This term describes water's ability to absorb and retain heat, helping regulate body temperature and ecosystems.
What is heat vaporization?
This type of carbohydrate is formed by bonding two monosaccharides together.
What is a disaccharide?
The type of lipid that forms when glycerol combines with three fatty acids.
What is a triglyceride?
These molecules are the building blocks of proteins
What are amino acids?
These are organic molecules that help regulate body processes and often work with enzymes.
vitamins
The oxygen in a water molecule has this type of charge due to electronegativity.
What is a partial negative charge?
Plants use this polysaccharide for strength and rigidity in their cell walls
What is cellulose?
This is the process of breaking down lipids by adding water molecules.
What is hydrolysis?
this part of an amino acid distinguishes one amino acid from another.
R group
This mineral is essential for strong bones and teeth
calcium
This term refers to molecules like water, where charges are unevenly distributed.
What is polar?
This nutrient is indigestible by humans but crucial for healthy digestion and intestinal mobility.
What is fiber?
This function of lipids helps organisms maintain temperature and protect their skeleton.
What is insulation?
The chemical bond formed between amino acids.
peptide bond
The vitamin that is best known to promote the health of the eyes.
vitamin A
Ice forms this type of structure, explaining why it is less dense than liquid water.
What is a lattice structure?
These three monosaccharides share the formula C₆H₁₂O₆ but differ in structure.
What are glucose, fructose, and galactose?
This type of fatty acid contains only single bonds between carbon atoms and is solid at room temperature.
What is a saturated fat?
When a protein chain coils and R groups interact, it achieves this level of structur
What is the tertiary structure?
This vitamin is essential for blood clotting, and its deficiency leads to abnormal bleeding.
vitamin K
this image represents what property of water?
That the solid form is less desnse then the liquid form
what is this molecule 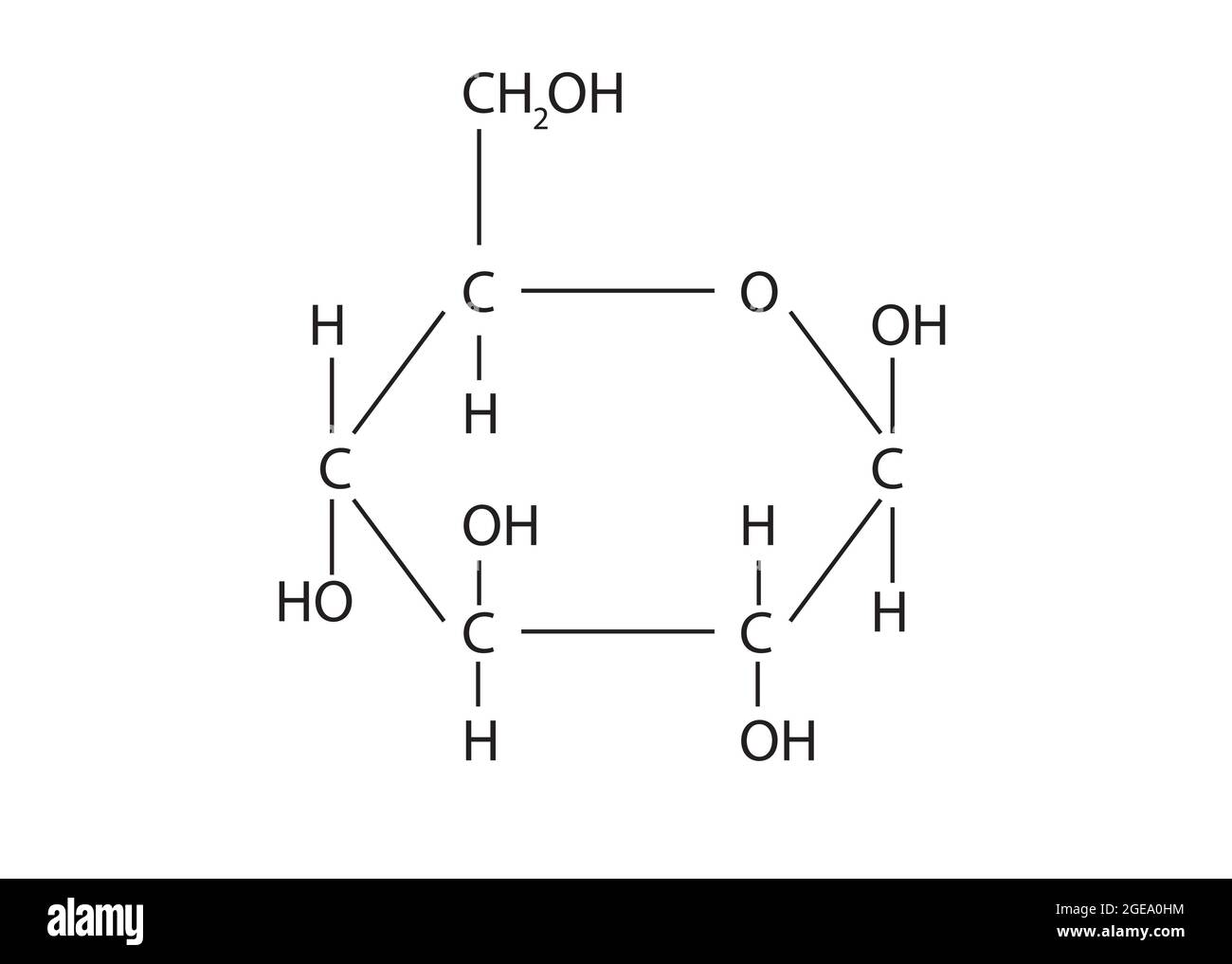
Glucose- or a monosaccharide
what is this molecule?
triglyceride (saturated)
what is this molecule?
Amino acid
These vitamins are stored in fatty tissues for future use
What are fat-soluble vitamins?