Anterior to the descending aorta in PLAX is pericardial, posterior to descending aorta in PLAX is pleural.
What test is gold standard for diagnosis of PTHN?
RHC
What will MV M-mode look like with obstructive HCM patient?
during systole the MV closure will bow towards the septum and possibly touch
These are the three leaflets of the TV.
What is Septal, Anterior, Posterior
This is the most common location of atrial thrombus.
What is LAA?
What pathology results in a pericardial knock murmur?
This is how you calculate RAP....
Include all 4 IVC scenarios and what pressure would be.
Collapses/normal size 3 mmHg
Collapses/dilated 8 mmHg
Plethoric/normal size 8 mmHg
Plethoric/dilated 15 mmHg
Scenarios/diseases where a patient may have HFPEF?
infiltrative disease, HCM, HTN, pericardial disease
This type of CM can create LV thrombi.
What is dilated cardiomyopathy?
What conditions can predispose a patient to endocarditis?
Older, prosthesis (valvular or device), valve disease, congenital malformations
This is the location of a type B dissection.
Anywhere not including the ascending aorta
Conditions in which exaggerated respiratory variations of the MV/TV E velocities may occur
What is tamponade/effusion, constriction, lung disease (COPD, emphysema)
This is the blood pressure at which hypertension begins.
What is 130/80 mmHg?
This is the leading cause of sudden death in young athletes.
What is HOCM?
This is the appropriate time to perform the initial baseline exam after prosthetic valve.
What is 4-6 weeks post op
This is the most common cause of TR.
What is secondary TR from dilated RV/RA.(most likely from left-sided disease).
Pericardial effusion can often be seen in patients with...
viral infection, metastatic cancer, restrictive cardiomyopathy, SLE
What BP is considered HTN emergency?
>180/120
M-mode features of DCM
What is increased EPSS of MV, tapered systolic closure of the AV, B-bump of the MV
This causes attenuation artifact and this is how you fix it.
Contrast pushed too fast and makes apex ovesaturated and mid/base too dark. Need to slow injection
What is the most common cause of a dilated PA?
PHTN
E/e' ratio is used to estimate?
Left atrial pressure
Calculate the RVSP...
IVC is dilated, it collapses greater than 50%
TR velocity is 3.0 m/s
36 + 8 = 44 mmHg
What causes jugular vein distention?
Backup of blood into the SVC - can see it in tamponade, PHTN, TS/severe TR, pericarditis
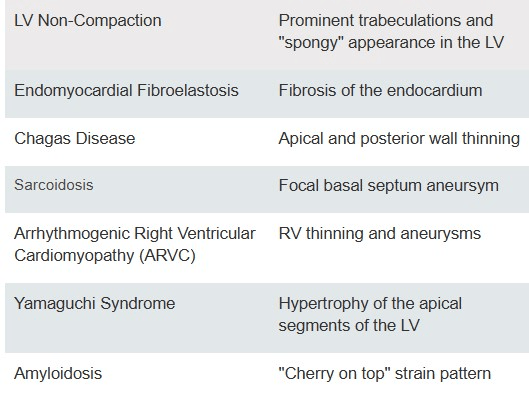
Match the cardiomyopathy with its echo features.
What effect does beta blocker have on the heart?
lowers heart rate, contractility, BP
Tell me about rheumatic TS
Results in RAE, most common cause of TS, features commissural fusion, almost never isolated