Enzymes are which type of macromolecule?
Protein
Name 5 organelles that help with making energy
Answers will vary:
cell membrane, cell wall, cytoplasm, lysosomes, vacuoles, vesicles, mitochondria, chloroplasts
The phospholipid heads are hydro ____ (phobic/philic).
The phospholipid tails are hydro ____ (phobic/philic).
Heads are philic (on the water side)
Tails are phobic (away from the water)
Which molecule contains more energy:
ADP or ATP
ATP - the extra phosphate means more energy
How does ATP production compare between anaerobic and aerobic respiration?
Anaerobic: 2 ATP
Aerobic: ~36 ATP
What are the 4 macromolecules?
Carbohydrates (carbs)
Lipids
Proteins
Nucleic Acids
Name ALL 6 organelles that help with making proteins
Nucleus, nucleolus, ribosomes, rough ER, smooth ER, golgi apparatus
How is facilitated diffusion different from active transport?
Active transport requires energy (ATP) because it goes against the concentration gradient.
Where in the chloroplast do the 2 reactions (light and dark) take place?
Light reactions - Thylakoid
Dark reactions - Stroma
True or False:
Glycolysis occurs in BOTH anaerobic and aerobic respiration
True
Glycolysis is the first step of cellular respiration regardless of the presence of oxygen.
Enzymes ___ (lower/raise/don't affect) the activation energy of a reaction
lower

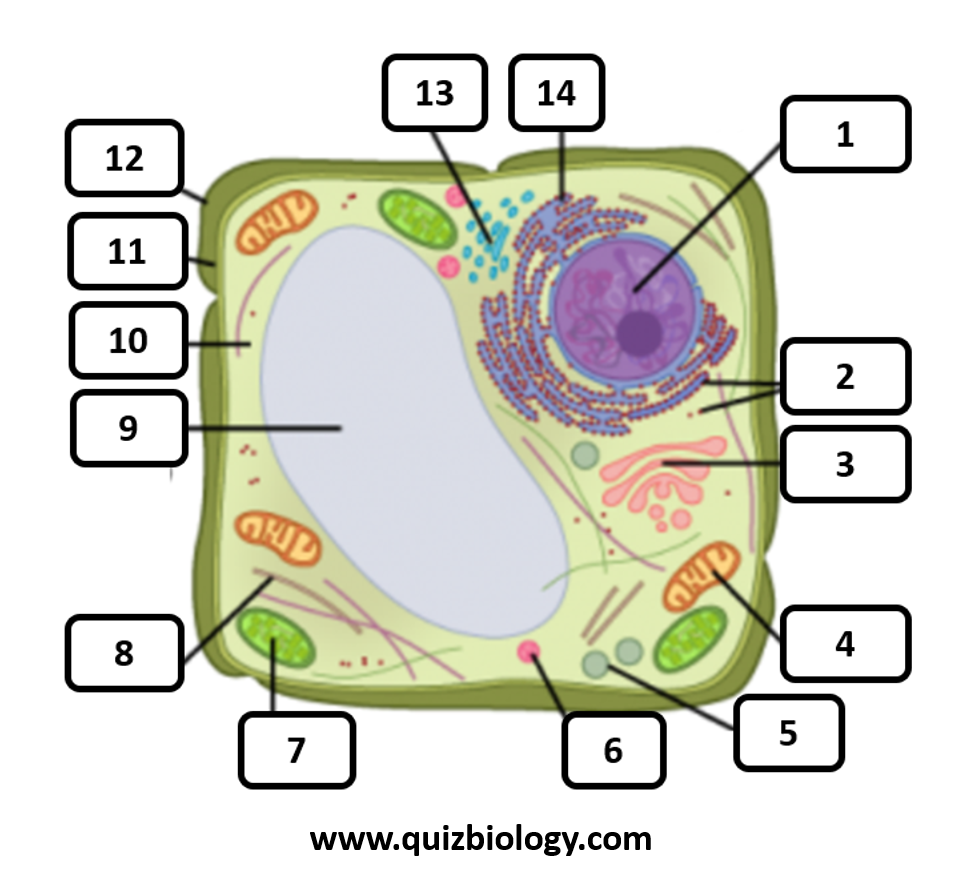
Which organelle is represented by number 12?
Rough ER
How does a HYPERtonic solution affect:
Animal cells
Plant cells
Animal cells: shrink
Plant cells: plasmolysize
Carbon dioxide is needed in photosynthesis to produce which molecule and during which reaction (dark/light)?
glucose; during the dark reactions
Name the 2 types of fermentation
Alcoholic
Lactic acid
What is specific to each enzyme's active site?
Which organelle is represented by number 2?
Ribosome
How does a HYPOtonic solution affect:
Animal cells
Plant cells
Animal cells: burst/pop
Plant cells: become turgid
Which 4 molecules cycle between the light and dark reactions?
NADPH (from light to dark)
ATP (from light to dark)
NADP+ (from dark to light)
ADP (from dark to light)
Name ALL of the steps of aerobic respiration that produce ATP.
Glycolysis, Krebs cycle, ETC
Which type of inhibitor only affects the enzyme with chemical signals?
non-competitive inhibitors
Which 2 organelles do plant cells have that animal cells do NOT?
chloroplasts
cell wall
What are the 5 ways molecules can cross a membrane (into and/or out of)?
Simple diffusion, facilitated diffusion, active transport, endocytosis, exocytosis
What is the relationship between photosynthesis and cellular respiration?
The products of one become the reactants of the other.
Oxygen is needed during the ETC to produce large amounts of ATP. Oxygen is needed to produce the waste product, water. Where do the hydrogens come from?
Hydrogens come from the electron carriers (NADH, FADH2)