Electrons found in the _____________ energy level of an atom; they determine how atoms bond.
outermost
a ___________________ shows the number of valence electrons in an atom in pictorial fashion.
electron dot diagram
What is an ionic bond?
the attraction between two oppositely charged ions
What is a covalent bond?
chemical bond formed when 2 atoms share electrons
The properties of solid metals can be explained by the bonding among metal atoms.
true
a bond formed when one or more electrons are ________________ from on atom to another
transferred
Which is a property shared by most molecular compounds?
low melting point
What is an ion?
an atom or group of atoms that has an electric charge
what is a double bond?
two pairs of electrons shared between two atoms
What is ductility?
can be bent easily and pulled into wires.
What is an alloy?
A mixture of two or more elements, one of which is a metal
The number of _________________ in the atoms of an element determines its chemical properties.
valence electrons
T/F: when electrons are transferred between two atoms, a covalent bond is formed
false; ionic
Molecular compounds that dissolve in water do not conduct electricity because no _____________ are present.
ions
T/F: Metals conduct heat easily because the valence electrons within a metal are free to move
true
a bond where electrons are shared equally between atoms
in an electron dot diagram of sulfur (S), how many dots should be draw around the symbol? Why?
6; it is in group 16 and there are 6 valence electrons
In an ionic compound, which part is written first?
positive ion
t/f: a low melting point is one property of molecular compounds.
true
Name an example of a metal object that shows both luster and malleability .
ex: gold or silver jewelry.
Aluminum foil – shiny (luster) and can be bent or flattened easily (malleable).
Copper wire – shiny reddish color (luster) and can be stretched or shaped easily (malleable).
Silver spoon – shiny surface (luster) and can be shaped or engraved (malleable).
Steel pan – polished surface (luster) and can be formed into different shapes (malleable).
What is does it mean to be malleable?
the property of metals that allows them to be hammered or rolled into thin sheet.
List 3 elements from the group containing the most reactive nonmetals 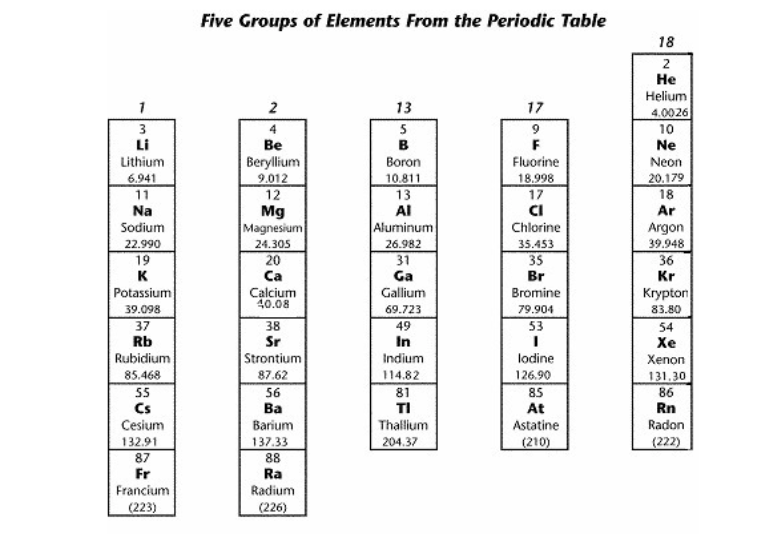
any elements from group 17
Explain how a bond forms between sodium and chlorine in sodium chloride (NaCl).
Sodium has one valence electron and chlorine has seven valence electrons. Sodium gives its extra electron to chlorine. This creates a positive sodium ion (Na⁺) and a negative chloride ion (Cl⁻). The opposite charges attract, and together they form sodium chloride (NaCl), a neutral compound.
What is a difference between covalent and ionic bonds?
Covalent bond: electrons are shared between atoms; usually occurs between nonmetals
ionic bond: electrons are transferred from on atom to another; occurs between a metal and a nonmetal
Explain why metals are such good conductors of heat and electricity
A metal is made of positive metal ions surrounded by a “sea” of free-moving electrons. Heat moves through material when particles bump into each other and pass on their energy. In metals, the particles and free electrons move easily, so heat spreads quickly. Electricity moves when charged particles can flow. In metals, the free electrons can move anywhere, so electricity also flows easily.