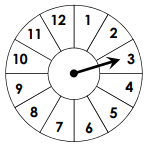
 P(even number) =
P(even number) =
6/12 = 1/2 = 0.5 = 50%
There are 2 blue, 6 yellow, 10 red, 3 green, 5 orange, and 4 purple marbles in a jar. One marble is chosen at random.
P(red or blue)=
12/30 = 2/5 = 0.4 = 40%
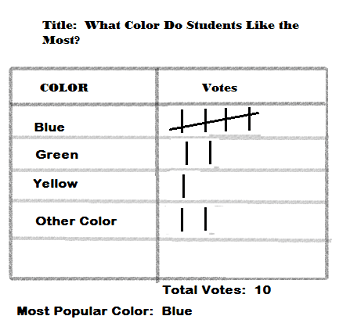
What is the experimental probability of choosing green based on the data?
2/10 = 1/5 = 0.2 = 20%
Randomly select a colored marble from a bag that contains 5 red marbles, 5 blue marbles, 5 green marbles, 5 yellow marbles, and 5 purple marbles.
What is my sample space?
{R, B, G, Y, P}
Randomly select a coin from a jar that contains 14 quarters, 26 dimes, 12 nickels, and 8 pennies.
Draw the probability model.
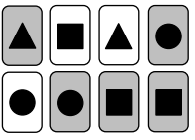
P(not a triangle)=
6/8 = 3/4 = 0.75 = 75%
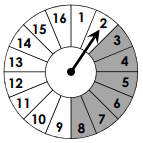
P(grey)=
6/16 = 3/8 = 0.375 = 37.5%
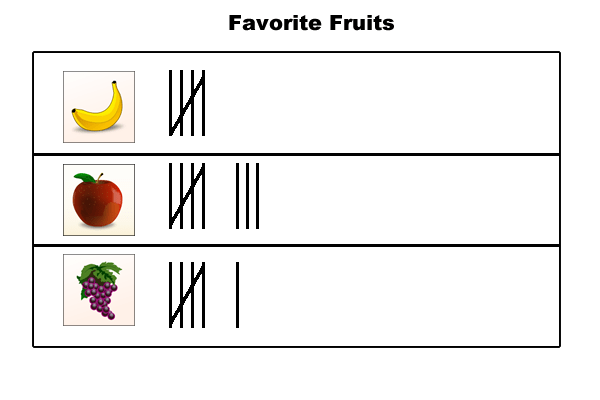
What is the experimental probability of choosing grapes based on the data?
round to the nearest percent
6/19 = 0.32 = 32%
Randomly select a colored marble from a bag that contains 5 red marbles, 5 blue marbles, 5 green marbles, 5 yellow marbles, and 5 purple marbles.
What is P(G)?
1/5
What is always the sum of every probability model?
1 whole or 100%
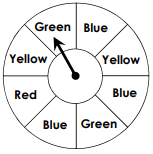
P(green or blue)=
5/8 = 0.625 = 62.5%
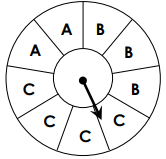
P(C)=
4/9 = 0.444444 = 44%
A piece of fruit was selected from a basket 40 times. The results are shown in the table below.
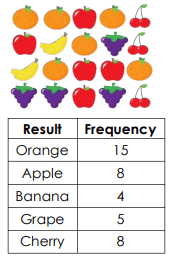
What is the experimental probability of choosing a banana or a cherry?
12/40 = 3/10 = 0.3 = 30%
Randomly select a colored marble from a bag that contains 5 red marbles, 5 blue marbles, 5 green marbles, 5 yellow marbles, and 5 purple marbles.
Are the probabilities equally likely?
Yes, because every color of the marbles has the same chance of being selected.
How can we tell when a probability model is uniform?
When all of the probabilities have the same chances of occurring.
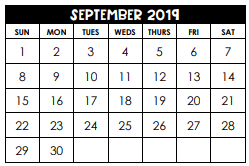
P(a date that is a multiple of 5)=
6/30 = 1/5 = 0.2 = 20%
Cara is playing a number game where she has two tiles for each number 0 – 9.
P(a number less than 3)=
6/20 = 3/10 =0.3 = 30%
A marble is picked from a jar 60 times. Results are shown in the table below.
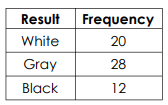
What is the experimental probability of not choosing a black marble?
48/60 = 4/5 = 0.8 = 80%
You randomly choose a letter from the word
P R O B A B I L I T Y and replace it each time.
What is the probability you will choose a vowel (not y) then a B?
Round to the nearest percent.
8/121 = 0.07 = 7%
You have a deck of 52 cards. You choose a red card, keep it, then choose another red card.
Round the probability to the nearest percent.
(In a deck of cards, 26 are red and 26 are black)
25/104 = 0.24 = 24%
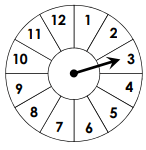
P(prime number)=
(round to the nearest percent)
5/12 = 0.42 = 42%
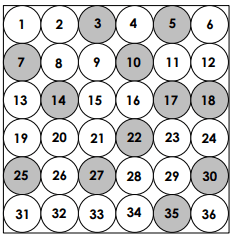
P(grey)=
(round to the nearest percent)
12/36 = 1/3 = 0.33 = 33%
A number between 1 and 3 is chosen at random 30 times.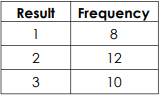
What is the experimental probability of choosing a 1? What would be the theoretical probability of choosing a 1?
Round to the nearest percent.
Experimental: 8/30 = 4/15 = 0.27 = 27%
Theoretical: 10/30 = 1/3 = .33 = 33%
You throw a number cube three times. What is
the probability that you roll an odd number all
three times?
Round to the nearest percent.
1/8 = 0.13 = 13%
You have a bag of 50 jelly beans. 15 are
green. What is the probability of pulling out a
color other than green, eating it, then pulling out a
green?
Round your answer to the nearest percent.
3/14 = 0.21 = 21%