smallest unit of life
the cell
True or false? Both plant and animal cells are examples of prokaryotic cells
False
Pro = No: Prokaryotic cells have no nucleus and no membrane bound organelles.
Plant and animal cells have both of those so they are Eukaryotic
This structure is found in all cells and is the fluid that holds all the structures in the cell in place
Cytoplasm
This organelle is responsible for the storage of genetic information. It contains pores that allows those instructions to be transported to the ribosome.
Nucleus
How many phosphates does ATP have?
3 phosphates
This type of cell transport does not require energy
passive transport
Name the 3 parts of the cell theory
1. All living things are made of cells
2. The cell is the smallest unit of life
3. All new cells come from pre-existing cells.
This organelle is essential in a plant cell. It has a rigid outer layer that that protects the cell and helps it stand up.
Cell wall
What is the main difference between Eukaryotic cells and Prokaryotic Cells?
Eukaryotic cells have a nucleus and membrane bound organelles
Prokaryotic have free floating DNA (no nucleus)
Describe the function of the Chloroplast
Only present in plant cells: Converts sun energy into chemical energy (does photosynthesis)
Can be related to a dead battery, this molecule contains no energy
adenosine diphosphate (ADP)
In active transport, molecules move from ______ to _______ concentrations.
low to high
How is a scientific theory accepted?
needs to be supported by evidence collected by many scientists.
This organelle is present in both plant and animal cells and is responsible for housing DNA and controlling cellular activities
Nucleus
This organelle is found in all cell types. It is the thin outer covering composed of phospholipids. Food, water, and gases can enter the cell while wastes are allowed to leave?
Cell membrane
This organelle can be called the stomach of the cell. It is composed of enzymes that aid in the digestion and removal of waste products in the cell.
Lysosome
What is required for energy to be released from a molecule of ATP?
The bond between the first 2 phosphate groups must be broken
This type of transport requires the use of a channel protein and moves molecules from high concentration to low concentration
Facilitated Diffusion
A form of passive transport that does not require energy
All living things are made of cells
Explain the role of the large vacuole in a plant cell.
The vacuole stores water, food, and waste. When it is full it keeps the plant standing upright, when it is not the plant may wilt.
Ribosome
This organelle is found in both plant and animal cells. They are the powerhouses of the cell. They carry out cellular respiration to produce water, carbon dioxide, and lots of energy
Mitochondria
What is the process that transforms glucose into ATP?
Cellular respiration
The term used when vesicles move large molecules like fatty acids and sugars into the cell in active transport.
endocytosis
A biology student is observing the process of cytokinesis during the cell cycle. This is when a singular cell becomes 2 different cells. Which part of the cell theory does it most likely support?
All cells come from pre-existing cells.
How is the food making process different in plant cells than in animal cells?
Plant cells have chloroplasts to help make their food and animals must consume
Characteristics of 2 different cells are shown below.
Cell 1: free-floating DNA, flagella attached, simple organism
Cell 2: Cell wall, DNA is contained, complex organs within
Determine which types of cells are being described
A. 1: Animal Cell, 2: Plant Cell
B. 1: Plant cell, 2: Bacterial Cell
C. 1: Bacterial Cell, 2: Prokaryotic Cell
D. 1: Prokaryotic Cell, 2: Eukaryotic Cell
This organelle is located closely to the ER and is responsible for modifying and transporting proteins to different parts of the cell/body
Name the largest component of the cell membrane AND write down the name that describes its function.
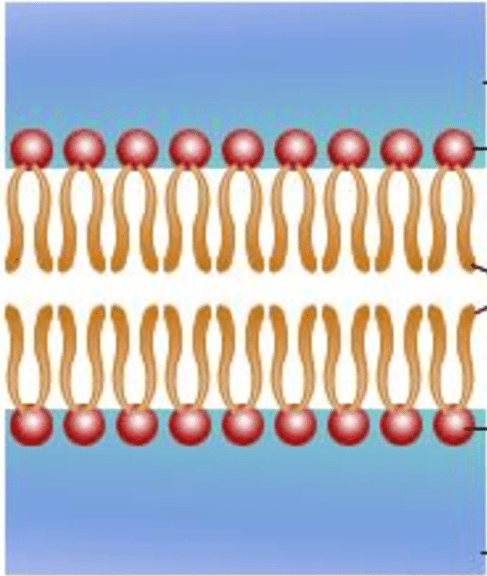
Phospholipids
Semi-permeable: allows specific molecules to enter and leave the cell
This type of transport uses a carrier protein to move molecules against their concentration gradient.
Active transport: Pumps