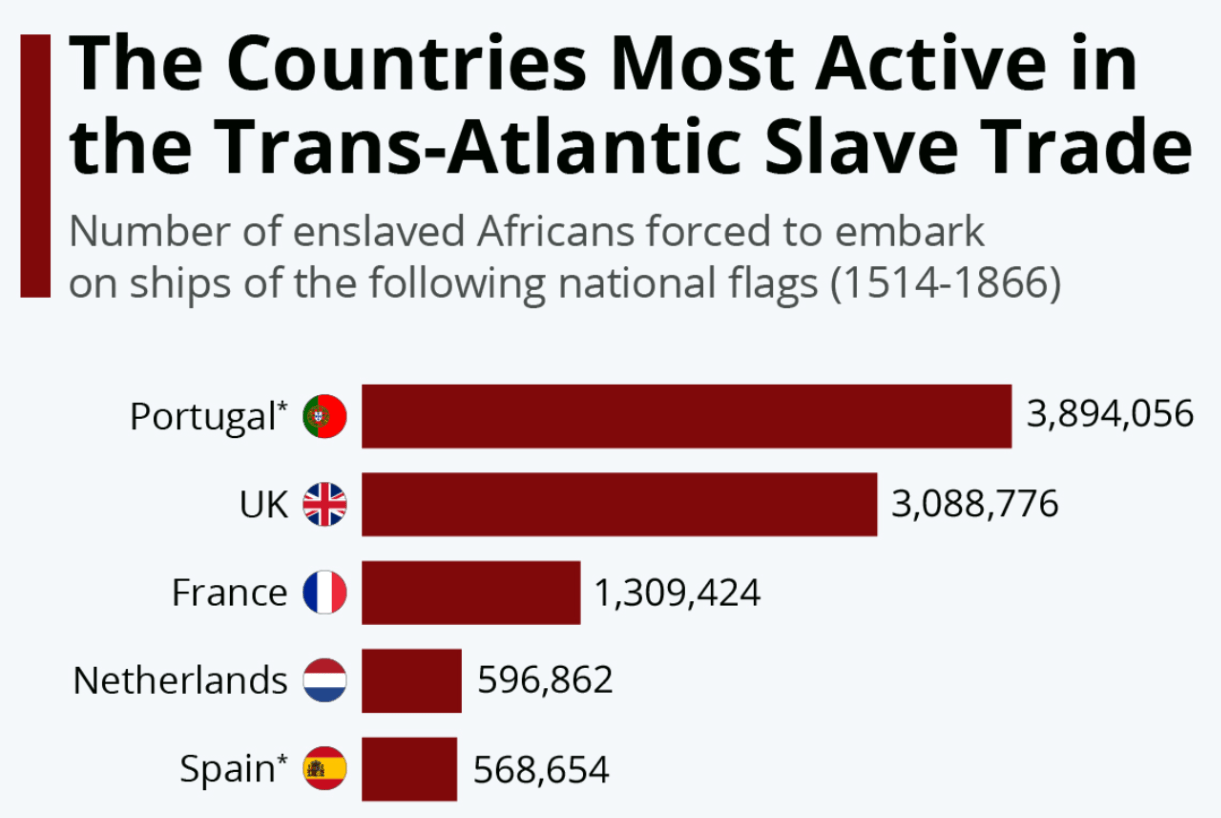
Name the five main countries involved in transatlantic trade
Spain, Portugal, The Netherlands, France, and Great Britain
Two examples of early self-government (in Virginia and Massachusetts)
House of Burgesses (VA) and the Mayflower Compact (MA)
Draw a basic map of the transatlantic slave trade (include the regions involved and the goods exchanged)

One way indigenous people reacted to European colonization.
attempted alliances with French/Dutch for trade
relocation from their homeland
- self-defense
Enslaved Africans resisted slavery in both overt and covert ways. Give one example of each.
Overt: rebellions, running away, suicide, self-harm
Covert: slow work, preserving African traditions, secret religious practices, gaining an education
Define indentured servants
Poor Europeans who agreed to work 4-7 years in exchange for passage to the Americas, food, and shelter. They were free after their contract ended

Name two features that distinguished the Southern plantation colonies from New England colonies.
Southern: plantations, enslaved labor, cash crops, plantation elite
New England: small farms, town meetings, mixed economy, Puritan base
One way the indigenous people in the Americas were affected by transatlantic trade.
Spread of disease (population decline)
Dependency on European goods (weapons, tools)
Economic disruption and shifting power balances
Forced labor (South America)
Forced relocation
Explain how maize cultivation contributed to both economic and social development among Native societies. (need 1 economic development and 1 social development)
Economic: surplus food supported growth, irrigation, trade
Social: promoted permanent villages, hierarchies, division of labor
Explain one reason why slavery expanded in the Southern colonies more than in New England.
Long growing seasons, labor-intensive crops (tobacco, rice, indigo), plantation economy
What was the Holy Experiment?
William Penn's plan to establish the colony of Pennsylvania as a sanctuary for Quakers and other persecuted religious groups, built on Quaker principles of religious tolerance, brotherly love, and participatory government