What type of interspecific relationship is being shown here?

Predation
________________________________ is the process in which different species act as selective forces upon each other
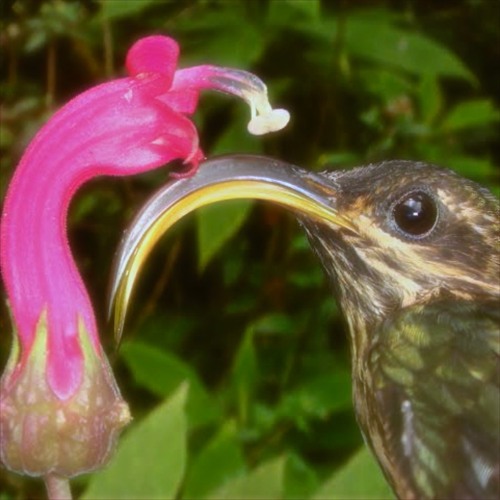

Coevolution
Which of the communities below has a greater species evenness?
Community 1
The ___________-_____________ _____________ is a phenomenon in which larger islands contain more species than smaller islands
Species-Area effect
True or false: Interspecific competition refers to competition between members of the same species, while intraspecific competition refers to competition between members of different species
False; switch
True or False: Competition is positive (+/+) for both species involved
False; (-/-)
__________ ____________ ________ identifies the best strategy by which an organism can maximize energy per unit of time (a predator's way of deciding which prey items to eat)
Optimal foraging theory
______________ _________________ refers to how many different species occupy a given area
Species richness
A small island will have a smaller ___________________ rate than a large island. This will ___________________ the equilibrium species number

Immigration; decrease
The yucca moth and yucca require each other's presence in order to survive. Is this an example of facultative or obligate mutualism?
Obligate
What kind of interspecies interaction has a (+/-) relationship where one species derives nutrients from a host species?
Parasitism
Which prey strategy is being implemented in the picture shown below: predator swamping, crypticity, or aposematic coloring?
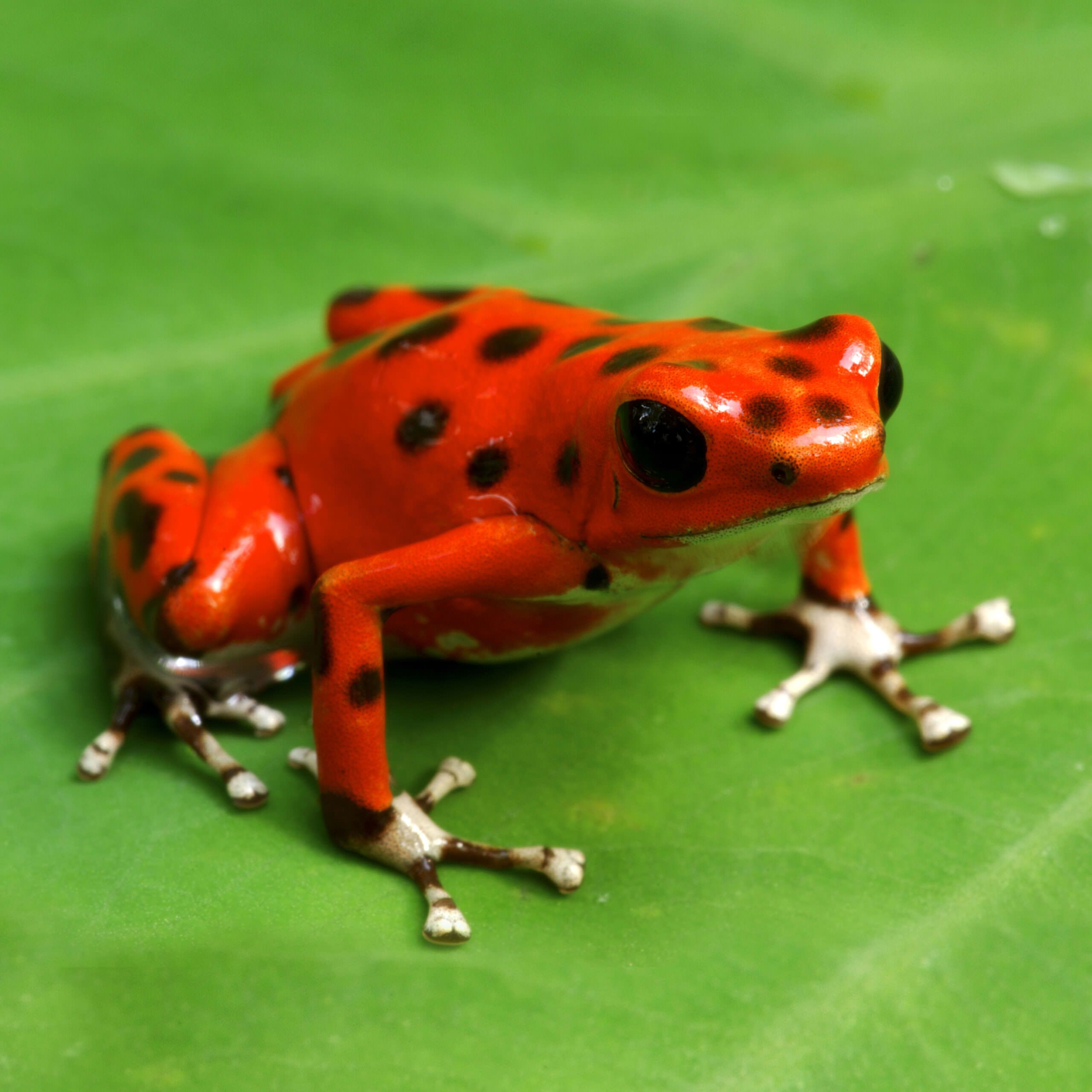

Aposematic coloring
______________ _________________ refers to the relative abundance of each species within a given area
Species evenness
A small island will have a higher ___________________ rate than a large island. This will ___________________ the equilibrium species number

Extinction; decrease
True or false: greater species diversity results when disturbances like wildfires and floods happen rarely
False; intermediate disturbance hypothesis
Cattle egrets eat bugs stirred up by feeding cattle, but cattle remain unaffected by the cattle egrets. What kind of relationship is this?
Commensalism
Identify which of the pictures below is an example of Batesian mimicry, and which picture is an example of Mullerian mimicry


Bees and wasps: Mullerian mimicry
Milk snake and coral snake: Batesian mimicry
_________________, or the boundaries between terrestrial habitats, usually have high species diversity

Ecotones
A near island will have a higher ____________________ rate than a far island. This will ____________________ the equilibrium species number

True or False: More complex habitats tend to have lower species diversity because they are more difficult to live in
False: complex habitats have higher species diversity because they have more exploitable niches
Clownfish and sea anemones benefit from each other's presence; clownfish receive protection and sea anemones receive additional food. What kind of relationship is this?
Mutualism
Draw the three functional response curves generated by a predator's response to increasing prey numbers, and briefly explain the shape of each curve in terms of handling time
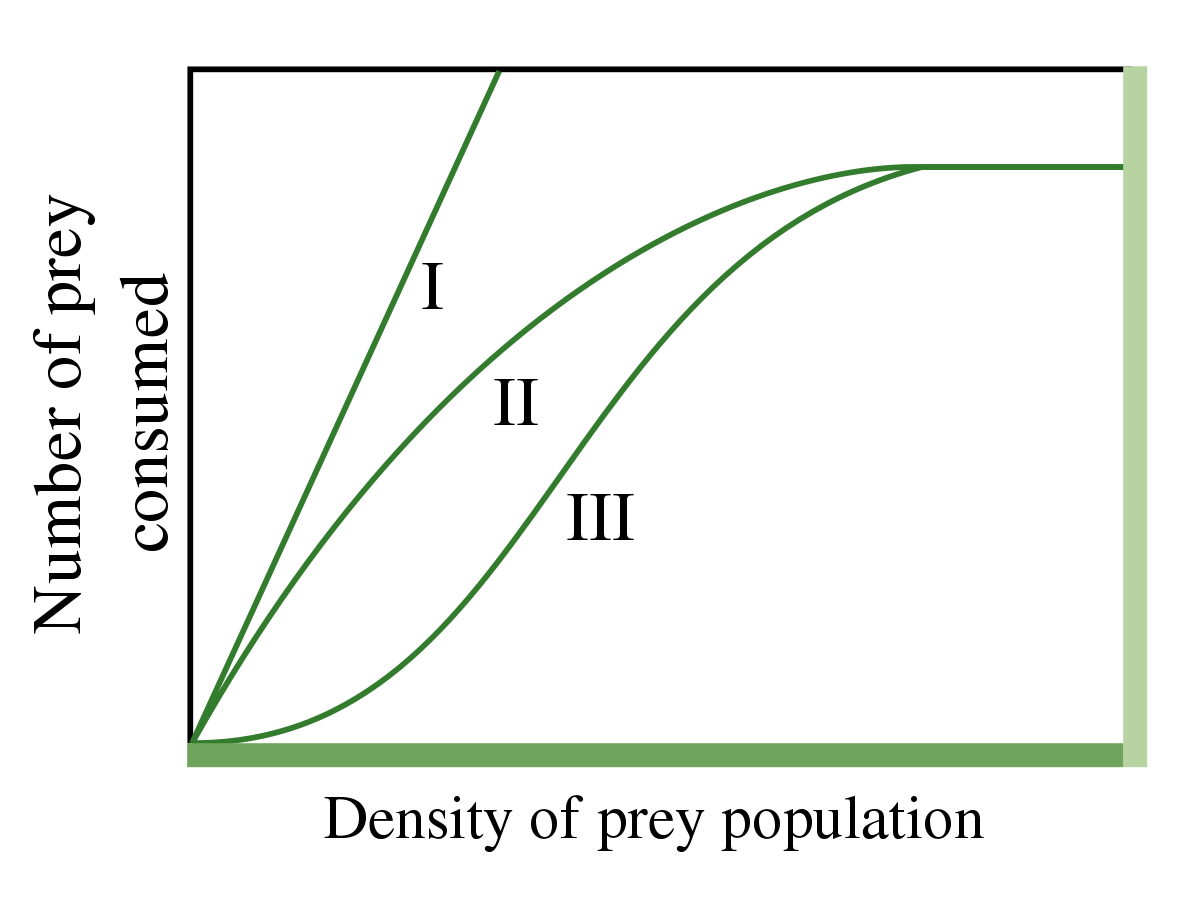
Type I: No handling time, so more prey = more prey eaten
Type II: Significant handling time, so # of prey eaten plateaus at high prey density
Type III: Predators are visual, so few prey are caught when prey #'s are low. Prey consumed plateaus at high numbers due to handling time
The diversification of a taxonomic group to fill a set of newly available niches is known as ____________________ ____________________. For example, mammals diversifying after the extinction of the dinosaurs

Adaptive radiation
How many species occupy the near, large island? How many species occupy the far, small island?
Near, large: 8 species
Small, far: 4 species
True or False: Lower latitudes (like the equator) tend to support more species diversity than higher latitudes
True; overall a greater area of land, plus intermediate disturbances and greater habitat complexity around lower latitudes