The location of the light-independent reactions.
What is the stroma?
The primary energy carrier produced directly from ADP and Pi.
What is ATP?
The initial component of a biochemical pathway that results in a product.
What is a product?
An anaerobic process whereby glucose is broken down through a biochemical pathway.
What is fermentation?
The specific molecule that enzymes react with.
What is a substrate?
The location of the light-dependent reactions.
What are thylakoids/grana?
The partial breakdown of glucose within the cytosol.
What is glycolysis?
A molecule required to catalyse a reaction.
What is an enzyme?
The output of anaerobic fermentation in animals.
What is lactic acid?
The region of the enzyme that a molecule binds to.
What is an active site?
The common name of the light-independent reaction.
What is the Calvin cycle?
This process does not require the input of oxygen and results in less ATP.
What is anaerobic respiration?
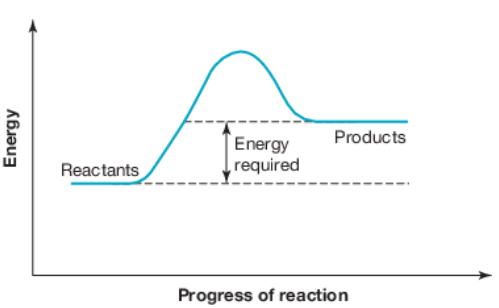
The name given to the 'energy required' in a reaction.
What is activation energy?
The output of anaerobic fermentation in yeat/plants/fungus.
What is ethanol?
A complex organic molecule required for an enzyme's metabolic activity, it assists with the catalysis of a reaction.
What is a coenzyme?
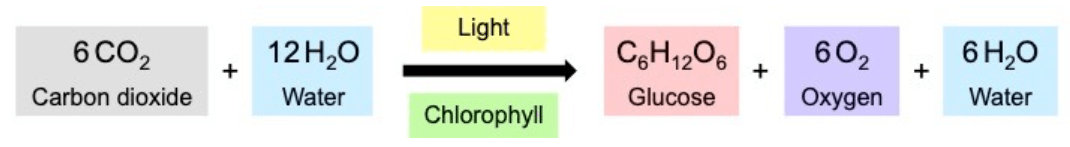
The process with hydrogen and ATP as inputs, with oxygen as a waste product.
What is the light-independent reaction?
Pyruvate is converted to Acetyl CoA then introduced to this cycle within the mitochondrial matrix.
What is the Krebs Cycle?
The organic matter from living things such as plants and animals.
What is biomass?
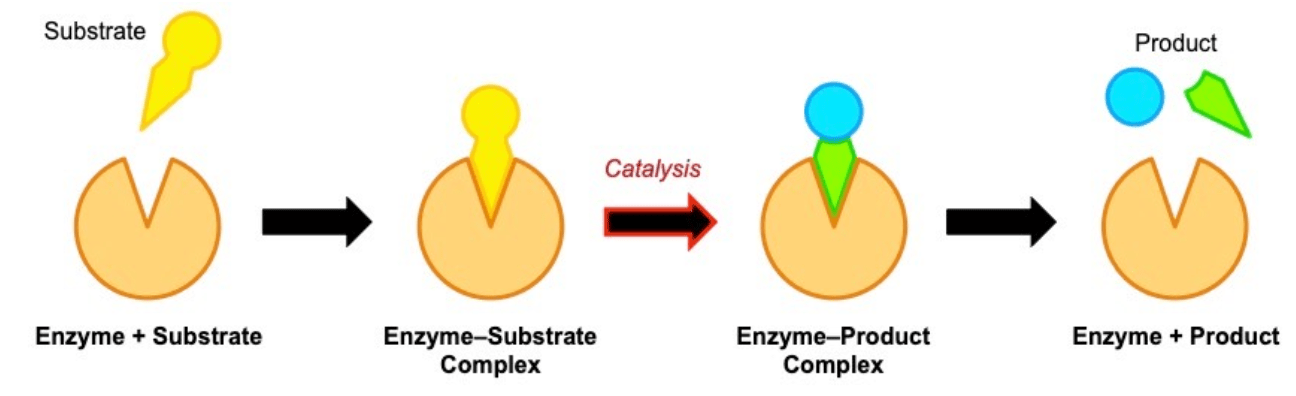
The model shown in this image.
What is the 'lock and key' model?
This process involves the production of a 5-C compound called Ribulose.
What is the Calvin cycle?
The cristae of the mitochondria.
Where is the electron transport chain?
These pathways break down complex molecules into more simple molecules.
What is a catabolic pathway?
_____________ decompose dead plants and animals, causing them to rot or decay, leading to the production of methane and biogas.
What are bacteria and fungi?
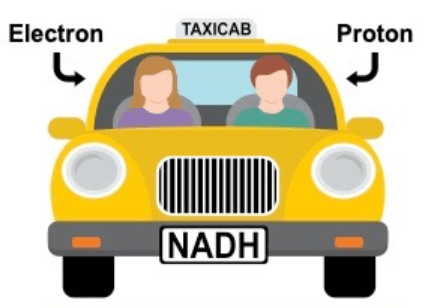
This molecule is said to function like a 'chemical taxi' and is required in reactions such as photosynthesis and cellular respiration.
What is a hydrogen carrier/coenzyme?