Gene expression means cells can turn on and off certain ____________ when exposed to certain chemical or temperatures.
A. proteins
B. genes
C. mRNA
D. chromosomes
B. genes
Transcribe the following DNA strand into mRNA:
TACGATTCT
AUG | CUA | AGA
Mutation where one nitrogen base is replaced by another is called--
A. Insertion
B. Substitution
C. Deletion
D. Inversion
B. Substitution
Give one way a mutation can benefit a species.
-Mutations provide variation to genetic code
-Mutations create new strains of bacteria or viruses
A fox is usually brown all over, but when temperatures drop blow 30 degrees, a pigment that causes them to turn white is produced. What is likely the cause of this change?
A. Poor health of the fox
B. A change in hormones
C. Temperature change causes certain genes to be turned on
D. Infection
C. Temperature change causes certain genes to be turned on
Give the peptide strand for the DNA strand shown below:
TACAGGCCCACT
A. Methionine, Serine, Histidine, STOP B. Methionine, Serine, Proline, STOP
C. Methionine, Phenylalanine, Glycine, STOP D. Methionine, Serine, Glycine, STOP
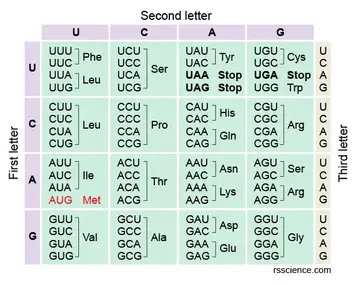
mRNA: AUG | UCC | GGG | UGA
D. Methionine, Serine, Glycine, STOP
Mutations can lead to problems because--
A. all cells need DNA
B. the DNA in each cell of the body is different
C. a mutation can lead to the production of an incorrect molecule like sugar
D. a mutation can cause an incorrect protein to be made
D. a mutation can cause an incorrect protein to be made, NOT SUGARS!!!
Which codon will lead to translation stopping?
A. UGG B. AAG C. AAA D. UAG
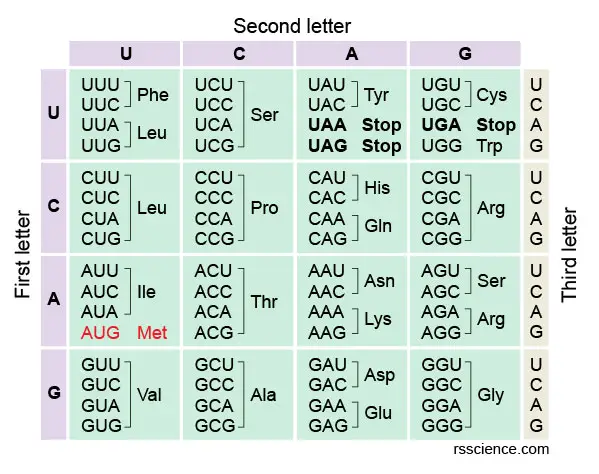
D. UAG
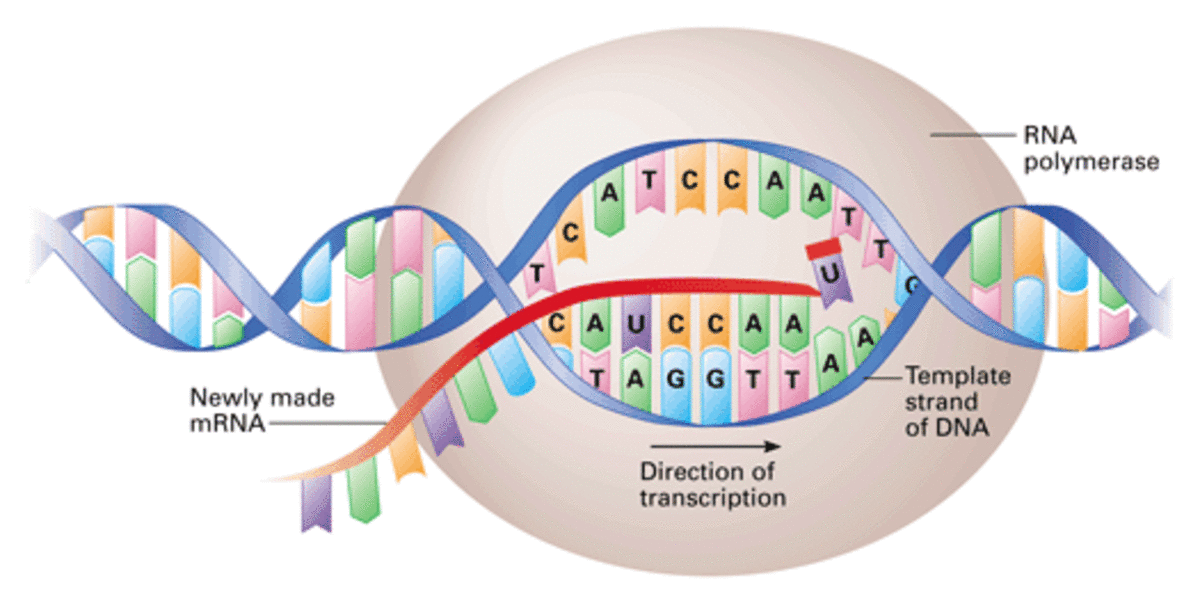
What process is shown in the diagram, transcription or translation?
Transcription (DNA to mRNA)
Which amino acids are coded for in the DNA below?
GTA | ATG | CGC | TCA
A. Leucine - Alanine - Serine - Tyrosine C. Histidine - Leucine - Tyrosine - Alanine
B. Histidine - Tyrosine - Alanine - Serine D. Alanine - Histidine - Alanine - Serine

GTA ATG CGC TCA
mRNA: CAU UAC GCG AGU
His Tyr Ala Ser
B. Histidine - Tyrosine - Alanine - Serine
Normal DNA: TGAGGTCTCCTC
Mutated DNA: TGAGGTCACCTC
What type of mutation is shown above?
A. Substitution
B. Insertion
C. Frameshift
D. Deletion
A. Substitution (T to A)
What is the cause of an insertion mutation?
A. Bases are exchanged for others in the DNA strand.
B. Bases are deleted from the DNA strand.
C. Bases are damaged on the DNA strand.
D. Bases are added to the DNA strand.
D. Bases are added to the DNA strand.
All cells in an organisms have the same ________ but they are able to express different ________.
A. proteins, DNA
B. traits, genes
C. genomes, proteins
D. genes, chromosomes
C. genomes, proteins
A DNA triplet reads: GCC
Which change to the DNA triplet will affect the amino acid produced?
A. GCA
B. GCT
C. GCG
D. GTC
GCC --> CGG --> Arginine
A. GCA --> CGU --> Arginine
B. GCT --> CGA --> Arginine
C. GCG --> CGC --> Arginine
D. GTC --> CAG --> Glutamine
The following is given as a DNA strand:
AAT | TCG | GGT | CGA | ATT
Which of the following shows a frameshift mutation of the DNA strand?
A. AAT | TCG | GGA | CGA | ATT
B. AAT | TCG | GGT | CGA | ATT
C. UUA | UGC | CCA | GCU | UAA
D. AAT | TCG | GGC | GAA | TT
A. AAT | TCG | GGA | CGA | ATT (SUB)
B. AAT | TCG | GGT | CGA | ATT (SUB)
C. UUA | UGC | CCA | GCU | UAA
D. AAT | TCG | GGC | GAA | TT (DELETION)
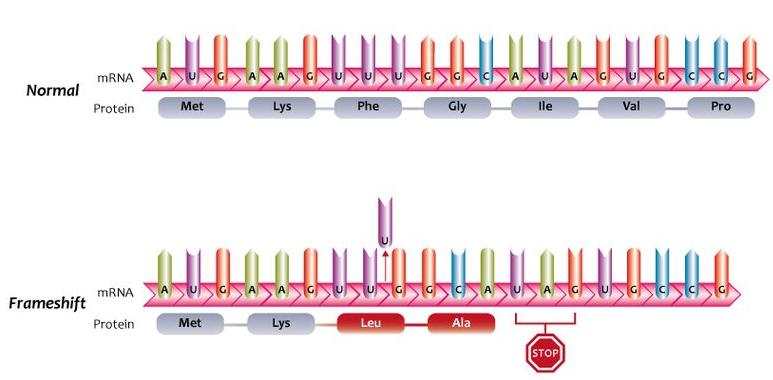
What mutation has occurred above?
A. deletion of a nitrogen base has produced a new nucleotide
B. substitution of a base has produced a different polypeptide
C. insertion of a base has led to the production of a new polypeptide
D. deletion of a base has caused the production of a different polypeptide
D. deletion of a base has caused the production of a different polypeptide
A DNA sequence is given: GGG CCA AAT AGA
Which mutated sequence has the greatest effect on the protein?
A. GGG CAA AAT AGA B. GGG CCT AAT AGA
C. GGG CTA ATT AGA D. GGG CCC AAT AGA

GGG CCA AAT AGA
CCC GGU UUA UCU
PRO GLY LEU SER
A. CCC GUU UUA UCU
PRO VAL LEU SER
B. CCC GGA UUA UCU
PRO GLY LEU SER
C. CCC GAU UAA UCU
PRO ASP STOP
D. CCC GGG UUA ACA
PRO GLY LEU THR
Why do some mutations cause changes to the protein produced while others don't?
A. Each protein requires multiple amino acids
B. Some amino acids occur more frequently than others
C. Proteins require many codon combinations
D. Each amino acid is coded for by multiple mRNA codons
D. Each amino acid is coded for by multiple mRNA codons