An inner tendency to judge or evaluate something or someone either positively or negatively
Attitudes
organisms that are similar tend to mate with each other
Assortative mating
building up resistance to attempts at persuading
attitude inoculation
occurs when you behave in response to a direct order from a higher status person
obedience

voluntarily conforming to group standards when we are uncertain about the correct answer or behavior;
Informational social influence
model that proposes that new attitudes override old ones
model of dual attitudes
learn attitudes by observing others and imitating them
social learning theory
a direct systematic path to persuasion: a direct, explicit, "central" route and an indirect, implicit, "peripheral" route
elaboration likelihood model
occurs when you behave in response to a direct or indirect request
compliance
occurs when we perceive a stationary object as moving due to natural, intermittent movements of our own eyes (called saccades)
Auto-Kinect effect
an attitude object is either good or bad--but not both
univalenced decisions

when we learn to associate one thing in the environment with another due to personal experience
Classical Conditioning
arguments that follow direct, elaborate, and systematic path
central path to persuassion
rules that indicate how people are expected to behave in particular social situations
social norms
conforming thoughts or behaviors shared with others
Public conformity
when we infer our emotions from what our face is doing
facial feedback hypothesis
learning how to predict outcomes of given behaviors based on the outcomes we've experienced for those same behaviors in the past
operant conditioning
indirect route to persuasion
peripheral persuasion
tendency to blindly follow the direction your group is moving toward
herd mentality
cultural belief or norm that transcends the replacement of people
Generational influence
attitudes are only one of three categories of beliefs (give the name of theory and the three categories)
theory of planned behavior
1. attitudes
2.subjective norms
3.perceived control
True False:
Do attitudes come from primarily nurture?
False; they come from both nature and nurture
six step persuasion model
communication persuasion matrix
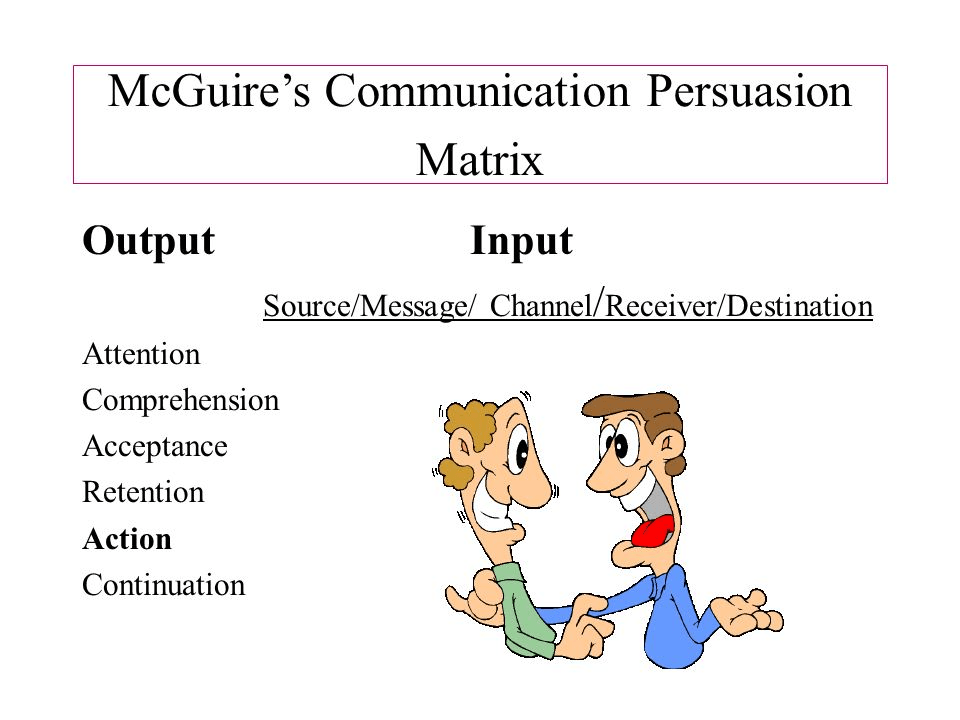
four forms of social influence
Implicit expectations: conformity and social roles
explicit expectations: compliance and obedience
when we publicly conform, often to gain social acceptance and avoid rejection.
Normative social influence