This is the study of how words are formed.
Morphology
This skill requires a mastery of grammar in more than one language: the act of inserting words or phrases in longer stretches of another language.
Code-Switching
The act of reaching beyond one's self to understand what another person is thinking or feeling. aka, "putting yourself in someone else's shoes."
Empathy
The ideas, customs, skills, arts and tools that characterize a given group of people in a given period of time.
Culture
This is the study of the sounds of words.
Phonology
This commandment refers to breaking down the walls students use to protect their ego.
Lower Inhibitions
The 4-step sequence of first language learning development.
L-S-R-W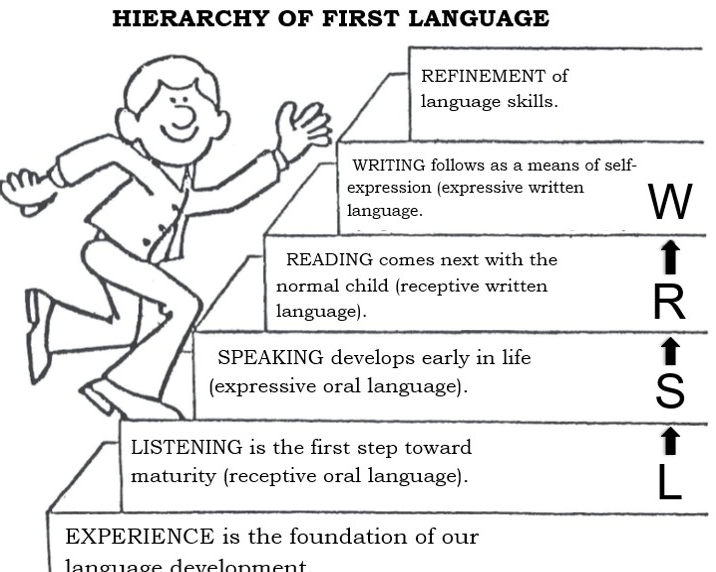
The developmental process wherein certain functions are stabilized in the left or right hemisphere of the brain.
Lateralization
This term refers to a willingness to attempt speaking a new language with the understanding that they will likely make mistakes.
Risk-taking
A mistaken idea or belief people have about a group based on how they look on the outside.
Cultural Stereotype
This distinct mode of pronunciation is sometimes referred to as "the flavor of language."
Accent
This commandment advises the teacher make their classroom environment feel like a community.
Engage in Cooperative Learning
Vygotsky's idea about assessing where a child is on a learning scale and providing scaffolding for them to acquire more knowledge.
Zone of Proximal Development (ZPD)
This affective consideration is defined as the invisible walls put up around a person in order to protect their ego, their sense of self, or the persona they project to the world.
Inhibitions
The identity a person develops in reference to the language they speak.
Language Ego
James Cummins' idea of skills in the day-to-day spoken language needed to interact socially with other people.
Basic Interpersonal Communication Skills (BICS)
This describes people who have one sense of word meanings in their head, new language is translated through that original meaning.
Coordinate bilingual
This commandment refers to the necessity of teaching the students tools to deal with stress.
Promote Ambiguity Tolerance
This theorist identified the concept of Deep Structure and Surface Structure. 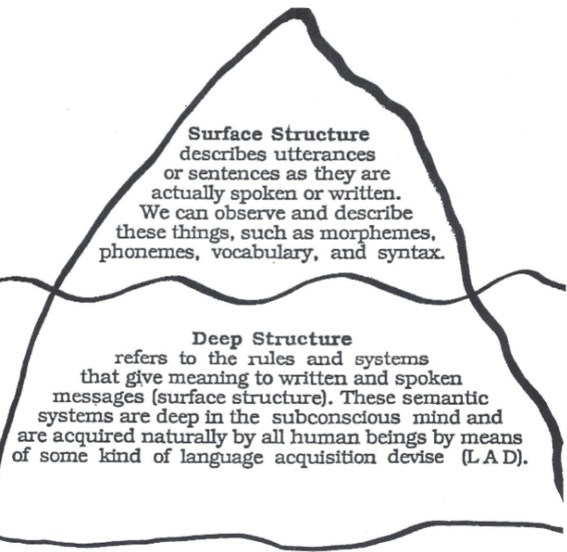
Noam Chomsky
This word describes people who understand more than one language but lack the ability or confidence to generate speech in their non-native language.
Receptive or Passive bilingual
These are two differing states of anxiety where one helps keep a person balanced and alert, and the other form brings about a weakened state of being.
Facilitative vs. Debilitative Anxiety
This term refers to linguistic features from a person's first language becoming permanent errors in the way they speak a new language.
Fossilization
People who have this trait in high quantity are equipped with the ability to adapt to situations where expectations may be unclear.
Tolerance of Ambiguity
This commandment requires the teacher to be in tune with their ability to know when to correct errors and praise students for good guesses.
Practice Intuition
This psychological approach is based on the idea that children are wired to learn language and they will acquire language no matter what.
Nativist Approach
These styles of teaching describe the teacher's role in the classroom; where teachers either directly deliver information for students to obtain, or provide interactive experiences to promote learning.
Teacher- Centered vs. Student Centered Classroom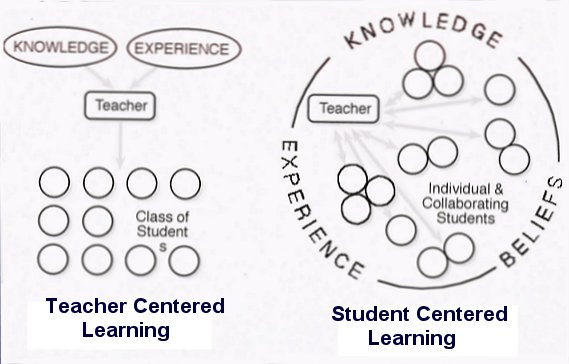
This form of motivation comes from within a person, to achieve their goals or achieve personal enjoyment.
Intrinsic (Integrative) Motivation
This is the process of recognizing why a student makes errors, and how to fix them.
Error Analysis
James Cummins' idea of skills in formal academic, or written, language.
Cognitive Academic Language Proficiency (CALP)
This commandment can be best honored by telling the student explicitly that you believe in them.
Build Self-Confidence
This Natural Approach utilizes the new language and culture to teach a certain topic, thereby encouraging new language acquisition.
Content-Based Instruction (CBI)
This theorist proposed a learning scale which breaks down the most affective ways we learn. With experiencing and teaching information as the most affective processes to acquire learning.
William Glasser
This is an assessment of one's own worth based on specific traits as intelligence or athletic ability.
Situational Self-esteem
This is Stephen Krashen's hypothesis that differentiates the conscious and subconscious methods of learning or acquiring a new language.
Acquisition Learning Hypothesis
This describes a teacher's ability to use their favorite methods of teaching mixed with their students' most appealing method of acquisition.
Enlightened Eclecticism
This commandment advises the teacher to help students become excited about the prospect of learning a new language.
Develop Intrinsic Motivation